Abstract
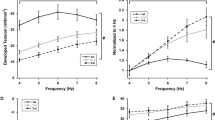
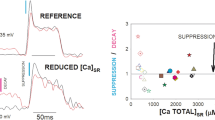
Thapsigargin (TG) and cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) have been reported to be potent inhibitors of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ uptake in isolated SR vesicles and cells. We have examined the effect of TG and CPA on (1) the Ca2+ uptake by the SR in saponinskinned rat ventricular trabeculae, using the amplitude of the caffeine-induced contraction to estimate the Ca2+ content loaded into the SR, (2) the spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations at pCa 6.6 using force oscillation as the indicator, and (3) the myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in Triton X-100-treated preparations. Inhibition of Ca2+ loading by TG and CPA increased with time of exposure to the inhibitor over 18–24 min. TG and CPA produced half inhibition of Ca2+ loading at 34.9 and 35.7 μM respectively, when 18–24 min were allowed for diffusion. The spontaneous force oscillations were more sensitive to the inhibitors: 10 μM TG and 30 μM CPA both abolished the oscillations in this time. The myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity was not affected by 10 and 300 μM TG or CPA. The results show that the concentrations of TG and CPA necessary to inhibit the SR Ca2+ uptake of skinned ventricular trabeculae are much higher than the reported values for single intact myocytes. One reason for this may be slow diffusion of the inhibitors into the multicellular trabecula preparation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassani JWM. Bassani RA, Bers DM (1993) Twitch-dependent SR Ca accumulation and release in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 265:C533-C540
Baudet S, Shaoulian R. Bers DM (1993) Effects of thapsigargin and cyclopiazonic acid on twitch force and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ content of rabbit muscle. Circ Res 73:813–819
Christensen SB (1985) Radiolabelling of the histamine-liberat- ing sesquiterpene lactone, thapsigargin. J Label Comp Radiopharm 22:71–77
Du GG, Ashley CC, Lea TJ (1994) Effects of thapsigargin and cyclopiazonic acid on the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump of skinned fibres from frog skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch 429:169–175
Du GG, Ashley CC, Lea TJ (1995) The effects of cyclopiazonic acid and thapsigargin on Ca2+ uptake by sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles from frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 487. 160P.
Endo M, Kitazawa T (1978) E-C coupling studies in skinned cardiac fibers. In: Morad M (ed) Biophysical aspects of cardiac muscle. Academic Press, New York, pp 307–327
Fabiato A (1983) Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol 245:C1-C14
Fabiato A (1985) Effect of ryanodine in skinned cardiac cells. Fed Proc 44:2970–2976
Fabiato A, Fabiato F (1979) Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 75:463–505
Hove-Madsen L, Bers DM (1993) SR Ca uptake and thapsigargin sensitivity in permeabilised rabbit and rat ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 73:820–828
Janczewski AM, Lakatta EG (1993) Thapsigargin inhibits Ca2+ uptake, and Ca2+ depletes sarcoplasmic reticulum in intact cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol 265:H517-H522
Kijima Y, Ogunbunmi E, Fleischer S (1991) Drug action of thapsigargin on the Ca2+ pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 266:22912–22918
Kirby MS, Sugara Y, Gaa S, Inesi G, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (1992) Thapsigargin inhibits contraction and Ca2+ transient in cardiac cells by specific inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem 267:12545–12551
Kort AA, Capogrossi MC, Lakatta EG (1985) Frequency, amplitude, and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca2+- dependent contractile waves in intact adult rat cardiac muscle and isolated myocytes. Circ Res 57:844–855
Kurebayashi N, Ogawa Y (1991) Discrimination of Ca2+- ATPase activity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum from actomyosin-type ATPase activity of myofibrils in skinned mammalian skeletal muscle fibres: distinct effects of cyclopiazonic acid on the two ATPase activities. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12:355–365
Lahouratate P, Quiniou MJ, Léoty C (1992) Cyclopiazonic acid. In: Frank GB et al (eds) Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle. Plenum, New York, pp 343–345
Lakatta EG. Capogrossi MC, Kort AA, Stern MD (1985) Spontaneous myocardial calcium oscillations: overview with emphasis on ryanodine and caffeine. Fed Proc 44:2977-2983 18. Lewartowski B, Wolska BM (1993) The effect of thapsigargin on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ content and contractions in single myocytes of guinea-pig heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 25:23–29
Lytton J, Westlin M. Hanley MR (1991) Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic reticulum and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem 266: 17067–17071
Sagara Y, Inesi G (1991) Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum transport ATPase by thapsigargin at subnanomolar concentrations. J Biol Chem 266:13503–13506
Seidler NW, Jona I, Vegh M, Martonosi A (1989) Cyclopiazonic acid is a specific inhibitor of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 264:17816–17823
Steele DS, Smith GL, Miller DJ (1990) The effects of taurine on Ca2+ uptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum and Ca2+ sensitivity of chemically skinned rat heart. J Physiol (Lond) 422, 499–511
Stern MD (1992) Theory of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Biophys J 63:497–517
Zhu Y, Nosek TM (1991) Inositol trisphosphate enhances Ca2+ oscillations but not Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Pflügers Arch 418:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, GG., Ashley, C.C. & Lea, T.J. Effects of thapsigargin and cyclopiazonic acid on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake, spontaneous force oscillations and myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in skinned rat ventricular trabeculae. Pflügers Arch — Eur J Physiol 432, 59–65 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050105