Abstract
Main conclusion
Plant growth regulators, sucrose concentration, and light quality significantly impact in vitro regeneration of 'Harmony'. Blue light promotes photomorphogenesis by enhancing light energy utilization, adjusting transcription of light signal genes, and altering hormone levels.
Abstract
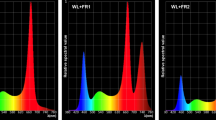
Hydrangea quercifolia cv. 'Harmony', celebrated for lush green foliage and clusters of white flowers, has been extensively researched for its regenerative properties. Regeneration in stem segments, leaves, and petioles is facilitated by exogenous auxin and cytokinins (CTKs), with the concentration of sucrose (SC) being a key determinant for shoot regeneration from leaves. The study also highlights the significant impact of light conditions on photomorphogenesis. With an increase in the proportion of red (R) light, there is an inhibitory effect, leading to a reduction in leaf area, a decrease in the quantum yield of PSII (ΦPSII), and an increase in non-photochemical quenching (ΦNPQ) and non-regulated energy dissipation in PSII (ΦNO). Conversely, blue (B) light enhances growth, characterized by an increase in leaf area, elevated ΦPSII, and stable ΦNPQ and ΦNO levels. Additionally, B light induces the upregulation of HqCRYs, HqHY5-like, HqXTH27-like, and HqPHYs genes, along with an increase in endogenous CTKs levels, which positively influence photomorphogenesis independent of HqHY5-like regulation. This light condition also suppresses the synthesis of endogenous gibberellins (GA) and brassinosteroids (BR), further facilitating photomorphogenesis. In essence, B light is fundamental in expediting photomorphogenesis in 'Harmony', demonstrating the vital role in plant growth and development.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alabadí D, Gil J, Blázquez MA, García-Martínez JL (2004) Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness. Plant Physiol 134(3):1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.035451
Arinaitwe G, Rubaihayo PR, Magambo MJS (2000) Proliferation rate effects of cytokinins on banana (Musa spp.) cultivars. Sci Hortic 86 (1):13–21.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(00)00124-2
Asim M, Guo M, Khan R, Sun YG, Du SS, Liu WT, Li Y, Wang XL, Wang MY, Shi Y, Zhang Y (2022a) Investigation of sugar signaling behaviors involved in sucrose-induced senescence initiation and progression in N. tabacum. Plant Physiol Biochem 184:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.05.024
Asim M, Hussain Q, Wang X, Sun Y, Liu H, Khan R, Du S, Shi Y, Zhang Y (2022b) Mathematical modeling reveals that sucrose regulates leaf senescence via dynamic sugar signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 23(12):6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126498
Atta R, Laurens L, Boucheron-Dubuisson E, Guivarc’h A, Carnero E, Giraudat-Pautot V, Rech P, Chriqui D (2009) Pluripotency of Arabidopsis xylem pericycle underlies shoot regeneration from root and hypocotyl explants grown in vitro. Plant J 57(4):626–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03715.x
Chen H, Zhang JY, Neff MM, Hong SW, Zhang HY, Deng XW, Xiong LM (2008) Integration of light and abscisic acid signaling during seed germination and early seedling development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(11):4495–4500. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0710778105
Cochran DR, Benitez-Ramirez M, Fulcher A (2014) Effect of branch-inducing treatments on growth of tissue culture and cutting-propagated Hydrangea quercifolia ‘Alice.’ J Environ Hortic 32(4):182–188. https://doi.org/10.24266/0738-2898.32.4.182
da Silva MHM, Debergh PC (1997) The effect of light quality on the morphogenesis of in vitro cultures of Azorina vidalii (Wats.) Feer. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 51(3):187–193. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005988621036
Dai X, Wang J, Wang L, Liu Z, Li Q, Cai Y, Li S, Xiang F (2022) HY5 inhibits in vitro shoot stem cell niches initiation via directly repressing pluripotency and cytokinin pathways. Plant J 110(3):781–801. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15703
van Emden HF, Harrington R (eds2017) Aphids as crop pests, 2nd edn. CABI, Wallingford, UK
Fankhauser C, Chory J (1999) Photomorphogenesis: Light receptor kinases in plants! Curr Biol 9(4):R123–R126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80078-5
Feng S, Martinez C, Gusmaroli G, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang F, Chen L, Yu L, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Kircher S, Schaefer E, Fu X, Fan L-M, Deng XW (2008) Coordinated regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins. Nature 451(7177):475–479. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06448
Franklin KA, Allen T, Whitelam GC (2007) Phytochrome A is an irradiance-dependent red light sensor. Plant J 50(1):108–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03036.x
Frede K, Winkelmann S, Busse L, Baldermann S (2023) The effect of LED light quality on the carotenoid metabolism and related gene expression in the genus Brassica. BMC Plant Biol 23(1):328. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04326-4
Gangappa SN, Botto JF (2016) The multifaceted roles of HY5 in plant growth and development. Mol Plant 9(10):1353–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.07.002
Gardener NSE (2020) Plant toolbox: Hydrangea quercifolia. https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/hydrangea-quercifolia
Genty B, Briantais JM, Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron-transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta 990(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80016-9
Hall SM, Hillman JR (1975) Correlative inhibition of lateral bud growth in Phaseolus vulgaris L. timing of bud growth following decapitation. Planta 123(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00383862
Hasan MM, Bashir T, Ghosh R, Lee SK, Bae H (2017) An overview of LEDs’ effects on the production of bioactive compounds and crop quality. Molecules 22(9):1420
Hennig L, Funk M, Whitelam GC, Schafer E (1999) Functional interaction of cryptochrome 1 and phytochrome D. Plant J 20(3):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00599.x
Hogewoning SW, Trouwborst G, Maljaars H, Poorter H, van Ieperen W, Harbinson J (2010) Blue light dose-responses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light. J Exp Bot 61(11):3107–3117. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq132
Islam MJ, Ryu BR, Rana MS, Cheong EJ, Wang MH, Lim JD, Hossain MA, Lim YS (2022) Cannabinoid accumulation in hemp depends on ROS generation and interlinked with morpho-physiological acclimation and plasticity under indoor LED environment. Front Plant Sci 13:984410. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.984410
Jeong BR, Sivanesan I (2018) Impact of light quality and sucrose on adventitious shoot regeneration and bioactive compound accumulation in Ajuga multiflora Bunge. Sci Hortic 236:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.03.056
Jiao Y, Lau OS, Deng XW (2007) Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nature Rev Genetics 8(3):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2049
Jing Y, Zhang D, Wang X, Tang W, Wang W, Huai J, Xu G, Chen D, Li Y, Lin R (2013) Arabidopsis chromatin remodeling factor PICKLE interacts with transcription factor HY5 to regulate hypocotyl cell elongation. Plant Cell 25(1):242–256. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.105742
Klughammer C, Schreiber U (2008) Saturation pulse method for assessment of energy conversion in PS I. PAM Application Notes 1:11–14
Ledbetter DI, Preece JE (2004) Thidiazuron stimulates adventitious shoot production from Hydrangea quercifolia Bartr leaf. explants. Sci Hortic 101(1–2):121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2003.09.014
Lin C (2000) Plant blue-light receptors. Trends Plant Sci 5(8):337–342
Lin C, Ahmad M, Gordon D, Cashmore AR (1995) Expression of an Arabidopsis cryptochrome gene in transgenic tobacco results in hypersensitivity to blue, UV-A, and green light. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(18):8423–8427. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.18.8423
Liu W, Ni J, Shah FA, Ye K, Hu H, Wang Q, Wang D, Yao Y, Huang S, Hou J, Liu C, Wu L (2019) Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression pattern analysis of APYRASE family members in response to abiotic and biotic stresses in wheat. Peer J 7:e7622. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7622
Liu X, Yu Y, Yao W, Yin Z, Wang Y, Huang Z, Zhou J-Q, Liu J, Lu X, Wang F, Zhang G, Chen G, Xiao Y, Deng H, Tang W (2023) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated simultaneous mutation of three salicylic acid 5-hydroxylase (OsS5H) genes confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 21(9):1873–1886. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.14099
Lou YX, Zhang QY, Xu QY, Yu XY, Wang WX, Gai RA, Ming F (2023) PhCHS5 and PhF3’5’H genes over-expression in Petunia (Petunia hybrida) and Phalaenopsis (Phalaenopsis aphrodite) regulate flower color and branch number. Plants-Basel 12(11):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112204
Lucas M, Davière J-M, Rodríguez-Falcón M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Sv L, Fankhauser C, Blázquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008) A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451(7177):480–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06520
Ma Y, Steeves TA (1992) Auxin effects on vascular differentiation in Ostrich Fern. Ann Bot 70(3):277–282. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a088470
Malik K, Birla D, Yadav H, Sainger M, Chaudhary D, Jaiwal PK (2017) Evaluation of carbon sources, gelling agents, growth hormones and additives for efficient callus induction and plant regeneration in Indian wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes using mature embryos. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 20:185–192
Marks CO, Lechowicz MJ (2006) A holistic tree seedling model for the investigation of functional trait diversity. Ecol Model 193(3–4):141–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.09.011
Marks TR, Simpson SE (1999) Effect of irradiance on shoot development in vitro. Plant Growth Regul 28(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006276724956
Mason MG, Ross JJ, Babst BA, Wienclaw BN, Beveridge CA (2014) Sugar demand, not auxin, is the initial regulator of apical dominance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(16):6092–6097. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1322045111
Mathew MM, Prasad K (2021) Model systems for regeneration: Arabidopsis. Development 148 (6): dev195347. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.195347
Matsui A, Yokoyama R, Seki M, Ito T, Shinozaki K, Takahashi T, Komeda Y, Nishitani K (2005) AtXTH27 plays an essential role in cell wall modification during the development of tracheary elements. Plant J 42(4):525–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02395.x
Miao Y-X, Wang X-Z, Gao L-H, Chen Q-Y, Mei Q (2016) Blue light is more essential than red light for maintaining the activities of photosystem II and I and photosynthetic electron transport capacity in cucumber leaves. J Integr Agric 15(1):87–100
Mohammadi MA, Wai MH, Rizwan HM, Qarluq AQ, Xu MJ, Wang LL, Cheng Y, Aslam M, Zheng P, Wang XM, Zhang WB, Qin Y (2023) Advances in micropropagation, somatic embryogenesis, somatic hybridizations, genetic transformation and cryopreservation for Passiflora improvement. Plant Methods 19(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-023-01030-0
Moret B, Marhava P, Fandino ACA, Hardtke CS, ten Tusscher KHW (2020) Local auxin competition explains fragmented differentiation patterns. Nature Commun 11:2965. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16803-7
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nassarawa SS, Luo ZS (2022) Effect of light irradiation on sugar, phenolics, and GABA metabolism on postharvest grape (Vitis vinifera L.) during storage. Food Bioprocess Technol 15(12):2789–2802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02919-9
Nedbal L, Trtilek M, Kaftan D (1999) Flash fluorescence induction: a novel method to study regulation of photosystem II. J Photochem Photobiol B 48(2–3):154–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1011-1344(99)00032-9
Nie CR, Zhang YJ, Zhang XQ, Xia WS, Sun HB, Zhang SS, Li N, Ding ZQ, Lv YM, Wang N (2023) Genome assembly, resequencing and genome-wide association analyses provide novel insights into the origin, evolution and flower colour variations of flowering cherry. Plant J 114(3):519–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16151
Ninu L, Ahmad M, Miarelli C, Cashmore AR, Giuliano G (1999) Cryptochrome 1 controls tomato development in response to blue light. Plant J 18(5):551–556
Oyama T, Shimura Y, Okada K (1997) The Arabidopsis HY5 gene encodes a bZIP protein that regulates stimulus-induced development of root and hypocotyl. Genes Dev 11(22):2983–2995. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.22.2983
Pedmale UV, S-sC H, Zander M, Cole BJ, Hetzel J, Ljung K, Reis PAB, Sridevi P, Nito K, Nery JR, Ecker JR, Chory J (2016) Cryptochromes interact directly with PIFs to control plant growth in limiting blue light. Cell 164(1–2):233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.018
Ranade SS, Garcia-Gil MR (2023) Clinal variation in PHY (PAS domain) and CRY (CCT domain)-signs of local adaptation to light quality in Norway spruce. Plant Cell Environ 46:2391–2400. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14638
Rasool S, Markou A, Hannula SE, Biere A (2023) Effects of tomato inoculation with the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium brunneum on spider mite resistance and the rhizosphere microbial community. Front Microbiol 14:1197770. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197770
Schreiber U, Bilger W, Neubauer C (1995) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a nonintrusive indicator for rapid assessment of in vivo photosynthesis. In: Schulze ED, Caldwell MM (eds) Ecophysiology of photosynthesis. Springer, pp 49–70
Shi Q-M, Yang X, Song L, Xue H-W (2011) Arabidopsis MSBP1 is activated by HY5 and HYH and is involved in photomorphogenesis and brassinosteroid sensitivity regulation. Mol 4(6):1092–1104. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr049
Shi H, Lyu M, Luo Y, Liu S, Li Y, He H, Wei N, Deng XW, Zhong S (2018) Genome-wide regulation of light-controlled seedling morphogenesis by three families of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(25):6482–6487. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1803861115
Skylar A, Sung F, Hong F, Chory J, Wu X (2011) Metabolic sugar signal promotes Arabidopsis meristematic proliferation via G2. Dev Biol 351(1):82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.019
Soltani S, Arouiee H, Salehi R, Nemati SH, Moosavi-Nezhad M, Gruda NS, Aliniaeifard S (2023) Morphological, phytochemical, and photosynthetic performance of grafted tomato seedlings in response to different LED light qualities under protected Ccultivation. Horticulturae 9(4):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040471
Song X, Guo P, Xia K, Wang M, Liu Y, Chen L, Zhang J, Xu M, Liu N, Yue Z, Xu X, Gu Y, Li G, Liu M, Fang L, Deng XW, Li B (2023) Spatial transcriptomics reveals light-induced chlorenchyma cells involved in promoting shoot regeneration in tomato callus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120(38):e2310163120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2310163120
Su PF, Ding SS, Wang DC, Kan WJ, Yuan M, Chen X, Tang CG, Hou JY, Wu LF (2023) Plant morphology, secondary metabolites and chlorophyll fluorescence of Artemisia argyi under different LED environments. Photosynthesis Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-023-01026-w
Sugimoto K, Jiao YL, Meyerowitz EM (2010) Arabidopsis regeneration from multiple tissues occurs via a root development pathway. Dev Cell 18(3):463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.02.004
Sun Y, Chen Z, Chen H, Wang C, Li B, Qin L, Lin X, Cai Y, Zhou D, Ouyang L, Zhu C, He H, Peng X (2023) Analysis of the genetic stability of insect and herbicide resistance genes in transgenic rice lines: A laboratory and field experiment. Rice 16:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-023-00624-5
Tiika RJ, Wei J, Cui GX, Ma YJ, Yang HS, Duan HR (2021) Transcriptome-wide characterization and functional analysis of Xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase/hydrolase (XTH) gene family of Salicornia europaea L under salinity and drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 21:491. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03269-y
Vandenbussche F, Habricot Y, Condiff AS, Maldiney R, Van Der Straeten D, Ahmad M (2007) HY5 is a point of convergence between cryptochrome and cytokinin signalling pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 49(3):428–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02973.x
Vissenberg K, Fry SC, Pauly M, Höfte H, Verbelen JP (2005) XTH acts at the microfibril-matrix interface during cell elongation. J Exp Bot 56(412):673–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri048
Wang W, Lu X, Li L, Lian H, Mao Z, Xu P, Guo T, Xu F, Du S, Cao X, Wang S, Shen H, Yang H-Q (2018) Photoexcited cryptochrome1 interacts with dephosphorylated BES1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30(9):1989–2005. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00994
Weller JL, Vr H, Vander Schoor JK, Davidson SE, Ross JJ (2009) Light regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis in pea is mediated through the COP1/HY5 pathway. Plant Cell 21(3):800–813. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.063628
Williams LE (2021) Genetics of shoot meristem and shoot regeneration. Annu Rev Genet 55(1):661–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-071719-020439
Wu L-Y, Shang G-D, Wang F-X, Gao J, Wan M-C, Xu Z-G, Wang J-W (2022) Dynamic chromatin state profiling reveals regulatory roles of auxin and cytokinin in shoot regeneration. Dev Cell 57(4):526–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.019
Xu P, Chen H, Li T, Xu F, Mao Z, Cao X, Miao L, Du S, Hua J, Zhao J, Guo T, Kou S, Wang W, Yang H-Q (2021) Blue light-dependent interactions of CRY1 with GID1 and DELLA proteins regulate gibberellin signaling and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 33(7):2375–2394. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab124
Yokoyama R, Nishitani K (2001) Endoxyloglucan transferase is localized both in the cell plate and in the secretary pathway destined for the apoplast in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Physiol 42(3):292–300. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pce034
Zhou T, He Y, Han X, Sun Q, Xuan YH (2023) β-Glucanase family genes promote resistance to sheath blight in rice by inhibiting the permeability of plasmodesmata. J Agric Food Chem 71(25):9667–9676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01127
Zhu Z, Lin C (2016) Photomorphogenesis: When blue meets red. Nature Plants 2(3):16019. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2016.19
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Engineer Jin Li for the useful comments on the data analysis of the study, as well as for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201521), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (Grant No. 2021447), the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (202204c06020045), the Chinese Academy of Sciences-Henan Province Achievement transfer and Transformation Project (2022110 and 2022211), and the Grant of the President Foundation of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences (YZJJZX202013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS: investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. DW: validation. PW and YG: investigation. HJ: writing—review. JH: founding acquisition, conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. LW: conceptualization, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or non-financial interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, P., Wang, D., Wang, P. et al. In vitro regeneration, photomorphogenesis and light signaling gene expression in Hydrangea quercifolia cv. 'Harmony' under different LED environments. Planta 259, 71 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04335-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04335-z