Abstract
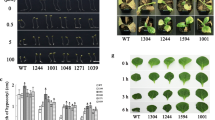
Treatment of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) plants with lithium induces the formation of necrotic lesions and leaf curling as in the case of incompatible pathogen interactions. Further similarities at the molecular level include accumulation of ethylene and of salicylic and gentisic acids, and induced expression of pathogenesis-related PR-P, PR5 and PR1 genes. With the exception of PR1 induction, lithium produced the same effects in transgenic tobacco plants that do not accumulate salicylate because of overexpression of the bacterial hydroxylase gene nahG. On the other hand, inhibition of ethylene biosynthesis with aminoethoxyvinylglycine prevented lithium-induced cell death and PR5 expression. These results suggest that lithium triggers a hypersensitive-like response where ethylene signalling is essential.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AVG:
-
aminoethoxyvinylglycine
- HR:
-
hypersensitive response
- PR:
-
pathogenesis related
- SA:
-
salicylic acid
- SAR:
-
systemic acquired resistance
References
Alvarez ME, Pennell RI, Meijer P-J, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 92:773–784
Becker F, Buschfeld E, Schell J, Bachmair A (1993) Altered response to viral infection by tobacco plants perturbed in ubiquitin system. Plant J 3:875–881
Beers EP, McDowell JM (2001) Regulation and execution of programmed cell death in response to pathogens, stress and developmental cues. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:561–567
Bellés JM, Garro R, Fayos J, Navarro P, Primo J, Conejero V (1999) Gentisic acid as a pathogen-inducible signal, additional to salicylic acid for activation of plant defenses in tomato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:227–235
Berridge MJ (1993) Inositol triphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361:315–325
Birch NJ (ed) (1991) Lithium and the cell: pharmacology and biochemistry. Academic Press, San Diego
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Lam BCH (1998) Early signal transduction pathways in plant–pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci 3:342–346
Boller T (1984) Superinduction of ACC synthase in tomato pericarp by lithium ions. In: Fuchs Y, Chalutz E (eds) Ethylene: biochemical, physiological and applied aspects. Nijhoff/Junk, The Hague, pp 87–88
Boller T (1990) Ethylene and plant–pathogen interaction. In: Flores HE, Arteca RN, Shannon JC (eds) Polyamines and ethylene: biochemistry, physiology and interactions. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, MD, pp 138–145
Church GM, Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1991–1995
Conejero V, Bellés JM, García-Breijo F, Garro R, Hernández-Yago J, Rodrigo I, Vera P (1990) Signaling in viroid pathogenesis. In: Fraser RSS (ed) Recognition and response in plant-virus interactions. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1883–1886
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Delaney TP, Uknes S, Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Weymann K, Negrotto D, Gaffney T, Gut-Rella M, Kessmann H, Ward E, Ryals J (1994) A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science 266:1247–1250
Dichtl B, Stevens A, Tollervey D (1997) Lithium toxicity is due to inhibition of RNA processing enzymes. EMBO J 16:7184–7195
Dietrich RA, Delaney TP, Uknes SJ, Ward EJ, Ryals JA, Dangl JL (1994) Arabidopsis mutants simulating disease resistance response. Cell 77:565–578
Ecker JR, Davis RW (1987) Plant defense genes are regulated by ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5202–5206
Enyedi AJ, Yalpani N, Silverman P, Raskin I (1992) Localization, conjugation and function of salicylic acid in tobacco during the hypersensitive reaction to tobacco mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2480–2484
Forment J, Naranjo MA, Roldán M, Serrano R, Vicente O (2002) Expression of Arabidopsis SR-like splicing proteins confers salt tolerance to yeast and transgenic plants. Plant J 30:511–519
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993) Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261:754–756
Gillaspy GE, Keddie JS, Oda K, Gruissem W (1995) Plant inositol monophosphatase is a lithium-sensitive enzyme encoded by a multigene family. Plant Cell 7:2175–2185
Gil-Mascarell R, López-Coronado JM, Bellés JM, Serrano R, Rodríguez PL (1999) The Arabidopsis HAL2-like gene family includes a novel sodium-sensitive phosphatase. Plant J 17:373–383
Greenberg T, Guo A, Klessig DF, Ausubel FM (1994) Programmed cell death in plants: a pathogen-triggered response activated coordinately with multiple defense functions. Cell 76:345–348
Guo A, Salih G, Klessig DF (2000) Activation of a diverse set of genes during the tobacco resistance response to TMV is independent of salicylic acid; induction of a subset is also ethylene independent. Plant J 21:409–418
Herbers K, Meuwly P, Frommer WB, Metraux J-P, Sonnewald U (1996) Systemic acquired resistance mediated by the ectopic expression of invertase: possible hexose sensing in the secretory pathway. Plant Cell 8:793–803
Huh G-H, Damsz B, Matsumoto TK, Reddy MP, Rus AM, Ibeas JI, Narasimhan ML, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2002) Salt causes ion disequilibrium-induced programmed cell death in yeast and plants. Plant J 29:649–659
Kiedrowsky S, Kawalleck P, Hahlbrock K, Somssich IE, Dangl JL (1992) Rapid activation of a novel plant defense gene is strictly dependent on the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease defense locus. EMBO J 11:4677–4684
Klein PS, Melton DA (1996) A molecular mechanism for the effect of lithium on development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8455–8459
Lawton KA, Potter SL, Uknes S, Ryals J (1994) Acquired resistance signal transduction in Arabidopsis is ethylene independent. Plant Cell 6:581–588
Liang X, Shen NF, Theologis A (1996) Li+-regulated 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 10 1027–1036
López F, Leube M, Gil-Mascarell R, Navarro-Aviñó JP, Serrano R (1999) The yeast inositol monophosphatase is a lithium- and sodium-sensitive enzyme encoded by a non-essential gene pair. Mol Microbiol 31:1255–1264
Maleck K, Dietrich RA (1999) Defense on multiple fronts: how do plants cope with diverse enemies? Trends Plant Sci 4:215–219
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London, pp 461–479
Mittler R, Shulaev V, Lam E (1995) Coordinated activation of programmed cell death and defense mechanisms in transgenic tobacco plants expressing a bacterial proton pump. Plant Cell 7:29–42
Murguía JR, Bellés JM, Serrano R (1996) The yeast HAL2 nucleotidase is an in vivo target of salt toxicity. J Biol Chem 271:29029–29033
Nahorski SR, Ragan CI, Challiss RAJ (1991) Lithium and the phosphoinositide cycle: an example of uncompetitive inhibition and its pharmacological consequences. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:297–303
Payne G, Parks TD, Burkhart W, Dincher S, Ahl P, Metraux JP, Ryals J (1988a) Isolation of the genomic clone for pathogenesis-related protein 1a from Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc. Plant Mol Biol 11:89–94
Payne G, Middlesteadt W, Williams S, Desai N, Parks TD, Dincher S, Carnes M, Ryals J (1988b) Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a novel cDNA clone encoding the major form of pathogenesis-related protein R. Plant Mol Biol 11:223–224
Payne G, Ahl P, Moyer M, Harper A, Beck J, Meins F, Ryals J (1990) Isolation of complementary DNA clones encoding pathogenesis-related proteins P and Q, two acidic chitinases from tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:98–102
Raskin I, Turner IM, Melander WR (1989) Regulation of heat production in the inflorescences of an Arum lily by endogenous salicylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2214–2218
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Serrano R, Mulet JM, Ríos G, Márquez JA, de Larrinoa IF, Leube MP, Mendizabal I, Pascual-Ahuir A, Proft M, Ros R, Montesinos C (1999) A glimpse of the mechanisms of ion homeostasis during salt stress. J Exp Bot 50:1023–1036
Sticher L, Mauch-Mani B, Metraux JP (1997) Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 35:235–270
Tadege M, Bucher M, Stahli W, Suter M, Dupuis I, Kuhlemeier C (1998) Activation of plant defense responses and sugar efflux by expression of pyruvate decarboxylase in potato leaves. Plant J 16:661–671
Ward ER, Ukness SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Wiederhold DL, Alexander DC, Ahl-Goy P, Metraux J-P, Ryals JA (1991) Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3:1085–1094
Zonia LE, Tupy J (1995a) Lithium treatment of Nicotiana tabacum microspores blocks polar nuclear migration, disrupts the partitioning of membrane-associated Ca2+, and induces symmetrical mitosis. Sex Plant Reprod 8:152–160
Zonia L, Tupy J (1995b) Lithium-sensitive calcium activity in the germination of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.), tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.), and potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) pollen. J Exp Bot 46:973–979
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Jonathan D.G. Jones (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for providing seeds of the transgenic nahG tobacco plants. This work was supported by grants from the Consellería de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (Generalitat Valenciana, Valencia, Spain) to R.S., and from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (Madrid, Spain, project BMC2000-1130) to O.V. C.R. was a fellow of the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Cultura (Madrid, Spain). We thank V. Conejero, Jose L. Vaya and F.A. Culiañez-Macia for their help at different stages of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naranjo, M.A., Romero, C., Bellés, J.M. et al. Lithium treatment induces a hypersensitive-like response in tobacco. Planta 217, 417–424 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1017-4