Abstract
Main conclusion
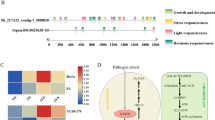
Soybean contains a group of 64 L-type lectin receptor-like kinases. Three LecRKs were involved in the interactions with Phytophthora sojae and Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens.
Abstract
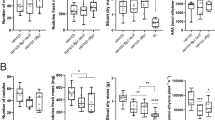
L-type lectin receptor-like kinases (LecRKs) comprise an important class of membrane-localized receptor-like kinases that are involved in plant adaptation. In this study, we performed an inventory analysis of LecRKs in Glycine max (soybean). In total, 64 GmLecRKs containing the canonical LecRK feature were identified. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that 48 GmLecRKs have close orthologs in Arabidopsis or Solanum lycopersicum, while 16 are likely present only in the leguminous plant species. Transcriptome analyses revealed that expressions of multiple GmLecRK genes are either induced or suppressed during infection by the soybean root rot pathogen Phytophthora sojae. In addition, overexpression of the three LecRKs (Glyma.17G085000, Glyma.05G041300 or Glyma.17G224600) in the soybean hairy roots enhanced resistance to P. sojae. Upon inoculation with Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens, overexpression of Glyma.17G085000 in the soybean hairy roots does not significantly influence the nodulation, while overexpression of Glyma.05G041300 or Glyma.17G224600 slightly reduced the number and dry weight of nodules. This study highlights the importance of LecRKs in regulating plant–microbe interactions and provides new knowledge on the deployment of LecRKs to increase resistance in soybean.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- dai:
-
Day after inoculation
- LecRKs:
-
L-type lectin receptor-like kinases
- SD:
-
Segmental duplication
- TD:
-
Tandem duplication
- WGD:
-
Whole genome duplication
References
Balagué C, Gouget A, Bouchez O, Souriac C, Haget N, Boutet-Mercey S, Govers F, Roby D, Canut H (2017) The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling. Mol Plant Pathol 18(7):937–948. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12457
Berrabah F, Bourcy M, Eschstruth A, Cayrel A, Guefrachi I, Mergaert P, Wen J, Jean V, Mysore KS, Gourion B, Ratet P (2014) A nonRD receptor-like kinase prevents nodule early senescence and defense-like reactions during symbiosis. New Phytol 203(4):1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12881
Bourcy M, Brocard L, Pislariu CI, Cosson V, Mergaert P, Tadege M, Mysore KS, Udvardi MK, Gourion B, Ratet P (2013) Medicago truncatula DNF2 is a PI-PLC-XD-containing protein required for bacteroid persistence and prevention of nodule early senescence and defense-like reactions. New Phytol 197(4):1250–1261. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12091
Bouwmeester K, Govers F (2009) Arabidopsis L-type lectin receptor kinases: phylogeny, classification, and expression profiles. J Exp Bot 60(15):4383–4396. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp277
Bouwmeester K, de Sain M, Weide R, Gouget A, Klamer S, Canut H, Govers F (2011) The lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is a novel Phytophthora resistance component and a potential host target for a RXLR effector. PLoS Pathog 7(3):e1001327. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001327
Brechenmacher LKM, Benitez M, Li M, Joshi T, Calla B, Lee MP, Libault M, Vodkin LO, Xu D, Lee SH, Clough SJ, Stacey G (2008) Transcription profiling of soybean nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21(5):631–645. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-21-5-0631
Chen D, Cao Y, Li H, Kim D, Ahsan N, Thelen J, Stacey G (2017) Extracellular ATP elicits DORN1-mediated RBOHD phosphorylation to regulate stomatal aperture. Nat Commun 8(1):2265. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02340-3
Chinchilla D, Shan L, He P, de Vries S, Kemmerling B (2009) One for all: the receptor-associated kinase BAK1. Trends Plant Sci 14(10):535–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.08.002
Choi J, Tanaka K, Cao Y, Qi Y, Qiu J, Liang Y, Lee SY, Stacey G (2014) Identification of a plant receptor for extracellular ATP. Science 343(6168):290–294. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.343.6168.290
Delaux PM, Schornack S (2021) Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes. Science 371(6531):eaba6605. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba6605
Desclos-Theveniau M, Arnaud D, Huang TY, Lin GJ, Chen WY, Lin YC, Zimmerli L (2012) The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. PLoS Pathog 8(2):e1002513. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002513
Domonkos A, Horvath B, Marsh JF, Halasz G, Ayaydin F, Oldroyd GED, Kalo P (2013) The identification of novel loci required for appropriate nodule development in Medicago truncatula. BMC Plant Biol 13(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-157
Eggermont L, Verstraeten B, Van Damme EJM (2017) Genome-wide screening for lectin motifs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2017.02.0010
Gouhier-Darimont C, Schmiesing A, Bonnet C, Lassueur S, Reymond P (2013) Signalling of Arabidopsis thaliana response to Pieris brassicae eggs shares similarities with PAMP-triggered immunity. J Exp Bot 64(2):665–674. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers362
Gouhier-Darimont C, Stahl E, Glauser G, Reymond P (2019) The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.8 is involved in insect egg perception. Front Plant Sci 10:623–623. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00623
Groux R, Stahl E, Gouhier-Darimont C, Kerdaffrec E, Jimenez-Sandoval P, Santiago J, Reymond P (2021) Arabidopsis natural variation in insect egg-induced cell death reveals a role for LECTIN RECEPTOR KINASE-I.1. Plant Physiol 185(1):240–255. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiaa022
Hofberger JA, Nsibo DL, Govers F, Bouwmeester K, Schranz ME (2015) A complex interplay of tandem- and whole-genome duplication drives expansion of the L-type lectin receptor kinase gene family in the brassicaceae. Genome Biol Evol 7(3):720–734. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evv020
Huang PY, Yeh YH, Liu AC, Cheng CP, Zimmerli L (2014) The Arabidopsis LecRK-VI.2 associates with the pattern-recognition receptor FLS2 and primes Nicotiana benthamiana pattern-triggered immunity. Plant J 79(2):243–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12557
Limpens E, Bisseling T (2003) Signaling in symbiosis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6(4):343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(03)00068-2
Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, Willemse J, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2003) LysM domain receptor kinases regulating rhizobial Nod factor-induced infection. Science 302(5645):630–633. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090074
Liu PL, Huang Y, Shi PH, Yu M, Xie JB, Xie L (2018) Duplication and diversification of lectin receptor-like kinases (LecRLK) genes in soybean. Sci Rep 8(1):5861. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24266-6
Luo XM, Xu N, Huang JK, Gao F, Hs Z, Boudsocq M, Coaker G, Liu J (2017) A lectin receptor-like kinase mediates pattern-triggered salicylic acid signaling. Plant Physiol 174(4):2501–2514. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00404
Miyazawa H, Oka-Kira E, Sato N, Takahashi H, Wu GJ, Sato S, Hayashi M, Betsuyaku S, Nakazono M, Tabata S, Harada K, Sawa S, Fukuda H, Kawaguchi M (2010) The receptor-like kinase KLAVIER mediates systemic regulation of nodulation and non-symbiotic shoot development in Lotus japonicus. Development 137(24):4317–4325. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.058891
Navarro-Gochicoa MT, Camut S, Timmers AC, Niebel A, Herve C, Boutet E, Bono JJ, Imberty A, Cullimore JV (2003) Characterization of four lectin-like receptor kinases expressed in roots of Medicago truncatula. Structure, location, regulation of expression, and potential role in the symbiosis with Sinorhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol 133(4):1893–1910. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.027680
Pfeilmeier S, George J, Morel A, Roy S, Smoker M, Stransfeld L, Downie JA, Peeters N, Malone JG, Zipfel C (2019) Expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana immune receptor EFR in Medicago truncatula reduces infection by a root pathogenic bacterium, but not nitrogen-fixing rhizobial symbiosis. Plant Biotechnol J 17(3):569–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12999
Pham AQ, Cho S-H, Nguyen CT, Stacey G (2020) Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase P2K2 is a second plant receptor for extracellular ATP and contributes to innate immunity. Plant Physiol 183(3):1364–1375. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.01265
Rae AE, Rolland V, White RG, Mathesius U (2021) New methods for confocal imaging of infection threads in crop and model legumes. Plant Methods 17(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00725-6
Ryu H, Laffont C, Frugier F, Hwang I (2017) MAP kinase-mediated negative regulation of symbiotic nodule formation in Medicago truncatula. Mol Cells 40(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.2211
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10763–10768. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.181141598
Singh P, Zimmerli L (2013) Lectin receptor kinases in plant innate immunity. Front Plant Sci 4:124–124. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00124
Singh P, Kuo YC, Mishra S, Tsai CH, Chien CC, Chen CW, Desclos-Theveniau M, Chu PW, Schulze B, Chinchilla D, Boller T, Zimmerli L (2012) The lectin receptor kinase-VI.2 is required for priming and positively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 24(3):1256–1270. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.095778
Stegmann M, Monaghan J, Smakowska-Luzan E, Rovenich H, Lehner A, Holton N, Belkhadir Y, Zipfel C (2017) The receptor kinase FER is a RALF-regulated scaffold controlling plant immune signaling. Science 355(6322):287–289. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal2541
Tang DZ, Wang GX, Zhou JM (2017) Receptor kinases in plant-pathogen interactions: more than pattern recognition. Plant Cell 29(4):618–637. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00891
Tripathi D, Zhang T, Koo AJ, Stacey G, Tanaka K (2018) Extracellular ATP acts on jasmonate signaling to reinforce plant defense. Plant Physiol 176(1):511–523. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01477
Tyler BM (2007) Phytophthora sojae: root rot pathogen of soybean and model oomycete. Mol Plant Pathol 8(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00373.x
Vaid N, Pandey PK, Tuteja N (2012) Genome-wide analysis of lectin receptor-like kinase family from Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol 80(4–5):365–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9952-8
Van Holle S, Van Damme EJ (2015) Distribution and evolution of the lectin family in soybean (Glycine max). Molecules 20(2):2868–2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022868
Van Holle S, Van Damme EJM (2019) Messages from the past: new insights in plant lectin evolution. Front Plant Sci 10:36. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00036
Wang Y, Bouwmeester K (2017) L-type lectin receptor kinases: new forces in plant immunity. PLoS Pathog 13(8):e1006433. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006433
Wang Y, Bouwmeester K, Beseh P, Shan WX, Govers F (2014) Phenotypic analyses of Arabidopsis T-DNA insertion lines and expression profiling reveal that multiple L-type lectin receptor kinases are involved in plant immunity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27(12):1390–1402. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-06-14-0191-R
Wang Y, Cordewener JHG, America AHP, Shan W, Bouwmeester K, Govers F (2015a) Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinases LecRK-IX.1 and LecRK-IX.2 are functional analogs in regulating Phytophthora resistance and plant cell death. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28(9):1032–1048. https://doi.org/10.1094/mpmi-02-15-0025-r
Wang Y, Weide R, Govers F, Bouwmeester K (2015b) L-type lectin receptor kinases in Nicotiana benthamiana and tomato and their role in Phytophthora resistance. J Exp Bot 66(21):6731–6743. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv379
Wang C, Yu HX, Luo L, Duan LJ, Cai LY, He XX, Wen JQ, Mysore KS, Li GL, Xiao AF, Duanmu D, Cao YR, Hong ZL, Zhang ZM (2016) NODULES WITH ACTIVATED DEFENSE 1 is required for maintenance of rhizobial endosymbiosis in Medicago truncatula. New Phytol 212(1):176–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14017
Wang C, Zhou M, Zhang X, Yao J, Zhang Y, Mou Z (2017) A lectin receptor kinase as a potential sensor for extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in Arabidopsis thaliana. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25474
Wang C, Huang X, Li Q, Zhang Y, Li J-L, Mou Z (2019) Extracellular pyridine nucleotides trigger plant systemic immunity through a lectin receptor kinase/BAK1 complex. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12781-7
Woo JY, Jeong KJ, Kim YJ, Paek KH (2016) CaLecRK-S.5, a pepper L-type lectin receptor kinase gene, confers broad-spectrum resistance by activating priming. J Exp Bot 67(19):5725–5741. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw336
Wu T, Wang R, Xu X, He X, Sun B, Zhong Y, Liang Z, Luo S, Ye L (2014) Cucumis sativus L-type lectin receptor kinase (CsLecRK) gene family response to Phytophthora melonis, Phytophthora capsici and water immersion in disease resistant and susceptible cucumber cultivars. Gene 549(2):214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.07.058
Xiao W, Hu S, Zou X, Cai R, Liao R, Lin X, Yao R, Guo X (2021) Lectin receptor-like kinase LecRK-VIII.2 is a missing link in MAPK signaling-mediated yield control. Plant Physiol 187(1):303–320. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab241
Xu N, Luo X, Wu W, Xing Y, Liang Y, Liu Y, Zou H, Wei HL, Liu J (2020) A plant lectin receptor-like kinase phosphorylates the bacterial effector AvrPtoB to dampen its virulence in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 13(10):1499–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.09.016
Ye WW, Wang XL, Tao K, Lu YP, Dai TT, Dong SM, Dou DL, Gijzen M, Wang YC (2011) Digital gene expression profiling of the Phytophthora sojae transcriptome. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24(12):1530–1539. https://doi.org/10.1094/Mpmi-05-11-0106
Yekondi S, Liang FC, Okuma E, Radziejwoski A, Mai HW, Swain S, Singh P, Gauthier M, Chien HC, Murata Y, Zimmerli L (2018) Nonredundant functions of Arabidopsis LecRK-V.2 and LecRK-VII.1 in controlling stomatal immunity and jasmonate-mediated stomatal closure. New Phytol 218(1):253–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14953
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yao Zhao, Dr. Mian Wu, Zhichao Zhang and Maozhu Yin for suggestions. This project was supported by China Natural Science Foundation grants 31501622 and 31872927, and by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities KJQN201663”.
Funding
This article was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501622, and 31872927); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KJQN201663).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, M., Wan, B., Wang, L. et al. Identification and characterization of L-type lectin receptor-like kinases involved in Glycine max–Phytophthora sojae interaction. Planta 254, 128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03789-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03789-9