Abstract
Abscisic acid, stress, ripening proteins (ASR) are a family of plant-specific small hydrophilic proteins. Studies in various plant species have highlighted their role in increased resistance to abiotic stress, including drought, but their specific function remains unknown. As a first step toward their potential use in crop improvement, we investigated the structure and regulation of the Asr gene family in Musa species (bananas and plantains). We determined that the Musa Asr gene family contained at least four members, all of which exhibited the typical two exons, one intron structure of Asr genes and the “ABA/WDS” (abscisic acid/water deficit stress) domain characteristic of Asr genes. Phylogenetic analyses determined that the Musa Asr genes were closely related to each other, probably as the product of recent duplication events. For two of the four members, two versions corresponding to the two sub-genomes of Musa, acuminata and balbisiana were identified. Gene expression and protein analyses were performed and Asr expression could be detected in meristem cultures, root, pseudostem, leaf and cormus. In meristem cultures, mAsr1 and mAsr3 were induced by osmotic stress and wounding, while mAsr3 and mAsr4 were induced by exposure to ABA. mASR3 exhibited the most variation both in terms of amino acid sequence and expression pattern, making it the most promising candidate for further functional study and use in crop improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Drought, high salinity and freezing all impose osmotic stress on plants and negatively affect their growth, development and/or productivity. The ability of each species to tolerate water deficit plays a critical role in determining its productivity and its natural geographical distribution. The effects of water deficit both on plant physiology and at the cellular level are highly complex (Ingram and Bartels 1996). Yet, transcriptome and proteome analyses using various model organisms have revealed some of the underlying molecular processes related to water stress (Seki et al. 2001; Rajjou et al. 2006; Shinozaki and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki 2007). Many of the genes involved in this response have been identified (Xiong and Zhu 2002), some of which respond to osmotic stress through abscisic acid (ABA) signaling. Among these, the abscisic acid, stress, ripening (ASR) protein has fostered growing interest as a potential key regulator of plant response to a variety of stresses, including osmotic stress (Cakir et al. 2003; Carrari et al. 2004; Frankel et al. 2007; Konrad and Bar-Zvi 2008; Carpentier et al. 2010a).
The first ASR protein was identified as a water/ABA stress-induced protein in tomato (Iusem et al. 1993). Other members were later identified in tomato, revealing the existence of a gene family (Rossi et al. 1996). ASR proteins are specific to plants and the number of documented members in the Asr gene family differs among plant species. For example, there are six known members in rice (Philippe et al. 2010), four in tomato (Frankel et al. 2006), four in pine (Chang et al. 1996) and as many as nine in maize (highest number of members described so far; Zivy and Coursol, INRA, France, personal communication), but none in A. thaliana (Carrari et al. 2004; Yang et al. 2005). Comparison of sequences from different species suggests that family members from a single species are more closely related to each other than to Asr members from other species (Carrari et al. 2004; Philippe et al. 2010), suggesting that they originate from late duplication events and that the sub-function of each of the family members might be species specific (Philippe et al. 2010).
ASR proteins have been repeatedly identified as involved in the response to different abiotic stresses, such as water deficit, salt stress, and cold or osmotic stress in many plants such as tomato, potato, maize or rice (Amitai-Zeigerson et al. 1995; Gilad et al. 1997; Riccardi et al. 1998; Vaidyanathan et al. 1999; Maskin et al. 2001). Moreover, over-expression of the lily ASR in A. thaliana resulted in enhanced drought and salt resistance, confirming its role in stress response even in a system where it is not endogenously present (Yang et al. 2005).
ASR proteins are small hydrophilic proteins, the exact function of which remains unclear. They are characterized by the presence of the ABA/WDS (abscisic acid/water deficit stress) amino acid domain (PF02496) (Canel et al. 1995; Padmanabhan et al. 1997). Some ASR proteins also contain a zinc-dependent DNA-binding domain (Kalifa et al. 2004) and have been demonstrated to bind DNA both in a monomeric and a homodimeric form (Maskin et al. 2007). ASR proteins have been found in the cytosol, where they have been shown to exhibit chaperone-like activity, possibly stabilizing other cytosolic proteins against denaturation (Konrad and Bar-Zvi 2008). ASR proteins have also been reported to be localized in the nucleus in different cell types (Kalifa et al. 2004; Wang et al. 2005; Konrad and Bar-Zvi 2008), where they might play a regulatory role, possibly as transcription factors or as chaperones (Wang et al. 2005; Frankel et al. 2006; Konrad and Bar-Zvi 2008). Finally, the fact that the expression of most Asr genes is induced both by sugars and ABA has led to the hypothesis that it might serve as a link between sugar and ABA signaling, possibly through the regulation of hexose uptake (Cakir et al. 2003; Carrari et al. 2004; Frankel et al. 2007).
In the present report, we investigated the structure, diversity and regulation of the Asr gene family in Musa species (banana and plantains). As an important food crop, the yield of banana and plantains is economically important worldwide and crucial for the livelihood of many small farmers. Banana varieties differ widely in their ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, including drought. Most of the cultivated varieties are diploid or triploid and contain various relative proportions of the genomes of Musa acuminata (A genome) and Musa balbisiana (B genome). It is believed that varieties with a high proportion of the B genome are generally more resistant to abiotic stress (Thomas et al. 1998). This is supported by the fact that those varieties cover more northern and drier geographical regions (De Langhe and de Maret 1999; Perrier et al. 2009).
ASR proteins represent a promising candidate for Musa improvement. An ASR protein was initially identified in a proteomics screen of two varieties exhibiting contrasting tolerance to osmotic stress (Carpentier et al. 2007) and where a unique isoform was detected in a tolerant ABB variety. Asr sequences were also identified in a screen of DATAMUSA, an ensemble of Musa EST sequences, suggesting that ASR proteins can be expressed in all tissues tested (roots, peel green, male flowers and roots) (Santos et al. 2009). We recently discovered that the mASR1 protein was significantly up-regulated by osmotic stress (Carpentier et al. 2010a). Furthermore, an Asr gene (Asr1 according to our classification of the Musa Asr family members) was recently identified from a Musa sp. (the exact genomic group of the variety described as “Musa paradisiaca L. ABB group” is unclear to us, Liu et al. 2010). These authors argued that overexpression of MpASR resulted in increased drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Although only two transgenic lines were characterized in this study, and no correlation between increased drought tolerance and level of mASR expression in their transgenic A. thaliana lines was presented (Liu et al. 2010), these results together with the aforementioned findings suggest that ASR proteins play an important role in banana stress response as well. Here, we report on the structure, phylogenetic position and regulation of the Asr genes of various Musa cultivars and wild accessions.
Materials and methods
Plant material
Various Musa spp. (Musaceae, Musa) were used in conducting this study. They correspond to wild varieties and cultivated varieties (cultivars), and each contain a specific combinations of the genomes of the two main species of Musa: Musa acuminata L. A. Colla and Musa balbisiana L. A. Colla. All plant materials were originally obtained from the International Transit Center (ITC), Kasteelpark Arenberg 13 bus 2455, 3001 Leuven, Belgium and each Musa sp. can be uniquely identified by its ITC number.
Meristem culture
Multiple shoot meristem cultures of ‘Cachaco’ (ITC.0643), ‘Mbwazirume’ (ITC.0084), balbisiana (ITC.0545), ‘Populu’ (ITC.0335), banksii (ITC.0466) and ‘Williams’ (ITC.0365) were initiated and maintained on P4 medium (MS medium supplemented with 100 μM 6-benzylaminopurine and 1 μM indole acetic acid) as previously described (Strosse et al. 2006).
For the experiment investigating natural variation in Asr expression in different cultivars (Fig. 4) and the experiment investigating tissue-specific expression of Asr in ‘Williams’ (Fig. 5a), meristems were harvested 6 days after the last subculture and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. For the other experiments, only meristems from ‘Cachaco’ were used.
For the experiment investigating the effect of sucrose and wounding by cutting (Fig. 6a, b), meristems were divided into three groups. Following 1 week of growth on standard P4 medium, all groups were subcultured (i.e., differentiated tissue was cut and removed) on day 0 and placed back on their respective growth medium (not fresh). The cutting control group was harvested 24 h later. The “control” and “sucrose” groups were transferred to fresh standard P4 medium (0.09 M sucrose) or fresh P4 medium containing 0.4 M sucrose, respectively, on day 4 and meristems were harvested 2 days later (day 6) and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen.
For the experiment investigating the effect of ABA (Fig. 6a, c), meristems were divided into two groups. Both groups were subcultured and transferred to fresh P4 medium on day 1. On day 4, the “control” group was transferred to fresh P4 medium again, while the “ABA” group was transferred to fresh P4 medium containing 100 μM ABA. On day 7, all meristems were harvested and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Plant growth experiments in greenhouse conditions
For the experiment investigating tissue-specific expression of Asr (Fig. 5), plants were grown in pots in a greenhouse in which the photoperiod was extended to 12 h by artificial light when needed. The temperature reached 26 and 18°C in the day and night, respectively, while the relative humidity ranged between 70 and 90%. For the experiment comparing mAsr expression in leaves and meristem cultures from cultivar ‘Williams’ (Fig. 5a), leaf tissue was harvested from the fifth leaf of plants that were at least 6 months old. For the experiment investigating mAsr expression in the first and second leaf of ‘Cachaco’ plants and in the roots (Fig. 5b), “Leaf 1” corresponds to the youngest leaf (cigar leaf), “Leaf 2” corresponds to the second youngest leaf and “Root” material was collected by pooling five of the widest primary roots. Plants had produced at least 7 leaves (~2.5–3 months old) at the time of harvest. All tissue was flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after harvest.
Determination of the Musa ASR sequences
Screen of genomic DNA using degenerate primers: genomic DNA from ‘Cachaco’ (ABB) was used for the initial gene discovery. Primers were designed based on Musa sequences from EST libraries and publicly available databases (see Table 1 for primer sequences). Using these primers, the complete sequence of mAsr4 was obtained as well as fragments from the three other mAsr sequences ranging between 100 and 400 bp.
Screening of BAC libraries: BAC libraries were obtained from the Musa Genomics Resource Center (MGRC, http://lmcc.ieb.cz/dna-libraries/bananas) and screened to obtain the full-length genomic sequence of mAsr1, 2 and 3. Genomic BAC libraries from ‘Pisang Klutuk Wulung’ (BB cultivar, MBP library) and ‘Calcutta4’ (AA cultivar, MA4 library) were screened for the presence of the desired Asr sequence. Briefly, 18 or 12 “superpools”, for the MA4 and MBP libraries, respectively, were screened by PCR using degenerate primers designed from Asr sequences available in GenBank from Musa and other species. Positive superpools were screened further for identification of the positive BAC clone using the same PCR primers and conditions. Three positive clones, each harboring one of the mAsr1, mAsr2 and mAsr3 genes, were identified. Each of these three BACs was used as template to obtain full-length genomic sequences of mAsr1 (from ‘Calcutta4’), mAsr2 (from ‘Pisang Klutuk Wulung’) and mAsr3 (from ‘Calcutta4’).
Phylogenetic analysis of Asr sequences
Once full-length genomic sequences had been obtained from all four mAsr genes, sequences from other cultivars and wild accessions of Musa were obtained by PCR amplification using primers specific to each mAsr gene (see Table 1). Amplification was performed on genomic DNA either obtained from the Global Musa Genomics Consortium (GMGC, http://www.musagenomics.org) for ‘Tani’ (ITC.1120) and ‘Pisang Jari Buaya’ (ITC.0312) or from newly extracted genomic DNA from ‘Cachaco’ (ITC.0643), ‘Mbwazirume’ (ITC.0084), ‘Williams’ (ITC.0365), ‘Butuhan’ (ITC.0565), banksii (ITC.0466), balbisiana (ITC.0545), ‘Bluggoe’ (ITC.1404), ‘Pome’ (ITC.0125), ‘Pisang Awak (ITC.0339) and ‘Orishele’ (ITC.0517). PCR fragments were cloned and sequenced in both directions. The sequences obtained were cleaned of vector and primer sequences. Multiple sequences from the same cultivar or wild accession originate from independent cloning events. More clones per cultivar or wild accession were sequenced for the mAsr3 gene than for the other three mAsr genes, since it exhibited more variation within and between cultivars than the other three genes (see “Results”). Protein sequences were derived from genomic sequences after alignment of genomic sequences with cDNA sequence from at least one cultivar, removal of intron sequence and in silico translation. All mAsr1, mAsr2, partial mAsr3 and mAsr4 sequences obtained in the context of this study were deposited in Genbank under the following accession numbers: GU134740 to GU134760 for mAsr1, GU134761 to GU134775 for mAsr2, GU134776 to GU134782 for mAsr3 and GU134735 to GU134739 for mAsr4. Full-length mAsr3 sequences can be found in Online Resource 4.
Multiple alignments of DNA or protein sequences were created using the ClustalX freeware, version 2.1.12 (Larkin et al. 2007). ClustalX 2.1.12 was also used to construct phylogenetic trees, using the neighbor-joining algorithm, with 1,000 replicate bootstrap tests. Trees were visualized using the njplot freeware (http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr/software/njplot.html). Sequences used for phylogenetic analysis either originated from this work or from publicly available databases (National Center for Biotechnology Information, http://www.ncbi.nih.gov). For the alignment depicted in Fig. 2, different sequences of the same gene and from the same cultivar or wild accession were kept separate if the nucleotide sequences differed by more than 1%. If the nucleotide sequences differed by less than 1%, only one sequence was retained (in the case of only two sequences) or a consensus sequence was derived (if there were three or more sequences). For mAsr1 to mAsr4, a 1% error rate corresponds to a maximum of 4, 5, 5 and 4 bp, respectively. A detailed description of the origin of each of the sequences used for this phylogenetic analysis can be found in Online Resource 1.
Analysis of mASR gene expression
Sample material was harvested as described above and stored at −80°C until it was ground in liquid nitrogen for RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy plus mini kit (Qiagen Sciences), according to manufacturer’s recommendations except for the addition of PVP40000 to the lysis buffer to a final concentration of 5 mg/ml. Next, RNA was treated with DNaseI (Applied Biosystems/Ambion) for 45 min at 37°C. Last, RNA was purified through a phenol–chloroform/IAA precipitation purification step. To verify the absence of residual genomic DNA, a real-time PCR was performed using DNase-treated RNA as template (see below). Only samples for which no amplification products could be detected after 40 cycles of PCR amplification were further processed. cDNA synthesis was performed on a known amount of RNA (1,000–3,000 ng, depending on the experiment) using the RevertAid™ H Minus First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Fermentas) and olido(dT)18 primers, as recommended by the manufacturer.
Real-time RT-PCR was performed in a Corbett Rotor-Gene 3000 (Qiagen). Reactions included: 12.5 μl 2× Absolute SYBR® Green I master mix (Thermo Scientific, Epsom, United Kingdom), 150 nM of reverse and forward primers (see Table 1 for sequences), 2 μl of template (cDNA or gDNA or water) and water to reach a final volume of 25 μl. Each experiment included four to six biological replicates of each sample type and two technical replicates of all samples. For each independent experiment, all samples were run simultaneously. A set of six reference genes (actin, actin-11, 25S r-DNA, tubulin, elongation factor-1α (EF1α) and ribosomal protein L2 (L2); see Table 1 for primer sequences) were run in addition to the four mAsr genes. The most appropriate pair of reference genes was identified using geNorm v3.4, as previously described (Vandesompele et al. 2002) and used for normalization purposes. For comparison of cultivars (Fig. 4a), the two reference genes used for normalization were actin11 and tubulin. For comparison of tissue types in ‘Williams’ (Fig. 5a), the two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and 25S r-DNA. For comparison of tissue types in ‘Cachaco’ (Fig. 5b), the two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and L2. For investigating the effect of exposure to high concentration of sucrose (Fig. 6b), the two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and actin11. For investigating the effect of exposure to ABA (Fig. 6c), the two reference genes used for normalization were actin11 and L2. Finally, relative mRNA concentrations were averaged over all biological replicates. After checking for normality and homogeneity of variance, means were compared on a pair-wise basis using Student’s t tests and considered significantly different when the obtained P value was <0.05.
For investigating the effect of high concentration of sucrose, the phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) encoding gene was used as a positive control since it had been previously demonstrated that the protein was more abundant in meristem cultures after induction with high concentrations of sucrose (Carpentier et al. 2007; Carpentier et al. 2010b). For investigating the effect of exposure to ABA, the mARP (ABA-responsive protein) gene was used as a positive control based on its homology to the A. thaliana “ABA-responsive protein-like” gene (At5g13200), known to be up-regulated by ABA exposure (Yazaki et al. 2004).
Analysis of protein abundance
2D-Gel electrophoresis (2DE) was performed via phenol extraction as previously described (Carpentier et al. 2005). For Western blots, small immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips were used (7 cm pI 3_10 (GE Healthcare)). After 2DE, proteins were blotted to a nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare) via semi-dry transfer (Owl HEP-3 Semi Dry, Thermo Scientific) at 1 mA/cm2 for 60 min (cathode buffer: 0.04 M ε-aminocaproic acid, 10% SDS, 20% methanol; protein transfer buffer: 48 mM Tris, 39 mM glycine, 0.037% SDS, 20% methanol, MQ H2O; anode buffer I: 0.3 M Tris, 20% methanol; anode buffer II: 0.025 M Tris, 20% methanol). Membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk powder in PBST (20 mM potassium phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% (w/v) Tween-20, pH 7.2) for 60 min. After three washes in PBST, the membranes were incubated with primary antibody (1/2,000 in PBST) [rabbit anti-ASR polyclonal antibody was raised against a custom peptide matching the sequence ETAYSGGGDYASGYT (Eurogentec, Belgium)] overnight at 4°C. After washing in PBST, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibody goat anti-rabbit (GE Healthcare) (1/2,500 in PBST) for 60 min. Visualization of the proteins was realized with AEC (3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Sigma, Belgium).
Results
What is the structure of the mAsr gene family?
Through a combination of degenerate PCR, EST library screening and BAC sequencing, we discovered four Asr genes in banana. These genes have been named mAsr1 through mAsr4 (musa Asr). A total of more than 20,000 expressed sequence tags (EST) from cDNA libraries constructed from different tissue types or from samples subjected to various stresses (Santos et al. 2005; Roux et al. 2008; Carpentier et al. 2010a) were screened for additional banana Asr sequences.
All four genes contain two exons separated by a single intron, as do other Asr sequences from other species (Fig. 1). In banana, the mASR4 protein is shorter than the other three members of the family (103 vs. 144–146 amino acids, respectively). All four mASR proteins also contain the ABA/WDS domain, characteristic of the ASR family (PFAM domain PF02496).
Structure of the mAsr gene family. Intron–exon structure of the 4 mAsr genes from Musa. Each member contains two exons (boxes) separated by one short intron (line). The parts of the exons containing the ABA/WDS domain is highlighted in black. Numbers above the exons and introns indicate the length of these elements (bp). The length of the first exon in mAsr3 varies between 255 and 270 bp depending on the sequence
What is the phylogenetic relationship between the four mASR proteins?
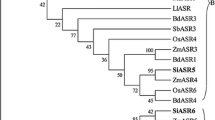
Once all four members of the mASR family were identified, each member was sequenced from different cultivars and wild varieties of Musa. Cultivars and wild varieties were chosen such that both diploid and triploid cultivars as well as most possible combinations of A and B genomes were represented. In total, we analyzed 18 mAsr1 sequences from 13 cultivars, 11 mAsr2 sequences from 7 cultivars, 9 mAsr3 sequences from 5 cultivars and 4 mAsr4 sequences from 4 cultivars. All genomic sequences were aligned (see “Materials and methods” for details) and a phylogenetic tree was constructed (Fig. 2). As expected from their size, mAsr4 sequences were most divergent, while the other three members of the family were relatively close to each other.
Phylogenetic relationship between mAsr genomic sequences in various wild and cultivated accessions of Musa. Full-length genomic sequences (including the intron) were aligned using ClustalX and a neighbor-joining tree was constructed (bootstrap of 1,000). The distance between sequences is indicated by branch length. Bootstrap values between major groups and >75% are indicated. Gray boxes indicate putative sub-clusters associated with the A and B genomes for mAsr1, mAsr2 and mAsr3. For each sequence, the name of the cultivar or wild variety is indicated and the genome composition in brackets. Sequences from the same cultivar or wild variety are distinguished by the name of the clone corresponding to each particular sequence. The gene ID of each of the genes used for the construction of this tree can be found in Online Resource 1
We originally focused on mASR1 because it was one of the most highly expressed proteins in our meristem cultures (Carpentier et al. 2007). The mAsr1 sequences obtained clearly clustered into two groups. The sequences present in each group and the genotype of the cultivars from which they originated was consistent with one cluster containing alleles from the A genome and the other containing alleles from the B genome (Fig. 2, gray box). Amino acid sequences from 13 Musa varieties (wild varieties and cultivated varieties) were aligned, and sequences in the A and B groups consistently differed by only two amino acids (Online Resource 3). Yet, on a 2DE gel, the A and the B isoforms were clearly separated (Carpentier et al. 2010b) (Fig. 4b).
Fewer sequences were obtained from mAsr2. Alignment of the genomic sequences, including the intron, allowed for the identification of two clusters, potentially corresponding to the A and B genomes (data not shown). Translation analysis of these sequences revealed no difference specific to the A and B version at the amino acid level. The cluster of mAsr3 genomic sequences also contained a sub-cluster (Fig. 2, in gray) that could correspond to the B version of this gene. Sequence variability in the mAsr3 genes and mASR3 proteins was much more pronounced than in the other members of the mASR family (Online Resource 4 and Table 2). Finally, the number of different genomic sequences obtained from mAsr4 was too limited (4, Table 2) to be conclusive as to the difference between the A and B versions of this gene.
Next, we investigated the position of the mASRs with respect to ASR sequences from other species. We included sequences from both the A and the B genomes of Musa: from ‘Williams’ (AAA), ‘Tani’ (BB) and/or balbisiana (wild BB) from the four mASR proteins and aligned them to previously identified ASR sequences from other species (Fig. 3). All four mASRs protein clustered together rather than with ASR proteins from other species, suggesting that they were the product of recent duplication events rather than orthologs of Asr genes found in other species. Interestingly, the relationship between mASR1, mASR2 and mASR3 was different when using protein sequences rather than genomic sequences (Figs. 2, 3). Specifically, the protein sequences of mAsr1 clustered with those of mAsr3, while genomic sequences of mAsr1 and mAsr2 clustered together. This relationship held true and was well supported when all mASR protein sequences obtained in the context of this study were aligned (data not shown).
Neighbor-joining tree of ASR protein sequences from various plants species. Full-length protein sequences were aligned using ClustalX and an unrooted neighbor-joining tree was constructed (bootstrap of 1,000). The distance between sequences is indicated by branch length. The four members of the mAsr family are enclosed in the gray box and represented by sequences from ‘Williams’ (AAA, mASR1_clone173, mASR2_clone193, mASR3_clone_a and mASR4_clone170), ‘Tani’ (BB, mASR1_clone140, mASR2_clone197) and balbisiana (BB, mASR3_clone1). Sequences from other plant species are available in NCBI: NP_001152333.1 (Maize B), XP_002447825.1 (Sorghum B), XP_002457802.1 (Sorghum A), AAT57940.1 (Sugarcane), CAA72998.1 (Maize A), ACZ50736 (mASR4), ACZ60133.1 (mASR1), ACZ60138.1 (mASR1), ACZ50744.1 (mASR2), ACZ50739.1 (mASR2), EEC72202 (Rice ASR2), NP_001045487 (Rice ASR6), BAD28236 (Rice ASR3), NP_001173936 (Rice ASR4), NP_001065841 (Rice ASR5), NP_001045459 (Rice ASR1), 2282019 (Tomato ASR1), 584787 (Tomato ASR2), 400471 (Tomato ASR3), AAY98032 (Tomato ASR4), 4098248 (Potato CI21A), 4098250 (Potato ci21B), 23095773 (Potato DS2), 6525055 (Lily) and 38532363 (Gingko). The nomenclature of the Rice ASR proteins comes from (Philippe et al. 2010)
Why did we not obtain an A version of mAsr1 from Cachaco?
Surprisingly, the cultivar from which ASR was originally identified, ‘Cachaco’, is of the ABB genomic composition, but no A version of mAsr1 could be found in the proteomics study (Fig. 4b), in the Musa cDNA libraries (Carpentier et al. 2010a) or when using PCR primers specific for the A version of mAsr1 at the gDNA level. Additionally, sequencing fragments that were amplified using primers that match perfectly to both the A and B version of Asr1 resulted in no ambiguous base at the positions where mAsr1A and B differ, while ambiguity was readily apparently in similar sequences obtained from other hybrid cultivars (data not shown). These results suggest that the mAsr1A transcript as well as its encoding gene are lacking in ‘Cachaco’. Further proteome analysis (2DE separation and de novo sequencing (Carpentier et al. 2010b) has revealed that ‘Cachaco’ does contain typical A genotype isoforms of other proteins. These data demonstrate that ‘Cachaco’ does indeed carry an A genome and that the A version of Asr was lost. A similar situation has been observed for other proteins in various cultivars (De Langhe et al. 2010). In the case of mAsr1, whether or not this is the result of positive selection for the B isoform remains to be determined.
Natural variation for mAsr expression. a Relative mRNA abundance of mAsr1 to mAsr4 in meristem cultures from three different cultivars. mRNA abundance was measured by quantitative RT-PCR (see “Materials and methods” for details). The two reference genes used for normalization were actin11 and tubulin. mRNA abundance was measured in ‘Cachaco’ (black bars), ‘Mbwaziume’ (white bars) and ‘Williams’ (gray bars) meristem cultures. Standard errors are represented. For each member of the mAsr family, mean relative abundance values were compared to each other on a pair-wise basis using Student’s t tests. Comparisons that were significant are indicated by one, two or three asterisks depending on whether the P value was <0.05, <0.01 or <0.001, respectively. b Two-dimensional gel of proteins extracted from meristem cultures of different Musa cultivars or wild accessions. Only the relevant portion of the gels, including the positions of the mASR1A (on the left) and mASR1B (on the right) proteins, is shown (Mw ~22 kDa and pI ~6.30 or 6.50 for the A or B versions of the protein, respectively). These positions are indicated by circles around the protein spots where the protein is present and empty circles where the protein is not detectable. A full gel image for ‘Cachaco’ meristems can be found at http://www.pdata.ua.ac.be/musa
Is there natural variation for mASR expression?
In the abovementioned proteomics screen investigating the effect of osmotic stress on gene regulation in banana meristems (Carpentier et al. 2007), ASR1 was identified as one of the most abundant proteins in meristem cultures of ‘Cachaco’ (ABB), a cultivar exhibiting enhanced resistance to osmotic stress in meristem cultures. In ‘Cachaco’, ASR4 protein could be detected as well, but weakly. Furthermore, the screening of an EST library containing over 10,000 transcripts from banana meristems grown under osmotic stress (Carpentier et al. 2010a) suggested also that mAsr1 was also one of the most abundant transcripts (73 hits), while mAsr2, 3 and 4 were either not present or only rarely found (1 hit, no hit and 3 hits, respectively).
To further document mAsr regulation, primers specific to each family member, but amplifying both the A and B version of each gene, were designed for expression analysis using quantitative real-time PCR (q-RT-PCR). Gene expression could be detected from all four mAsr genes in non-stressed meristem cultures of ‘Cachaco’ (ABB cultivar), demonstrating that at least one allele per mAsr gene is functional (Fig. 4).
Next, the expression level of the mAsr genes was investigated in other cultivars. mRNA abundance was compared between meristem cultures of ‘Cachaco’ and two AAA cultivars, ‘Williams’ and ‘Mbwazirume’ (Fig. 4a). All four mAsr genes were expressed in all three cultivars, but variation in relative expression levels could be identified. Specifically, the expression of all mAsr genes was significantly higher in ‘Mbwazirume’ than in ‘Cachaco’, especially for mAsr2 (>90-fold increase) and mAsr3 (~eightfold increase). mAsr expression was not significantly different in ‘Williams’ than in ‘Cachaco’ except for mAsr1, which exhibited slightly lower expression in ‘Williams’ than in ‘Cachaco’ (<twofold).
Finally, ASR1 protein could be detected in all cultivars tested using two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis as well (Fig. 4b). The A and B versions of the proteins were located in different spots, because two amino acids are consistently different between the A and B versions of the protein (Online Resource 3), resulting in a significant shift in isoelectric point. This is illustrated by the position of the mASR1 spot in various cultivars and the presence of two distinct spots in the AAB cultivar ‘Populu’ (Fig. 4b). As discussed above, only one spot could be detected in the ‘Cachaco’ (ABB) cultivar, due to the absence of the mAsr1A gene in the ‘Cachaco’ genome. The position of the ASR proteins identified on the 2D gels was verified by Western blotting using an anti-ASR1 peptide polyclonal antibody (data not shown).
Taken together, these results demonstrate that all four mAsr genes are active and that mAsr1 and mAsr4 are the most abundantly expressed, but the level of expression of mAsr2 and mAsr3 exhibited wide variations depending on the cultivar.
What is the pattern of expression of the mAsr genes?
To compare relative mRNA abundance in different tissues, q-RT-PCR was performed simultaneously on different tissues from the same cultivar (Fig. 5). First, mRNA abundance was compared between meristem cultures and greenhouse leaves of ‘Williams’ (Fig. 5a). The relative mRNA abundance of the mAsr genes was tissue specific. All mAsr genes exhibited high expression in leaves, except for mAsr4, which exhibited higher expression levels in meristems (Fig. 5a). The difference was particularly noticeable for mAsr2 and mAsr3 (~tenfold higher expression levels in leaves than in meristems). Similarly, mRNA abundance was compared in tissues from the first leaf (cigar leaf or last unrolled leaf), second leaf and roots of the ‘Cachaco’ cultivar (Fig. 5b). Again, all mAsr members were expressed in all tissue types tested, but at different levels and each gene exhibited a specific pattern of expression (Fig. 5b). The level of expression was significantly different in roots compared to the second leaf (all four mAsr members) and first leaf (mAsr4). Specifically, mAsr1 and mAsr2 expression was lower in roots than in the second leaf, whereas the opposite was observed for mAsr3 and mAsr4.
Developmental and tissue-specific expression of the mAsr family members. Relative mRNA abundance of mAsr1 to mAsr4 was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. For each member of the mAsr family, mean relative abundance values were calculated and compared to each other on a pair-wise basis using Student’s t tests. Standard errors are represented. Comparisons that were significant are indicated by one, two or three asterisks depending on whether the P value was <0.05, <0.01 or <0.001, respectively. a Comparison of mRNA abundance in greenhouse leaves and meristem cultures of the ‘Williams’ (AAA) cultivar. The two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and 25S r-DNA. Values obtained for leaves (gray bars) are expressed relative to values obtained for meristem cultures (black bars). b Comparison of mRNA abundance in the first (light gray bars) and second leaves (dark gray bars) as well as root tissue (white bars) from greenhouse plants of the ‘Cachaco’ (ABB) cultivar. The two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and L2
Finally, 2DE Western-blot analysis of ASR proteins was performed on tissue from roots, leaves, pseudostem and corm tissue from ‘Cachaco’ and confirmed that the ASR1 protein was present in all of these tissues (Online Resource 2).
Are the mAsr genes regulated by sugar and ABA?
Asr genes from various species have been demonstrated to be regulated by sugar and/or ABA (Rossi et al. 1998; Vaidyanathan et al. 1999). We tested whether this was true of the mAsr genes as well. mAsr expression was compared in ‘Cachaco’ meristems cultured on regular medium or on growth medium supplemented with 0.4 M sucrose. Additionally, the effect of the wounding stress associated with subculturing was also assessed (see “Materials and methods” for details). Relative mRNA abundance was compared between the three experimental treatments (Fig. 6a). As expected, the positive control (PGK) exhibited increased expression in sucrose-treated samples, while cutting did not affect its expression. We could show that the expression levels of both mAsr1 and mAsr3 were significantly increased by both high sucrose concentration and wounding by cutting (Fig. 6b).
Regulation of the mAsr members following exposure to sucrose, wounding (cutting) stress or ABA. The relative mRNA abundance of mAsr1 to mAsr4 was measured by quantitative RT-PCR on meristem cultures of the ‘Cachaco’ cultivar (ABB). For each member of the mAsr family, mean relative abundance values were compared to each other on a pair-wise basis using Student’s t tests. Standard errors are represented. Comparisons that were significant are indicated by one, two or three asterisks depending on whether the P value was <0.05, <0.01 or <0.001, respectively. a Schematic view of the treatments applied to each of the sample types. For the “sucrose experiment”, samples were cut on day 0 and put back on their respective standard growth media. The “cut” samples were harvested the next day. The other two types of samples were transferred to fresh medium (either standard growth medium or standard growth medium supplemented with 0.4 M sucrose) on day 4 and harvested 2 days later. For the “ABA experiment”, samples were cut on day 0 and placed on fresh growth media. On day 4, they were placed on either fresh standard growth medium or fresh standard growth medium supplemented with 100 μM ABA. Samples were harvested 3 days later. b Comparison of mRNA abundance in the different sample types illustrated in a: control (white bars), cut (light gray bars) and high sucrose samples (dark gray bars). The two reference genes used for normalization were EF1α and actin11. The expression of phosphoglycerate kinase (mPGK) was used as a positive control c Comparison of mRNA abundance in meristems grown on standard growth medium (white bars) or grown on standard growth medium supplemented with 100 μM ABA (black bars) for 3 days before harvest. The two reference genes used for normalization were actin11 and L2. The expression of an ABA-responsive protein (mARP) was used a positive control
Finally, a similar experiment was conducted comparing relative mRNA abundance in ‘Cachaco’ meristems grown on regular medium and samples grown for 3 days on medium supplemented with 100 μM ABA. As expected, expression of the positive control (mARP) was significantly induced by ABA exposure (Fig. 6c). We could show that the expression of mAsr3 and mAsr4 increased significantly in the presence of ABA (~4-fold and ~2-fold, respectively), but to lower extents than that of mARP (~12-fold).
Discussion
Asr genes encode small proteins with potentially important functions in response to a variety of stresses. This study aimed at characterizing the Asr gene family in Musa and to potentially identify promising candidates for crop improvement. We have identified 4 Asr genes from Musa, which all carry the ABA/WDS motif and the gene structure characteristic of Asr genes (Fig. 1). Through detailed analysis of the sequences of the mAsr genes (Figs. 2, 3) and documentation of their expression patterns (Figs. 4, 5, 6), we now have a detailed view of the specificities of each member of the family.
Origin of the four mAsrs
Banana is a monocotyledon, but only distantly related to the more well-studied model system of rice (Aert et al. 2004; Cheung and Town 2007), providing a different angle to investigate the evolution of the Asr gene family. Indeed, the four mAsr genes are phylogenetically close to each other, with respect to other Asr genes from other species including those of other monocots. This situation is similar to that observed in some species or group of species. For example, the four known Asr genes from pine all cluster together and away from Asr genes from other species, while Asr genes from tomato and potato all cluster together with an internal pair-wise organization of potato and tomato orthologs (Frankel et al. 2006). Interestingly, in tomato, all four Asr genes are located next to each other on chromosome IV (Frankel et al. 2006), suggestive of tandem duplications specific to Asr or a small portion of the genome containing Asr. In rice, on the other hand, the six Asr genes are located on four different chromosomes (Philippe et al. 2010). The mechanisms leading to the appearance of the different members of Asr families might thus be species dependent as well.
In banana, three of the four members cluster very closely together, while the fourth (mAsr4) clusters more distantly (Figs. 2, 3; Table 2). Possibly, one or several of the mAsr homologs originated from whole-genome duplication events. Indeed, a recent study of Musa BAC sequences suggested a whole genome duplication event specific to Musa species and estimated to have happened approximately 61 million years ago (Lescot et al. 2008). Assuredly, the sequence of the Musa genome (currently underway) will help shed light on the mechanisms underlying the evolution of the mAsr family in this genus. For example, it will indicate whether some of the mAsr genes are located on the same chromosome, suggestive of tandem duplication or whether another large-scale duplication event can be detected in the genome.
mAsr genes are ubiquitously expressed
We have demonstrated that at least one allele of each of the mAsr genes was expressed in all tissues sampled (roots, leaves, meristems, pseudostem, corm). Moreover, the expression level of the different members varied depending on the cultivar, the developmental stage (for example, young versus older leaves) or the tissue sampled. However, we cannot rule out the possibility that the observed variation is due to preferential or exclusive PCR amplification from a subset of the alleles in certain cultivars, since we used only one primer set per gene.
This type of observation could be consistent with sub-functionalization and has also been observed in other species. For example, in tomato, Asr1’s expression pattern exhibits very little variation, while the other members exhibit much more variable expression levels (Frankel et al. 2006): they exhibit variable responses to water-deficit stress and variable expression levels in different tissues (Maskin et al. 2008). Similarly, in banana meristems, mAsr1 was one of the most abundant proteins detected by 2D gel electrophoresis, while mAsr4 was detected at a much lower level (Carpentier et al. 2007) and mAsr2 and mAsr3 were undetected at the protein level.
Both the hypothesized role of ASR as a protein chaperone in the cytoplasm (Wang et al. 2005; Frankel et al. 2006; Konrad and Bar-Zvi 2008) or DNA chaperone in the nucleus could be consistent with our findings. The sequence of mASR4 is most different from that of the three other mASRs. Most strikingly, it is much shorter (103 vs. 144–150 for the other three mASR proteins). A similar situation has been observed in tomato, where ASR1, ASR2 and ASR3 are shorter (between 108 and 114 AAs), while ASR4 is much longer (297 AAs). Frankel et al. (2006) hypothesized that the extra domain encodes an additional biochemical function. Finally, ASR proteins have also been categorized as class seven of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins and five domains were identified within ASR sequences from various species (Battaglia et al. 2008). Domains 1, 2 and 3 are highly conserved, while domains 4 and 5 are only found in a subset of ASR proteins. Interestingly, all five domains are also found in mASR1, mASR2 and mASR3, while mASR4 lacks domain 5 and carries a heavily modified version of the middle domain (domain 1). It is thus possible that mASR4 performs a different or a subset of the function(s) performed by the other three members of the mAsr gene family.
mAsr3 exhibits the most variation
In our survey of the response of mAsr to abiotic stress, we have observed that mAsr3 expression was low in control samples, but most induced by high sucrose, wounding stress or ABA treatment. An in-depth analysis of the promoter sequence of mAsr3 would be instrumental to obtain more information about its potential role in stress response.
mAsr3 also exhibited the most sequence variation among the cultivars tested. Specifically, the sequences that formed the putative “B” cluster exhibited the highest variation of all sequences identified within the context of this work. Similar sequence variation has been observed for some members of Asr families from other species. In tomatoes, phylogenetic analysis of Asr2 genomic sequences from different varieties demonstrated accelerated positive selection correlated with colonization of dry environments (Frankel et al. 2003; Giombini et al. 2009). Similarly, an in-depth study of the rice Asr genes determined that OsAsr3 was the most divergent of the rice Asr genes and exhibited overall neutral selection at the species level, but directional selection in the sub-group of japonica found in tropical regions (Philippe et al. 2010). Musa balbisiana varieties are thought to be more drought tolerant than cultivars containing only A (from Musa acuminata) genomes (Nelson et al. 2006). Obtaining more sequences from mAsr3, especially from selected drought-tolerant and drought-sensitive varieties, will be instrumental in determining whether such a situation also occurs in Musa.
Supplementary materials
All sequences obtained in the context of this study have either been submitted to the nucleotide database at NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information, http://www.ncbi.nih.gov) or are available in Online Resource 4.
Abbreviations
- ASR:
-
Abscisic acid, stress, ripening
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- WDS:
-
Water deficit stress
- ITC:
-
International Transit Center
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- q-RT–PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- P4:
-
Proliferation medium
- 2DE:
-
Two-dimensional electrophoresis
- ARP:
-
ABA-responsive protein
References
Aert R, Sagi L, Volckaert G (2004) Gene content and density in banana (Musa acuminata) as revealed by genomic sequencing of BAC clones. Theor Appl Genet 109:129–139
Amitai-Zeigerson H, Scolnik PA, Bar-Zvi D (1995) Tomato Asr1 mRNA and protein are transiently expressed following salt stress, osmotic stress and treatment with abscisic acid. Plant Sci 110:205–213
Battaglia M, Olvera-Carrillo Y, Garciarrubio A, Campos F, Covarrubias AA (2008) The enigmatic LEA proteins and other hydrophilins. Plant Physiol 148:6–24
Cakir B, Agasse A, Gaillard C, Saumonneau A, Delrot S, Atanassova R (2003) A grape ASR protein involved in sugar and abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:2165–2180
Canel C, Bailey-Serres JN, Roose ML (1995) Pummelo fruit transcript homologous to ripening-induced genes. Plant Physiol 108:1323–1324
Carpentier SC, Witters E, Laukens K, Deckers P, Swennen R, Panis B (2005) Preparation of protein extracts from recalcitrant plant tissues: an evaluation of different methods for two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analysis. Proteomics 5:2497–2507
Carpentier SC, Witters E, Laukens K, Van Onckelen H, Swennen R, Panis B (2007) Banana (Musa spp.) as a model to study the meristem proteome: acclimation to osmotic stress. Proteomics 7:92–105
Carpentier SC, Vertommen A, Swennen R, Witters E, Fortes C, Souza MT, Panis B (2010a) Sugar-mediated acclimation: The importance of sucrose metabolism in meristems. J Proteome Res 9:5038–5046
Carpentier SC, Panis B, Renaut J, Samyn B, Vertommen A, Vanhove A-C, Swennen R, Sergeant K (2010b) The use of 2D-electrophoresis and de novo sequencing to characterize inter- and intra-cultivar protein polymorphisms in an allopolyploid crop. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.10.016
Carrari F, Fernie AR, Iusem ND (2004) Heard it through the grapevine? ABA and sugar cross-talk: the ASR story. Trends Plant Sci 9:57–59
Chang S, Puryear JD, Dias MADL, Funkhouser EA, Newton RJ, Cairney J (1996) Gene expression under water deficit in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda): isolation and characterization of cDNA clones. Physiol Plant 97:139–148
Cheung F, Town CD (2007) A BAC end view of the Musa acuminata genome. BMC Plant Biol 7:29
De Langhe E, de Maret P (1999) Tracking the banana: its significance in early agriculture. In: Gosden C, Hather J (eds) The prehistory of food. Appetites for change. Routledge, London and New York, pp 377–396
De Langhe E, Hřibová E, Carpentier S, Doležel J, Swennen R (2010) Did backcrossing contribute to the origin of hybrid edible bananas? Ann Bot 106:849–857
Frankel N, Hasson E, Iusem ND, Rossi MS (2003) Adaptive evolution of the water stress-induced gene Asr2 in Lycopersicon species dwelling in arid habitats. Mol Biol Evol 20:1955–1962
Frankel N, Carrari F, Hasson E, Iusem ND (2006) Evolutionary history of the Asr gene family. Gene 378:74–83
Frankel N, Nunes-Nesi A, Balbo I, Mazuch J, Centeno D, Iusem ND, Fernie AR, Carrari F (2007) ci21A/Asr1 expression influences glucose accumulation in potato tubers. Plant Mol Biol 63:719–730
Gilad A, Amitai-Zeigerson H, Bar-Zvi D, Scolnik PA (1997) ASR1, a tomato water-stress regulated gene: genomic organization, developmental regulation and DNA-binding activity. Acta Hort 447:447–454
Giombini MI, Frankel N, Iusem ND, Hasson E (2009) Nucleotide polymorphism in the drought responsive gene Asr2 in wild populations of tomato. Genetica 136:13–25
Ingram J, Bartels D (1996) The molecular basis of dehydration tolerance in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:377–403
Iusem ND, Bartholomew DM, Hitz WD, Scolnik PA (1993) Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) transcript induced by water deficit and ripening. Plant Physiol 102:1353–1354
Kalifa Y, Gilad A, Konrad Z, Zaccai M, Scolnik PA, Bar-Zvi D (2004) The water- and salt-stress-regulated Asr1 (abscisic acid stress ripening) gene encodes a zinc-dependent DNA-binding protein. Biochem J 381:373–378
Konrad Z, Bar-Zvi D (2008) Synergism between the chaperone-like activity of the stress regulated ASR1 protein and the osmolyte glycine-betaine. Planta 227:1213–1219
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lescot M, Piffanelli P, Ciampi A, Ruiz M, Blanc G, Leebens-Mack J, da Silva F, Santos C, D’Hont A, Garsmeur O, Vilarinhos A, Kanamori H, Matsumoto T, Ronning C, Cheung F, Haas B, Althoff R, Arbogast T, Hine E, Pappas G, Sasaki T, Souza M, Miller R, Glaszmann J-C, Town C (2008) Insights into the Musa genome: syntenic relationships to rice and between Musa species. BMC Genomics 9:58
Liu HY, Dai JR, Feng DR, Liu B, Wang HB, Wang JF (2010) Characterization of a novel plantain Asr gene, MpAsr, that is regulated in response to infection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense and abiotic stresses. J Integr Plant Biol 52:315–323
Maskin L, Gudesblat GE, Moreno JE, Carrari FO, Frankel N, Sambade A, Rossi M, Iusem ND (2001) Differential expression of the members of the Asr gene family in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Plant Sci 161:739–746
Maskin L, Frankel N, Gudesblat G, Demergasso MJ, Pietrasanta LI, Iusem ND (2007) Dimerization and DNA-binding of ASR1, a small hydrophilic protein abundant in plant tissues suffering from water loss. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:831–835
Maskin L, Maldonado S, Iusem ND (2008) Tomato leaf spatial expression of stress-induced Asr genes. Mol Biol Rep 35:501–505
Nelson A, Ploetz R, Kepler A (2006) Musa species (banana and plantain), ver. 2.2. In: Elevitch C (ed) Species profiles for Pacific Island agroforestry. Permanent agricultural resources (PAR). Holualoa, Hawai’i
Padmanabhan V, Dias DM, Newton RJ (1997) Expression analysis of a gene family in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) induced by water deficit stress. Plant Mol Biol 35:801–807
Perrier X, Bakry F, Carreel F, Jenny C, Horry J, Lebot V, Hippolyte I (2009) Combining biological approaches to shed light on the evolution of edible bananas. Ethnobot Res & Appl 7:199–216
Philippe R, Courtois B, McNally KL, Mournet P, El-Malki R, Le Paslier MC, Fabre D, Billot C, Brunel D, Glaszmann JC, This D (2010) Structure, allelic diversity and selection of Asr genes, candidate for drought tolerance, in Oryza sativa L. and wild relatives. Theor Appl Genet 121:769–787
Rajjou L, Belghazi M, Huguet R, Robin C, Moreau A, Job C, Job D (2006) Proteomic investigation of the effect of salicylic acid on Arabidopsis seed germination and establishment of early defense mechanisms. Plant Physiol 141:910–923
Riccardi F, Gazeau P, de Vienne D, Zivy M (1998) Protein changes in response to progressive water deficit in maize. Quantitative variation and polypeptide identification. Plant Physiol 117:1253–1263
Rossi M, Lijavetzky D, Bernacchi D, Hopp HE, Iusem N (1996) Asr genes belong to a gene family comprising at least three closely linked loci on chromosome 4 in tomato. Mol Gen Genet 252:489–492
Rossi M, Carrari F, Cabrera-Ponce JL, Vazquez-Rovere C, Herrera-Estrella L, Gudesblat G, Iusem ND (1998) Analysis of an abscisic acid (ABA)-responsive gene promoter belonging to the Asr gene family from tomato in homologous and heterologous systems. Mol Gen Genet 258:1–8
Roux N, Baurens FC, Dolezel J, Hribova E, Heslop-Harrison P, Town C, Sasaki T, Matsumoto T, Aert R, Remy S, Souza MT Jr, Lagoda P (2008) Genomics of banana and plantain (Musa spp.), major staple crops in the tropics. In: Moore PH, Ming R (eds) Genomics of tropical crop plants. Springer, New York, pp 83–111
Santos CMR, Martins NF, Horberg HM, de Almeida ER, Coelho MC, Togawa RC, da Silva FR, Caetano AR, Miller RN, Souza MT Jr (2005) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from Musa acuminata ssp. burmannicoides, var. Calcutta 4 (AA) leaves submitted to temperature stresses. Theor Appl Genet 110:1517–1522
Santos CMR, Martins NF, Melo de Araújo M, da Silva FRM, Togawa R, Souza MT Jr (2009) Screening of the DATA Musa database for orthologs of genes known to be related to biotic and abiotic stresses to identify and characterise candidate genes. Acta Hort 828:341–352
Seki M, Narusaka M, Abe H, Kasuga M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2001) Monitoring the expression pattern of 1,300 Arabidopsis genes under drought and cold stresses by using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant Cell 13:61–72
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2007) Gene networks involved in drought stress response and tolerance. J Exp Bot 58:221–227
Strosse H, Schoofs H, Panis B, Andre E, Reyniers K, Swennnen R (2006) Development of embryonic cells suspensions from shoot meristematic tissue in bananas and plantains (Musa spp.). Plant Sci 170:104–112
Thomas JE, Turner D, Eamus D (1998) Independent effects of the environment on the leaf gas exchange of three banana (Musa spp.) cultivars of different genomic constitution. Scient Hort 75:41–57
Vaidyanathan CP, Kuruvilla S, Thomas DS (1999) Characterization and expression pattern of an abscisic acid and osmotic stress responsive gene from rice. Plant Sci 140:21–30
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Wang H-J, Hsu C-M, Jauh GY, Wang CS (2005) A lily pollen ASR protein localizes to both cytoplasm and nuclei requiring a nuclear localization signal. Physiol Plant 123:314–320
Xiong L, Zhu JK (2002) Molecular and genetic aspects of plant responses to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:131–139
Yang CY, Chen YC, Jauh GY, Wang CS (2005) A lily ASR protein involves abscisic acid signaling and confers drought and salt resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:836–846
Yazaki J, Shimatani Z, Hashimoto A, Nagata Y, Fujii F, Kojima K, Suzuki K, Taya T, Tonouchi M, Nelson C, Nakagawa A, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Matsubara K, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Kikuchi S (2004) Transcriptional profiling of genes responsive to abscisic acid and gibberellin in rice: phenotyping and comparative analysis between rice and Arabidopsis. Physiol Genomics 17:87–100
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jaroslav Dolezel and Dr. Eva Hribova (Institute for Experimental Biology, Olomouc, Czech republic) for their work on the ITS region of Cachaco. We thank the Global Musa Genomics Consortium (GMGC) for providing us with BAC libraries and BAC clones as well as the genomic DNA collection. We thank László Sági for providing genomic DNA from various cultivars, and Els Thiry and An Krauss for technical help. This work was supported by the Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek–Vlaanderen (Grant G029606N and postdoc fellowship of S.C.C.), the KUL Bijzonder Onderzoek Fonds (to IMH, postdoctoral fellowship and to SP, predoctoral fellowship) and KUL Industriëel Onderzoek Fonds (Grant KP/08/001).
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, I.M., Carpentier, S.C., Pampurova, S. et al. Structure and regulation of the Asr gene family in banana. Planta 234, 785–798 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1421-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1421-0