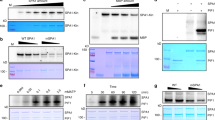
Abstract
Main conclusion
After blue-light exposure, ubiquitination of PHOTOTROPIN1 lysine 526 enhances phototropic responses.
Abstract
Arabidopsis blue-light photoreceptor, PHOTOTROPIN1 (PHOT1) mediates a series of blue-light responses that function to optimize photosynthesis efficiency. Blue-light sensing through the N-terminal sensory domain activates the C-terminal kinase activity of PHOT1, resulting in autophosphorylation. In addition to phosphorylation, PHOT1 lysine residue 526 (Lys526), after blue-light exposure, was found to carry a double glycine attachment, indicative of a possible ubiquitination modification. The functionality of PHOT1 Lys526 was investigated by reverse genetic approaches. Arginine replacements of PHOT1 Lys526, together with Lys527, complemented phot1-5 phot2-1 double mutant with attenuated phototropic bending, while blue-light responses: leaf expansion and stomatal opening, were restored to wild type levels. Transgenic seedlings were not different in protein levels of phot1 Lys526 527Arg than the wild type control, suggesting the reduced phototropic responses was not caused by reduction in protein levels. Treating the transformants with proteosome inhibitor, MG132, did not restore phototropic sensitivity. Both transgenic protein and wild type PHOT1 also had similar dark recovery of kinase activity, suggesting that phot1 Lys526 527Arg replacement did not affect the protein stability to cause the phenotype. Together, our results indicate that blocking Lys526 ubiquitination by arginine substitution may have caused the reduced phototropic phenotype. Therefore, the putative ubiquitination on Lys526 functions to enhance PHOT1-mediated phototropism, rather than targeting PHOT1 for proteolysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author. Accession numbers: Arabidopsis PHOT1, At3g45780.
Abbreviations
- NPH3:
-
NON-PHOTOTROPIC HYPOCOTYL 3
- PHOT1:
-
Wild type PHOTOTROPIN1 protein
- PHOT1 GFP :
-
Wild type PHOTOTROPIN1 cDNA with green fluorescent protein tag
- phot1 Lys526 527Arg:
-
Mutated phototropin1 protein with lysine residues 526, 527 replaced with arginine
References
Aggarwal C, Banaś AK, Kasprowicz-Maluśki A, Borghetti C, Labuz J, Dobrucki J, Gabryś H (2014) Blue-light-activated phototropin2 trafficking from the cytoplasm to Golgi/post-Golgi vesicles. J Exp Bot 65:3263–3276. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru172
Aihara Y, Tabata R, Suzuki T, Shimazaki K, Nagatani A (2008) Molecular basis of the functional specificities of phototropin 1 and 2. Plant J 56:364–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03605.x
Briggs WR (2014) Phototropism: some history, some puzzles, and a look ahead. Plant Physiol 164:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.230573
Christie JM (2007) Phototropin blue-light receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:21–45. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103951
Christie JM, Reymond P, Powell G, Nrnasconi P, Reibekas AA, Liscum E, Briggs WR (1998) Arabidopsis NPH1: a flavoprotein with the properties of a photoreceptor for phototropism. Science 282:1698–1701. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5394.169
Christie JM, Yang H, Richter GL, Sullivan S, Thomson CE, Lin J, Titapiwatanakun B, Ennis M, Kaiserli E, Lee OR, Adamec J, Peer WA, Murphy AS (2011) phot1 inhibition of ABCB19 primes lateral auxin fluxes in the shoot apex required for phototropism. PLoS Biol 9:e1001076. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001076
Christie JM, Suetsugu N, Sullivan S, Wada M (2018) Shining light on the function of NPH3/RPT2-like proteins in phototropin signaling. Plant Physiol 176:1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00835
Deng Z, Oses-Prieto JA, Kutschera U, Tseng TS, Hao L, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY, Briggs WR (2014) Blue light-induced proteomic changes in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings. J Proteome Res 13:2524–2533. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr500010z
Dikic I, Schulman BA (2023) An expanded lexicon for the ubiquitin code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 24:273–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-022-00543-1
Ding Z, Galván-Ampudia CS, Demarsy E, Łangowski Ł, Kleine-Vehn J, Fan Y, Morita MT, Tasaka M, Fankhauser C, Offringa R, Friml J (2011) Light-mediated polarization of the PIN3 auxin transporter for the phototropic response in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 13:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2208
Fankhauser C, Christie JM (2015) Plant phototropic growth. Curr Biol 25:R384-389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.020
Goh CH, Jang S, Jung S, Kim HS, Kang HG, Park YI, Bae HJ, Lee CH, An G (2009) Rice phot1a mutation reduces plant growth by affecting photosynthetic responses to light during early seedling growth. Plant Mol Biol 69:605–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9442-1
Grubb LE, Derbyshire P, Dunning KE, Zipfel C, Menke FLH, Monaghan J (2021) Large-scale identification of ubiquitination sites on membrane-associated proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant Physiol 185:1483–1488. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab023
Hart JE, Sullivan S, Hermanowicz P, Petersen J, Diaz-Ramos LA, Hoey DJ, Łabuz J, Christie JM (2019) Engineering the phototropin photocycle improves photoreceptor performance and plant biomass production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:12550–12557. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902915116
Herrou J, Crosson S (2011) Function, structure and mechanism of bacterial photosensory LOV proteins. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:713–723. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2622
Hicke L (2001) Protein regulation by monoubiquitin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1038/35056583
Hohm T, Preuten T, Fankhauser C (2013) Phototropism: translating light into directional growth. Am J Bot 100:47–59. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1200299
Huala E, Oeller PW, Liscum E, Han IS, Larsen E, Briggs WR (1997) Arabidopsis NPH1: a protein kinase with a putative redox-sensing domain. Science 278:2120–2123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5346.2120
Inada S, Ohgishi M, Mayama T, Okada K, Sakai T (2004) RPT2 is a signal transducer involved in phototropic response and stomatal opening by association with phototropin 1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:887–896. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.019901
Inoue S, Kinoshita T, Matsumoto M, Nakayama KI, Doi M, Shimazaki K (2008) Blue light-induced autophosphorylation of phototropin is a primary step for signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5626–5631. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709189105
Inoue S, Takemiya A, Shimazaki K (2010) Phototropin signaling and stomatal opening as a model case. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:587–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.09.002
Inoue S, Matsushita T, Tomokiyo Y, Matsumoto M, Nakayama KI, Kinoshita T, Shimazaki K (2011) Functional analyses of the activation loop of phototropin2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175943
Kaiserli E, Sullivan S, Jones MA, Feeney KA, Christie JM (2009) Domain swapping to assess the mechanistic basis of Arabidopsis phototropin 1 receptor kinase activation and endocytosis by blue light. Plant Cell 21:3226–3244. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.067876
Kinoshita T, Doi M, Suetsugu N, Kagawa T, Wada M, Shimazaki K (2001) Phot1 and phot2 mediate blue light regulation of stomatal opening. Nature 414:656–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/414656a
Komander D, Rape M (2012) The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem 81:203–229. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060310-170328
Łabuz J, Sztatelman O, Jagiełło-Flasińska D, Hermanowicz P, Bażant A, Banaś AK, Bartnicki F, Giza A, Kozłowska A, Lasok H, Sitkiewicz E, Krzeszowiec W, Gabryś H, Strzałka W (2021) Phototropin interactions with SUMO proteins. Plant Cell Physiol 62:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcab027
Liscum E, Briggs WR (1995) Mutations in the NPH1 locus of Arabidopsis disrupt the perception of phototropic stimuli. Plant Cell 7:473–485. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.4.473
Liscum E, Nittler P, Koskie K (2020) The continuing arc toward phototropic enlightenment. J Exp Bot 71:1652–1658. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa005
Loftfield JVG (1921) The behavior of stomata. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication 314, Washington, DC, pp 7–104
Losi A, Gärtner W (2012) The evolution of flavin-binding photoreceptors: an ancient chromophore serving trendy blue-light sensors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:49–72. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105538
MacGurn JA, Hsu PC, Emr SD (2012) Ubiquitin and membrane protein turnover: from cradle to grave. Annu Rev Biochem 81:231–259. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060210-093619
Möglich A, Yang X, Ayers RA, Moffat K (2010) Structure and function of plant photoreceptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:21–47. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112259
Motchoulski A, Liscum E (1999) Arabidopsis NPH3: A NPH1 photoreceptor-interacting protein essential for phototropism. Science 286:961–964. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5441.961
Paez Valencia J, Goodman K, Otegui MS (2016) Endocytosis and endosomal trafficking in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:309–335. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112242
Peng J, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Thoreen CC, Cheng D, Marsischky G, Roelofs J, Finley D, Gygi SP (2003) A proteomics approach to understanding protein ubiquitination. Nat Biotechnol 21:921–926. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt849
Roberts D, Pedmale UV, Morrow J, Sachdev S, Lechner E, Tang X, Zheng N, Hannink M, Genschik P, Liscum E (2011) Modulation of phototropic responsiveness in Arabidopsis through ubiquitination of phototropin 1 by the CUL3-Ring E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL3(NPH3). Plant Cell 23:3627–3640. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.087999
Romero-Barrios N, Vert G (2018) Proteasome-independent functions of lysine-63 polyubiquitination in plants. New Phytol 217:995–1011. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14915
Sakai T, Haga K (2012) Molecular genetic analysis of phototropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1517–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs111
Sakamoto K, Briggs WR (2002) Cellular and subcellular localization of phototropin 1. Plant Cell 14:1723–1735. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.003293
Saracco SA, Hansson M, Scalf M, Walker JM, Smith LM, Vierstra RD (2009) Tandem affinity purification and mass spectrometric analysis of ubiquitylated proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant J 59:344–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03862.x
Sullivan S, Thomson CE, Lamont DJ, Jones MA, Christie JM (2008) In vivo phosphorylation site mapping and functional characterization of Arabidopsis phototropin 1. Mol Plant 1:178–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssm017
Sullivan S, Waksman T, Paliogianni D, Henderson L, Lütkemeyer M, Suetsugu N, Christie JM (2021) Regulation of plant phototropic growth by NPH3/RPT2-like substrate phosphorylation and 14–3-3 binding. Nat Commun 12:6129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26333-5
Suryadinata R, Holien JK, Yang G, Parker MW, Papaleo E, Šarčević B (2013) Molecular and structural insight into lysine selection on substrate and ubiquitin lysine 48 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34. Cell Cycle 12:1732–1744. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.24818
Takemiya A, Inoue S, Doi M, Kinoshita T, Shimazaki K (2005) Phototropins promote plant growth in response to blue light in low light environments. Plant Cell 17:1120–1127. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.030049
Tseng TS, Briggs WR (2010) The Arabidopsis rcn1-1 mutation impairs dephosphorylation of Phot2, resulting in enhanced blue light responses. Plant Cell 22:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.066423
Tseng TS, Whippo C, Hangarter RP, Briggs WR (2012) The role of a 14–3-3 protein in stomatal opening mediated by PHOT2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1114–1126. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.092130
Walton A, Stes E, Cybulski N, Van Bel M, Iñigo S, Durand AN, Timmerman E, Heyman J, Pauwels L, De Veylder L, Goossens A, De Smet I, Coppens F, Goormachtig S, Gevaert K (2016) It’s time for some “site”-seeing: Novel tools to monitor the ubiquitin landscape in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 28:6–16. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00878
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Lynn Hartweck, University of Minnesota, for critical reading of the manuscript; and Professor Akira Nagatani, Kyoto University, for the gift of the PHOT1 cDNA transgenic plasmid, Pp1:P1G-nosT/pPZP211. We thank late Professor Winslow Briggs, Carnegie Institution, Stanford University, for generous supports.
Funding
This work was financially supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, (Grant number MOST110WFA1610040) to TST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TST conceived and drafted this project for research. CAC, and MHL helped with material preparations, experiment set up, and data collecting; TST together with help from CAC and MHL conducted and carried out the experiments. TST drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
425_2024_4332_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
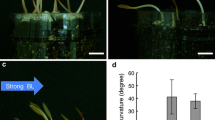
Supplementary file1 Supplementary Fig. S1 Representation of the PHOTOTROPIN1 protein. PHOT1: PHOTOTROPIN1 protein; LOV: LOV domain; J-alpha: J-alpha helix; number1: the starting methionine of PHOT1; K526: lysine residue at position 526 of PHOT1. Lower part shows detail amino acid residues (one letter) from position 501 to 560. The LOV2 core sequence was underlined, following by the double lysine pair at position 526 (underlined), and the other double lysine pair at position 550, used for mutagenesis to replace with arginine. Supplementary Fig. S2 a Phototropic responses after 8.5 h of blue light (1.5 μmol m-2 s-1) irradiance. Three-day-old etiolated seedlings of both gl1 and phot2-1 (functional PHOT1 only) were wild type controls. phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant exhibited residual bending angles. PHOT1 GFP complementation resorted the phototropic response of the phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant to the wild type level, while phot1 Lys526Arg GFP (phot1 K526R GFP), phot1 Lys527Arg GFP (phot1 K527R GFP), or phot1 Lys526 527Arg GFP (phot1 K526 527R GFP) transgenic lines had smaller bending angles than phot2-1. The asterisks above the bars indicate individual transgenic lines with significant smaller bending angles than phot2-1 (data represent: mean +SE; n>20; Student’s t test; P < 0.05). b Attenuated phototropic responses of phot1 Lys526Arg GFP and phot1 Lys527Arg GFP transgenic lines. Three-day-old etiolated seedlings were treated with 1 μmol m-2 s-1 of blue light and bending angles of hypocotyls were imaged for analyses at the time indicated (mean +SE; n>25). The phot2-1 mutant and PHOT1 GFP line were wild type controls. phot1 K526R GFP: phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant complemented with phot1 Lys526Arg GFP; phot1K527R GFP: phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant complemented with phot1 Lys527Arg GFP. The asterisks above the bars indicate the individual transgenic line with significant smaller bending angles than the phot2-1 control (functional PHOT1 only) (Student’s t test; P < 0.05). Similar results were obtained in two other experiments. Supplementary Fig. S3 phot1 Lys526 527Arg GFP replacements did not change the ubiquitination pattern of PHOT1. Etiolated three-day-old seedlings expressing PHOT1 GFP or phot1 Lys526 527Arg GFP (phot1 526 527R GFP) were irradiated with 100 μmol m-2 s-1 of blue light for two hours. Microsomal fractions made from these seedlings were immuno-precipitated with antibodies against GFP (IP: α -GFP). The immuno-precipitated proteins were resolved with SDS-PAGE and blotted for protein detection with PHOT1-specific antibodies (IB: α -PHOT1), or with P4D1 antibodies (IB: α -P4D1) that recognize ubiquitination modifications on pulled-down phot1 protein. Supplementary Fig. S4 Etiolated hypocotyl elongation and gravitropic responses of phot1Lys526 527Arg GFP individual, or double replacements transgenic lines. a Etiolated hypocotyl elongation. Hypocotyl elongation of etiolated seedlings grown on half-strength MS medium was imaged for measurement at the time indicated (mean +SE; n>20). b Gravitropic responses of etiolated seedlings. Seeds were germinated vertically on half-strength MS medium for three days in darkness. Medium plates were turned horizontally and hypocotyl bending angles were imaged for analyses at the time indicated (mean +SE; n>25). PHOT1 GFP: PHOT1 GFP line. phot1 K526R GFP: phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant complemented with phot1 Lys526Arg GFP. phot1 K527R GFP: phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant complemented with phot1 Lys527Arg GFP. phot1 K526 527R GFP: phot1-5/phot2-1double mutant complemented with phot1 Lys526 527Arg GFP. Similar trends were seen in two different experiments. Supplementary Fig. S5 phot1 Lys550 551Arg GFP transformant lines exhibited complementation in blue light responses of phototropic bending and stomatal opening. a Etiolated three-day-old seedlings of phot1 Lys550 551Arg GFP transformant line (phot1 K550 551R GFP) were treated with blue light (1 μmol m-2 s-1) for eight hours; the bending angles were determined (mean +SE; n>30). phot2-1 mutant was used as a control of PHOT1 functional only. b Stomatal opening in response to blue light treatments. Stomata from abaxial leaf surface of mature (5-week-old) phot1 Lys550 551Arg GFP transformants (phot1 K550 551R GFP) were treated with blue light (1 and 10 μmol m-2 s-1), superimposed with red light (50 μmol m-2 s-1) for two hours before harvesting for measurements (mean +SE; n>25). phot2-1 mutant was used as a control. Similar results were seen in two different experiments. No significant difference between the phot2-1 control and individual transgenic lines (Student’s t test; P < 0.05)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, TS., Chen, CA. & Lo, MH. PHOTOTROPIN1 lysine 526 functions to enhance phototropism in Arabidopsis. Planta 259, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04332-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04332-2