Abstract
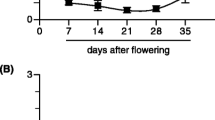
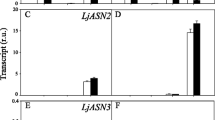
A pine asparagine synthetase gene expressed in developing seedlings has been identified by cloning its cDNA (PsAS1) from Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Genomic DNA analysis with PsAS1 probes and a sequence-based phylogenetic tree are consistent with the possibility of more than one gene encoding asparagine synthetase in pine. However, the parallel patterns of free asparagine content and PsAS1 products indicate that the protein encoded by this gene is mainly responsible for the accumulation of this amino acid during germination and early seedling development. The temporal and spatial patterns of PsAS1 expression together with the spatial distribution of asparagine content suggest that, early after germination, part of the nitrogen mobilized from the megagametophyte is diverted toward the hypocotyl to produce high levels of asparagine as a reservoir of nitrogen to meet later specific demands of development. Furthermore, the transcript and protein analyses in seedlings germinated and growth for extended periods under continuous light or dark suggest that the spatial expression pattern of PsAS1 is largely determined by a developmental program. Therefore, our results suggest that the spatial and temporal control of PsAS1 expression determines the re-allocation of an important amount of seed-stored nitrogen during pine germination.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Asparagine synthetase
- C:
-
Carbon
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- N:
-
Nitrogen
References
Ávila C, Suárez MF, Gómez-Maldonado J, Cánovas FM (2001) Spatial and temporal expression of two cytosolic glutamine synthetase genes in Scots pine: functional implications on nitrogen metabolism during early stages of conifer development. Plant J 25:93–102
Boehlein SK, Walworth ES, Richards NGJ, Schuster SM (1997a) Mutagenesis and chemical rescue indicate residues involved in beta-aspartyl-AMP formation by Escherichia coli asparagine synthetase B. J Biol Chem 272:12384–12392
Boehlein SK, Walworth ES, Schuster SM (1997b) Identification of cysteine-523 in the aspartate binding site of Escherichia coli asparagine synthetase B. Biochemistry 36:10168–10177
Bogdanovic M (1973) Chlorophyll formation in the dark. Chlorophyll in pine seedlings. Physiol Plant 29:17–18
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cánovas FM, Mclarney B, Silverthorne J (1993) Light-independent synthesis of LHCIIb polypeptides and assembly of the major pigmented complexes during the initial stages of Pinus palustris seedling development. Photosynth Res 38:89–97
Cánovas FM, Cantón FR, García-Gutiérrez A, Gallardo F, Crespillo R (1998) Molecular physiology of glutamine and glutamate biosynthesis in developing conifer seedlings. Physiol Plant 103:287–294
Cantón FR, Quail PH (1999) Both phyA and phyB mediate light-imposed repression of PHYA gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 121:1207–1215
Cantón FR, García-Gutiérrez A, Gallardo F, de Vicente A, Cánovas FM (1993) Molecular characterization of a cDNA clone encoding glutamine synthetase from a gymnosperm: Pinus sylvestris. Plant Mol Biol 22:819–828
Cantón FR, García-Gutiérrez A, Crespillo R, Cánovas FM (1996) High-level expression of Pinus sylvestris glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli - Production of polyclonal antibodies against the recombinant protein and expression studies in pine seedlings. FEBS Lett 393:205–210
Cantón FR, Suárez MF, José-Estanyol M, Cánovas FM (1999) Expression analysis of a cytosolic glutamine synthetase gene in cotyledons of Scots pine seedlings: developmental, light-dark regulation and spatial distribution of specific transcripts. Plant Mol Biol 40:623–634
Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine tree. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:113–116
Church GM, Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1991–1995
Davis KM, King GA (1993) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for a harvest induced asparagine synthetase from Asparagus officinalis L. Plant Physiol 102:1337–1340
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) Isolation of DNA from higher plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:19–21
Felton J, Michaelis S, Wright A (1980) Mutations in two unlinked genes are required to produce asparagine auxotrophy in Escherichia coli. J Bact 142:221–228
Flaig H, Mohr H (1992) Assimilation of nitrate and ammonium by the Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) seedling under conditions of high nitrogen supply. Physiol Plant 84:568–576
García-Gutiérrez A, Dubois F, Cantón FR, Gallardo F, Sangwan RS, Cánovas FM (1998) Two different modes of early development and nitrogen assimilation in gymnosperm seedlings. Plant J 13:187–199
Groome MC, Axler SR, Gifford DJ (1991) Hydrolysis of lipid and protein reserves in loblolly pine seeds in relation to protein electrophoretic patterns following imbibition. Physiol Plant 83:99–106
Hughes CA, Beard HS, Matthews BF (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of two cDNA encoding asparagine synthetase in soybean. Plant Mol Biol 33:301–311
Ireland RJ, Lea PJ (1999) The enzymes of glutamine, glutamate, asparagine, and aspartate metabolism. In: Singh BK (ed) Plant amino acids: biochemistry and biotechnology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 49–109
King JE, Gifford DJ (1997) Amino acid utilization in seeds of loblolly pine during germination and early seedling growth. I. Arginine and arginase activity. Plant Physiol 113:1125–1135
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lam H-M, Peng S, Coruzzi G (1994) Metabolic control of asparagine synthetase gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 106:1347–1357
Lam H-M, Hsieh M-H, Coruzzi G (1998) Reciprocal regulation of distinct asparagine synthetase genes by light and metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:345–353
Lam H-M, Wong P, Chan H-K, Yam K-M, Chen L, Chow C-M, Coruzzi GM (2003) Overexpression of the ASN1 gene enhances nitrogen status in seeds of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132:926–935
Larsen TM, Boehlein SK, Schuster SM, Richards NGJ, Thoden JB, Holden HM, Rayment I (1999) Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli asparagine synthetase B: a short journey from substrate to product. Biochemistry 38:16146–16157
Loopstra CA, Mouradov A, Vivian-Smith A, Glassick TV, Gale BV, Southerton SG, Marshall H, Teasdale RD (1998) Two pine endo-b-1,4-glucanases are associated with rapidly growing reproductive structures. Plant Physiol 116:959–967
Mariani P, De Carli ME, Rascio N, Baldan B, Casadoro G, Gennari G, Bodner M, Larcher W (1990) Synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthetic competence in etiolated and greening seedlings of Larix decidua as compared with Picea abies. J Plant Physiol 137:5–14
Møller MG, Taylor C, Rasmussen SK, Holm PB (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of two genes encoding asparagine synthetase in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Biochim Biophys Acta 1628:123–132
Murphy JB, Hammer MF (1994) Starch synthesis and localization in postgerminating Pinus edulis seedlings. Can J For Res 24:1457–1463
Osuna D, Gálvez-Valdivieso G, Piedras P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (2001) Cloning, characterization and mRNA expression analysis of PVAS1, a type I asparagine synthetase gene from Phaseolus vulgaris. Planta 213:402–410
Romagni JG, Dayan FE (2000) Measuring asparagine synthetase activity in crude plant extracts. J Agric Food Chem 48:1692–1696
Sakakibara H, Watanabe M, Hase T, Sugiyama T (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of complementary DNA encoding for ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase in maize leaf. J Biol Chem 266:2028–2035
Shi L, Twary SN, Yoshioka H, Gregerson RG, Miller SS, Samac DA, Gantt JS; Unkefer PJ, Vance CP (1997) Nitrogen assimilation in alfalfa: isolation and characterization of an asparagine synthetase gene showing enhanced expression in root nodules and dark-adapted leaves. Plant Cell 9:1339–1356
Stone SL, Gifford DJ (1999) Structural and biochemical changes in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) seeds during germination and early-seedling growth. II. Storage triacylglycerols and carbohydrates. Int J Plant Sci 160:663–671
Suárez MF, Ávila C, Gallardo F, Cantón FR, García-Gutiérrez A, Claros MG, Cánovas FM (2002) Molecular and enzymatic analysis of ammonium assimilation in woody plants. J Exp Bot 53:891–904
Todd CD, Gifford DJ (2002) The role of the megagametophyte in maintaining loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) seedling arginase gene expression in vitro. Planta 215:110–118
Todd CD, Cooke JEK, Mullen RT, Gifford DJ (2001) Regulation of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) arginase in developing seedling tissue during germination and post-germinative growth. Plant Mol Biol 45:555–565
Twary SN, Gregerson RG, Unkefer PJ, Vance CP (1994) Identification and characterization of a cDNA for alfalfa nocule-enhanced asparagine synthetase. Plant Physiol 105(suppl):152
Waterhouse RN, Smyth AJ, Massonneau A, Prosser IM, Clarkson DT (1996) Molecular cloning and characterization of asparagine synthetase from Lotus japonicus: dynamics of asparagine synthesis in N-sufficient conditions. Plant Mol Biol 30:883–897
Wong H-K, Chan H-K, Coruzzi GM, Lam H-M (2004) Correlation of ASN2 gene expression with ammonium metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:332–338
Yamamoto N, Mukai Y, Matsuoka M, Kano-Murakami Y, Ohashi Y, Tanaka Y, Ozeki Y, Odani K (1991) Light-independent expresión of cab and rbcS genes in dark-grown pine seedlings. Plant Physiol 95:376–383
Zalkin H, Smith JL (1998) Enzymes utilizing glutamine as an amide donor. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 72:87–144
Zaman Z, Verwilghen RL (1979) Quantitation of proteins solubilized in sodium dodecyl sulfate-mercaptoethanol-tris electrophoresis buffer. Anal Biochem 100:64–69
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Tahia Fernández and Dr Manuel Mari-Beffa for technical support with immunolocalization procedures. We also thank Javier Sánchez for help with asparagine content analysis. We are particularly grateful to Professor Carroll P. Vance (University of Minnesota, St Paul, MN, USA) for providing us with an aliquot of anti-alfalfa AS antibodies and Dr David Clapham (SLU, Uppsala, Sweden) for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education (PB98-1396, BMC2003-04772 and AGL2003-05191). FRC is supported by a contract from Spanish Ministry of Science and Education, Spain (Programa Ramón y Cajal). RC was supported by a predoctoral fellowship from Spanish Ministry of Science and Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cañas, R.A., de la Torre, F., Cánovas, F.M. et al. High levels of asparagine synthetase in hypocotyls of pine seedlings suggest a role of the enzyme in re-allocation of seed-stored nitrogen. Planta 224, 83–95 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0196-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0196-6