Abstract.
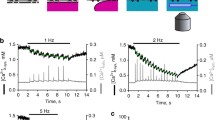
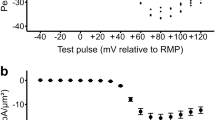
It has been suggested that the activity of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) increases during acidosis in cardiac muscle. Thus we have investigated the role of CaMKII during acidosis by monitoring intracellular Ca2+ (using fura-2) and I Ca (using the perforated patch clamp technique) during acidosis, in the absence and presence of the CaMKII inhibitor KN-93, in rat isolated ventricular myocytes. In the absence of KN-93, acidosis (pH 6.5) increased the amplitude of the fura-2 transient and prolonged its decay, but in the presence of KN-93 acidosis did not alter the amplitude and prolonged the decay more. In the absence of KN-93, acidosis increased the amplitude of the caffeine-induced fura-2 transient but did not alter its amplitude in the presence of KN-93. I Ca did not change significantly during acidosis in the absence of KN-93 but decreased during acidosis in the presence of KN-93. These results suggest that activation of CaMKII during acidosis helps to compensate for the direct inhibitory effects of acidosis on sarcoplasmic reticular Ca2+ uptake and I Ca.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 22 January 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komukai, K., Pascarel, C. & Orchard, C.H. Compensatory role of CaMKII on I Ca and SR function during acidosis in rat ventricular myocytes. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 353–361 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100549
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100549