Abstract
Main conclusion
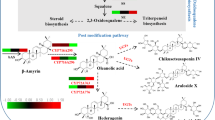
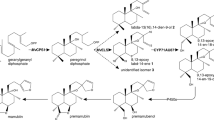
We identify two ferruginol synthases and a 11-hydroxyferruginol synthase from a traditional Chinese medicinal herb Isodon lophanthoides and propose their involvement in two independent abietane diterpenoids biosynthetic pathways.
Abstract
Isodon lophanthoides is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb rich in highly oxidized abietane-type diterpenoids. These compounds exhibit a wide range of pharmaceutical activities, yet the biosynthesis is barely known. Here, we describe the screening and functional characterization of P450s that oxidize the abietane skeleton abietatriene. We mainly focused on CYP76 family and identified 12 CYP76AHs by mining the RNA-seq data of I. lophanthoides. Among the 12 CYP76AHs, 6 exhibited similar transcriptional expression features as upstream diterpene synthases, including root or leaf-preferential expression pattern and highly MeJA inducibility. These six P450s were considered as first-tier candidates and functionally characterized in yeast and plant cells. In yeast assays showed that both CYP76AH42 and CYP76AH43 were ferruginol synthases hydroxylating the C12 position of abietatriene, whereas CYP76AH46 was characterized as a 11-hydroxyferruginol synthase which catalyzes two successive oxidations at C12 and C11 of abietatriene. Heterologous expression of three CYP76AHs in Nicotiana benthamiana resulted in the formation of ferruginol. qPCR analysis showed CYP76AH42 and CYP76AH43 were mainly expressed in the root, which was consistent with the distribution of ferruginol in the root periderms. CYP76AH46 was primarily expressed in the leaves where barely ferruginol or 11-hydroxyferruginol was detected. In addition to distinct organ-specific expression pattern, three CYP76AHs exhibited different genomic structures (w or w/o introns), low protein sequence identities (51–63%) and were placed in separate subclades in the phylogenetic tree. These results suggest that the identified CYP76AHs may be involved in at least two independent abietane biosynthetic pathways in the aerial and underground parts of I. lophanthoides.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The nucleotide sequences reported in this study have been deposited in the NCBI GenBankTM/EBI Data Bank with accession numbers: CYP76AH41, OP891584; CYP76AH42, OP891585; CYP76AH43, OP891586; CYP76AH44, OP891587; CYP76AH45, OP891588; CYP76AH46, OP891589; CYP76AH47, OP891590; CYP76AH48, OP891591; CYP76AH49, OP891592; CYP76AH50, OP891593; CYP76AH51, OP891594; CYP76AH52, OP891595.
Abbreviations
- diTPS:
-
Diterpene synthase
- (+)-CPS:
-
(+)-Copalyl diphosphate synthase
- P450:
-
Cytochrome P450
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- GGPP:
-
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate
- GGOH:
-
Geranylgeraniol
- TIC:
-
Total ion chromatogram
References
Bathe U, Tissier A (2019a) Cytochrome P450 enzymes: a driving force of plant diterpene diversity. Phytochemistry 161:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.12.003
Bathe U, Frolov A, Porzel A, Tissier A (2019b) CYP76 oxidation network of abietane diterpenes in Lamiaceae reconstituted in Yeast. J Agric Food Chem 67:13437–13450. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00714
Božić D, Papaefthimiou D, Brückner K, de Vos RC, Tsoleridis CA, Katsarou D, Papanikolaou A, Pateraki I, Chatzopoulou FM, Dimitriadou E, Kostas S, Manzano D, Scheler U, Ferrer A, Tissier A, Makris AM, Kampranis SC, Kanellis AK (2015) Towards elucidating carnosic acid biosynthesis in Lamiaceae: functional characterization of the three first steps of the pathway in Salvia fruticosa and Rosmarinus officinalis. PLoS ONE 10:e0124106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124106
Brandle JE, Telmer PG (2007) Steviol glycoside biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 68:1855–1863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.010
Ceunen S, Geuns JM (2013) Steviol glycosides: chemical diversity, metabolism, and function. J Nat Prod 76:1201–1228. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400203b
Chen F, Tholl D, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E (2011) The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom. Plant J 66:212–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04520.x
Gietz RD, Woods RA (2002) Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods Enzymol 350:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(02)50957-5
Guo J, Zhou YJ, Hillwig ML, Shen Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu W, Peters RJ, Chen X, Zhao ZK, Huang L (2013) CYP76AH1 catalyzes turnover of miltiradiene in tanshinones biosynthesis and enables heterologous production of ferruginol in yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:12108–12113. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218061110
Guo J, Ma X, Cai Y, Ma Y, Zhan Z, Zhou YJ, Liu W, Guan M, Yang J, Cui G, Kang L, Yang L, Shen Y, Tang J, Lin H, Ma X, Jin B, Liu Z, Peters RJ, Zhao ZK, Huang L (2016) Cytochrome P450 promiscuity leads to a bifurcating biosynthetic pathway for tanshinones. New Phytol 210:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13790
Hamberger B, Ohnishi T, Hamberger B, Séguin A, Bohlmann J (2011) Evolution of diterpene metabolism: Sitka spruce CYP720B4 catalyzes multiple oxidations in resin acid biosynthesis of conifer defense against insects. Plant Physiol 157:1677–1695. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.185843
Hansen CC, Nelson DR, Møller BL, Werck-Reichhart D (2021) Plant cytochrome P450 plasticity and evolution. Mol Plant 14:1772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.09.013
Hansen NL, Kjaerulff L, Heck QK, Forman V, Staerk D, Møller BL, Andersen-Ranberg J (2022) Tripterygium wilfordii cytochrome P450s catalyze the methyl shift and epoxidations in the biosynthesis of triptonide. Nat Commun 13:5011. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32667-5
Ignea C, Athanasakoglou A, Ioannou E, Georgantea P, Trikka FA, Loupassaki S, Roussis V, Makris AM, Kampranis SC (2016) Carnosic acid biosynthesis elucidated by a synthetic biology platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:3681–3686. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1523787113
Jin B, Cui G, Guo J, Tang J, Duan L, Lin H, Shen Y, Chen T, Zhang H, Huang L (2017) Functional diversification of kaurene synthase-like genes in Isodon rubescens. Plant Physiol 174:943–955. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00202
Ladeiras D, Monteiro CM, Pereira F, Reis CP, Afonso CA, Rijo P (2016) Reactivity of diterpenoid quinones: Royleanones. Curr Pharm Des 22:1682–1714. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666151211094521
Lin L, Dong Y, Yang B, Zhao M (2011) Chemical constituents and biological activity of Chinese medicinal herb “Xihuangcao.” Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 14:720–729. https://doi.org/10.2174/138620711796504352
Lin CZ, Zhao W, Feng XL, Liu FL, Zhu CC (2016) Cytotoxic diterpenoids from Rabdosia lophanthoides var. gerardianus. Fitoterapia 109:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.11.015
Liu Q, Manzano D, Tanić N, Pesic M, Bankovic J, Pateraki I, Ricard L, Ferrer A, de Vos R, van de Krol S, Bouwmeester H (2014) Elucidation and in planta reconstitution of the parthenolide biosynthetic pathway. Metab Eng 23:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.03.005
Liu M, Wang WG, Sun HD, Pu JX (2017) Diterpenoids from Isodon species: an update. Nat Prod Rep 34(9):1090–1140. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7np00027h
Ma Y, Cui G, Chen T, Ma X, Wang R, Jin B, Yang J, Kang L, Tang J, Lai C, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Shen Y, Zeng W, Peters RJ, Qi X, Guo J, Huang L (2021) Expansion within the CYP71D subfamily drives the heterocyclization of tanshinones synthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Nat Commun 12:685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-20959-1
Mafu S, Zerbe P (2017) Plant diterpenoid metabolis for manufacturing the biopharmaceuticals of tomorrow: prospects and challenges. Phytochem Rev 17:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-017-9513-5
Muchlinski A, Jia M, Tiedge K, Fell JS, Pelot KA, Chew L, Davisson D, Chen Y, Siegel J, Lovell JT, Zerbe P (2021) Cytochrome P450-catalyzed biosynthesis of furanoditerpenoids in the bioenergy crop switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Plant J 108:1053–1068. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15492
Pateraki I, Andersen-Ranberg J, Jensen NB, Wubshet SG, Heskes AM, Forman V, Hallström B, Hamberger B, Motawia MS, Olsen CE, Staerk D, Hansen J, Møller BL, Hamberger B (2017) Total biosynthesis of the cyclic AMP booster forskolin from Coleus forskohlii. Elife 6:e23001. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23001
Peng B, Plan MR, Carpenter A, Nielsen LK, Vickers CE (2017) Coupling gene regulatory patterns to bioprocess conditions to optimize synthetic metabolic modules for improved sesquiterpene production in yeast. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0728-x
Ro DK, Arimura G, Lau SY, Piers E, Bohlmann J (2005) Loblolly pine abietadienol/abietadienal oxidase PtAO (CYP720B1) is a multifunctional, multisubstrate cytochrome P450 monooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:8060–8065. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500825102
Sainsbury F, Thuenemann EC, Lomonossoff GP (2009) pEAQ: versatile expression vectors for easy and quick transient expression of heterologous proteins in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 7:682–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00434.x
Scheler U, Brandt W, Porzel A, Rothe K, Manzano D, Božić D, Papaefthimiou D, Balcke GU, Henning A, Lohse S, Marillonnet S, Kanellis AK, Ferrer A, Tissier A (2016) Elucidation of the biosynthesis of carnosic acid and its reconstitution in yeast. Nat Commun 7:12942. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12942
Sun HD, Huang SX, Han QB (2006) Diterpenoids from Isodon species and their biological activities. Nat Prod Rep 23:673–698. https://doi.org/10.1039/b604174d
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Ting HM, Wang B, Rydén AM, Woittiez L, van Herpen T, Verstappen FWA, Ruyter-Spira C, Beekwilder J, Bouwmeester HJ, van der Krol A (2013) The metabolite chemotype of Nicotiana benthamiana transiently expressing artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes is a function of CYP71AV1 type and relative gene dosage. New Phytol 199:352–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12274
Tu L, Su P, Zhang Z, Gao L, Wang J, Hu T, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Song Y, Tong Y, Lu Y, Yang J, Xu C, Jia M, Peters RJ, Huang L, Gao W (2020) Genome of Tripterygium wilfordii and identification of cytochrome P450 involved in triptolide biosynthesis. Nat Commun 11:971. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14776-1
van Herpen TW, Cankar K, Nogueira M, Bosch D, Bouwmeester HJ, Beekwilder J (2010) Nicotiana benthamiana as a production platform for artemisinin precursors. PLoS ONE 5:e14222. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014222
Wang Q, Hillwig ML, Okada K, Yamazaki K, Wu Y, Swaminathan S, Yamane H, Peters RJ (2012) Characterization of CYP76M5-8 indicates metabolic plasticity within a plant biosynthetic gene cluster. J Biol Chem 287:6159–6168. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.305599
Wu Y, Hillwig ML, Wang Q, Peters RJ (2011) Parsing a multifunctional biosynthetic gene cluster from rice: biochemical characterization of CYP71Z6&7. FEBS Lett 585:3446–3451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.09.038
Wu Y, Wang Q, Hillwig ML, Peters RJ (2013) Picking sides: distinct roles for CYP76M6 and CYP76M8 in rice oryzalexin biosynthesis. Biochem J 454:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20130574
Xiong X, Gou J, Liao Q, Li Y, Zhou Q, Bi G, Li C, Du R, Wang X, Sun T, Guo L, Liang H, Lu P, Wu Y, Zhang Z, Ro DK, Shang Y, Huang S, Yan J (2021) The Taxus genome provides insights into paclitaxel biosynthesis. Nat Plants 7:1026–1036. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-021-00963-5
Yang LB, Li L, Huang SX, Pu JX, Zhao Y, Ma YB, Chen JJ, Leng CH, Tao ZM, Sun HD (2011) Anti-hepatitis B virus and cytotoxic diterpenoids from Isodon lophanthoides var. gerardianus. Chem Pharm Bull 59:1102–1105. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.59.1102
Yang R, Du Z, Qiu T, Sun J, Shen Y, Huang L (2021) Discovery and functional characterization of a diverse diterpene synthase family in the medicinal herb Isodon lophanthoides Var. gerardiana. Plant Cell Physiol 62:1423–1435. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcab089
Zi J, Peters RJ (2013) Characterization of CYP76AH4 clarifies phenolic diterpenoid biosynthesis in the Lamiaceae. Org Biomol Chem 11:7650–7652. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ob41885e
Zi J, Mafu S, Peters RJ (2014) To gibberellins and beyond! Surveying the evolution of (di)terpenoid metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:259–286. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-035705
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance was provided by the National Science Foundation of Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant No. 31900250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH: designed the project; ZD, ZP, HY and HW: performed the experiments; JS: constructed the YS101 strain; LH: wrote the article. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Anastasios Melis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Z., Peng, Z., Yang, H. et al. Identification and functional characterization of three cytochrome P450 genes for the abietane diterpenoid biosynthesis in Isodon lophanthoides. Planta 257, 90 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04125-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04125-z