Abstract
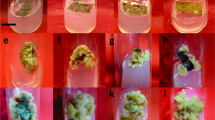
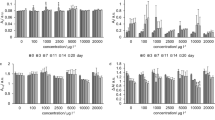
In vitro transgenic hairy root cultures provide a rapid system for physiological, biochemical studies and screening of plants for their phytoremediation potential. The hairy root cultures of Brassica juncea L. showed 92% decolorization of Methyl orange within 4 days. Out of the different redox mediators that were used to achieve enhanced decolorization, 2, 2′-Azinobis, 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) was found to be the most efficient. Laccase activity of 4.5 U mg−1 of protein was observed in hairy root cultures of Brassica juncea L., after the decolorization of Methyl orange. Intracellular laccase produced by B. juncea root cultures grown in MS basal medium was purified up to 2.0 fold with 6.62 U mg−1 specific activity using anion-exchange chromatography. Molecular weight of the purified laccase was estimated to be 148 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The purified enzyme efficiently oxidized ABTS which was also required for oxidation of the other tested substrates. The pH and temperature optimum for laccase activity were 4.0 and 40°C, respectively. The purified enzyme was stable up to 50°C and was stable in the pH range of 4.0–6.0. Laccase activity was strongly inhibited by sodium azide, EDTA, dithiothreitol and l-cysteine. The purified enzyme decolorized various textile dyes in the presence of ABTS as an efficient redox mediator. These findings contribute to a better understanding of the enzymatic process involved in phytoremediation of textile dyes by using hairy roots.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ABTS:
-
2,2′-Azinobis,3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- ACS:
-
Acetosyringone
- VAN:
-
Vanillin
- SGZ:
-
Syringaldazine
- HBT:
-
1-Hydroxybenzotriazole
- SA:
-
Syringic acid
- HQ:
-
Hydroquinone
- DMP:
-
2,6-Dimethoxy phenol
- PG:
-
Pyrogallol
- DCIP:
-
2,6-Dichlorophenol indophenol
- LMSs:
-
Laccase mediator systems
References
Abadulla E, Tzanov T, Costa S, Robra KH, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gubitz GM (2000) Decolourization and detoxification of textile dyes with a laccase from Trametes hirsute. Appl Environ Microb 66:3357–3362
Agostini E, Coniglio MS, Milrad SR, Tigier HA, Giulietti AM (2003) Phytoremediation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Brassica napus hairy root cultures. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 37:139–144
Ajungla L, Patil PP, Barmukh RB, Nikam TD (2009) Influence of biotic and abiotic elicitors on accumulation of hyoscyamine and scopolamine in root cultures of Datura metel L. Indian J Biotechnol 8:317–322
Arthur EL, Rice PJ, Anderson TA, Baladi SM, Henderson KLD, Coats IR (2005) Phytoremediation––an overview. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:109–122
Baldrian P (2004) Purification and characterization of laccase from the white rot fungus Daedalea quercina and decolorization of synthetic dyes by the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:560–563
Baldrian P (2006) Fungal laccases: occurrence and properties. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:215–242
Bizani E, Fytianos K, Poulios I, Tsiridis V (2006) Photocatalytic decolorization and degradation of dye solutions and wastewaters in the presence of titanium dioxide. J Hazard Mater 136:85–94
Call H, Mucke I (1997) Minireview: history, overview and applications of mediated ligninolytic systems, especially laccase-mediator-systems (Lignozym-Process). J Biotechnol 53:163–202
Chhabra M, Mishra S, Sreekrishnan T (2009) Laccase/mediator assisted degradation of triarylmethane dyes in a continuous membrane reactor. J Biotechnol 43:69–78
Claus H (2004) Laccases: structure, reactions, distribution. Micron 35:93–96
Claus H, Faber G, König H (2002) Redox-mediated decolorization of synthetic dyes by fungal laccases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:672–678
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085
Doran PM (2009) Applications of plant tissue cultures in phytoremediation research: incentives and limitations. Biotechnol Bioeng 103:60–76
Duckworth HW, Coleman JE (1970) Physicochemical and kinetic properties of mushroom tyrosinase. J Biol Chem 245:1613–1625
Ghodake G, Telke A, Jadhav J, Govindwar S (2009) Potential of Brassica juncea in order to treat textile effluent contaminated sites. Int J Phytorem 11:297–312
Jadhav SU, Ghodake GS, Telke AA, Tamboli DP, Govindwar SP (2009) Degradation and detoxification of disperse dye Scarlet RR by Galactomyces geotrichum MTCC 1360. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:409–415
Joo DJ, Shin WS, Choi JH, Choi SJ, Kim MC, Han MH, Ha TW, Kim YH (2007) Decolorization of reactive dyes using inorganic coagulants and synthetic polymer. Dyes Pigment 73:59–64
Kagalkar AN, Jagtap UB, Jadhav JP, Bapat VA, Govindwar SP (2009) Biotechnological strategies for phytoremediation of the sulfonated azo dye direct red 5B using Blumea malcolmii Hook. Bioresour Technol 100:4104–4110
Kagalkar AN, Jagtap UB, Jadhav JP, Bapat VA, Govindwar SP (2010) Studies on phytoremediation potentiality of Typhonium flagelliforme for the degradation of Brilliant Blue R. Planta 232:271–285
Kalme S, Jadhav S, Jadhav M, Govindwar S (2009) Textile dye degrading laccase from Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Enzym Microb Technol 44:65–71
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RL (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mathur N, Bhatnagar P, Bakre P (2005) Assessing mutagenicity of textile dyes from Pali (Rajasthan) using Ame’s bioassay. Appl Ecol Environ Res 4:111–118
Moldes D, Sanroman MA (2006) Amelioration of the ability to decolorize dyes by laccase: relationship between redox mediators and laccase isoenzymes in Trametes vericolor. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:1197–1204
Morozova OV, Shumakovich GP, Shleev SV, Yaropolov YI (2007) Laccase–mediator systems and their applications: a review. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43:523–535
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Plant Physiol 15:473–479
Murugesan K, Arulmani M, Nam IH, Kim YM, Chang YS, Kalaichelvan PT (2006) Purification and characterization of laccase produced by a white rot fungus Pleurotus sajorcaju under submerged culture condition and its potential in decolorization of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:939–946
Nagai M, Sato T, Watanabe H, Saito K, Kawata M, Enei H (2002) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:327–335
Newman L, Reynolds C (2004) Phytodegradation of organic compounds. Curr Opin Biotech 15:225–230
Patil P, Desai N, Govindwar S, Jadhav J, Bapat V (2009) Degradation analysis of reactive red 198 by hairy roots of Tagetes patula L (Marigold). Planta 230:725–735
Sharma P, Goel R, Capalash N (2007) Bacterial laccases. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:823–832
Sharma S, Singh P, Swami R, Sharma K (2009) Exploring fish bioassay of textile dye wastewaters and their selected constituents in terms of mortality and erythrocyte disorders. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83:29–34
Singh S, Melo JS, Eapen S, D’Souza SF (2006) Phenol removal using Brassica juncea hairy roots: role of inherent peroxidase and H2O2. J Biotechnol 123:43–49
Sterjiades R, Dean J, Eriksson K (1992) Laccase from Sycamore maple (Acer pseudoplatanus) polymerizes monolignols. Plant Physiol 99:1162–1168
Suresh B, Sherkhane PD, Kale S, Eapen S, Ravishankar GA (2005) Uptake and degradation of DDT by hairy root cultures of Cichorium intybus and Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 61:1288–1292
Switzer RC, Merril CR, Shifrin S (1979) A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 98:231–237
Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Dawkar VV, Govindwar SP (2009a) Influence of organic and inorganic compounds on oxidoreductive decolorization of sulfonated azo dye C.I. Reactive orange 16. J Hazard Mater 172:298–309
Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Jadhav UV, Parshetti GK, Govindwar SP (2009b) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from a Pseudomonas sp. LBC1. J Mol Catal B Enzym 61:252–260
Telke AA, Kadam AA, Jagtap SS, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2010) Biochemical characterization of blue laccase from Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146 and its potential for textile dye degradation. Biotechnol Biopro Eng 15:696–703
Tien M, Kirk T (1983) Lignin-degrading enzyme from the hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium burds. Science 221:661–663
Xu F (1997) Effects of redox potential and hydroxide inhibition on the pH activity profile of fungal laccases. J Biol Chem 272:924–928
Yun M, Yeon K, Park J, Lee C, Chun J, Lim D (2006) Characterization of biofilm structure and its effect on membrane permeability in MBR for dye wastewater treatment. Water Res 40:45–52
Zille A, Tzanov T, Gübitz GM, Cavaco-Paulo M (2003) Immobilized laccase for decolourization of reactive black 5 dyeing effluent. Biotechnol Lett 25:1473–1477
Acknowledgments
VAB, AAT and UBJ wish to thank and express gratitude to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, for Emeritus Scientist, Senior Research Fellowship and Junior Research Fellowship, respectively. ANK wishes to thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India, for Junior Research Fellowship. SPG wishes to thank University Grants Commission, New Delhi for SAP-DRS-1 support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Telke, A.A., Kagalkar, A.N., Jagtap, U.B. et al. Biochemical characterization of laccase from hairy root culture of Brassica juncea L. and role of redox mediators to enhance its potential for the decolorization of textile dyes. Planta 234, 1137–1149 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1469-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1469-x