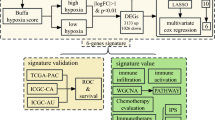
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is characterized by a massive fibrosis (desmoplasia), which is primarily caused by activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs). This leads to a hypoxic tumor microenvironment further reinforcing the activation of PSCs by stimulating their secretion of growth factors and chemokines. Since many of them elicit their effects via G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), we tested whether TRPC6 channels, effector proteins of many G-protein-coupled receptor pathways, are required for the hypoxic activation of PSCs. Thus far, the function of ion channels in PSCs is virtually unexplored. qPCR revealed TRPC6 channels to be one of the most abundant TRPC channels in primary cultures of murine PSCs. TRPC6 channel function was assessed by comparing PSCs from TRPC6−/− mice and wildtype (wt) littermates. Cell migration, Ca2+ signaling, and cytokine secretion were analyzed as readout for PSC activation. Hypoxia was induced by incubating PSCs for 24 h in 1% O2 or chemically with dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG). PSCs migrate faster in response to hypoxia. Due to reduced autocrine stimulation, TRPC6−/− PSCs fail to increase their rate of migration to the same level as wt PSCs under hypoxic conditions. This defect could not be overcome by the stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor. In line with these results, calcium influx is increased in wt but not TRPC6−/− PSCs under hypoxia. We conclude that TRPC6 channels of PSCs are major effector proteins in an autocrine stimulation pathway triggered by hypoxia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari D, Carvajo M, Bauden M, Andersson R (2017) Pancreatic cancer stroma: controversies and current insights. Scand J Gastroenterol 52:641–646
Apte M, Pirola RC, Wilson JS (2015) Pancreatic stellate cell: physiologic role, role in fibrosis and cancer. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 31:416–423
Bijlsma MF, van Laarhoven HW (2015) The conflicting roles of tumor stroma in pancreatic cancer and their contribution to the failure of clinical trials: a systematic review and critical appraisal. Cancer Metastasis Rev 34:97–114
Bynigeri RR, Jakkampudi A, Jangala R, Subramanyam C, Sasikala M, Rao GV, Reddy DN, Talukdar R (2017) Pancreatic stellate cell: Pandora’s box for pancreatic disease biology. World J Gastroenterol 23:382–405
Chigurupati S, Venkataraman R, Barrera D, Naganathan A, Madan M, Paul L, Pattisapu JV, Kyriazis GA, Sugaya K, Bushnev S, Lathia JD, Rich JN, Chan SL (2010) Receptor channel TRPC6 is a key mediator of Notch-driven glioblastoma growth and invasiveness. Cancer Res 70:418–427
Couvelard A, O'Toole D, Leek R, Turley H, Sauvanet A, Degott C, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Harris AL, Gatter K, Pezzella F (2005) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors is correlated with the presence of a fibrotic focus and angiogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Histopathology 46:668–676
Dietrich A, Mederos YSM, Gollasch M, Gross V, Storch U, Dubrovska G, Obst M, Yildirim E, Salanova B, Kalwa H, Essin K, Pinkenburg O, Luft FC, Gudermann T, Birnbaumer L (2005) Increased vascular smooth muscle contractility in TRPC6−/− mice. Mol Cell Biol 25:6980–6989
Dietrich A, Gudermann T (2014) TRPC6: physiological function and pathophysiological relevance. Handb Exp Pharmacol 222:157–188
Djamgoz MB, Coombes RC, Schwab A (2014) Ion transport and cancer: from initiation to metastasis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 369:20130092
Eguchi D, Ikenaga N, Ohuchida K, Kozono S, Cui L, Fujiwara K, Fujino M, Ohtsuka T, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M (2013) Hypoxia enhances the interaction between pancreatic stellate cells and cancer cells via increased secretion of connective tissue growth factor. J Surg Res 181:225–233
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J, Gleadle JM (2006) Concordant regulation of gene expression by hypoxia and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase inhibition: the role of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and other pathways. J Biol Chem 281:15215–15226
Erkan M, Reiser-Erkan C, Michalski CW, Kong B, Esposito I, Friess H, Kleeff J (2012) The impact of the activated stroma on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma biology and therapy resistance. Curr Mol Med 12:288–303
Fabian A, Fortmann T, Bulk E, Bomben VC, Sontheimer H, Schwab A (2011) Chemotaxis of MDCK-F cells toward fibroblast growth factor-2 depends on transient receptor potential canonical channel 1. Pflugers Arch 461:295–306
Fabian A, Bertrand J, Lindemann O, Pap T, Schwab A (2012) Transient receptor potential canonical channel 1 impacts on mechanosignaling during cell migration. Pflugers Arch 464:623–630
Fels B, Nielsen N, Schwab A (2016) Role of TRPC1 channels in pressure-mediated activation of murine pancreatic stellate cells. Eur Biophys J 45:657–670
Ferdek PE, Jakubowska MA, Gerasimenko JV, Gerasimenko OV, Petersen OH (2016) Bile acids induce necrosis in pancreatic stellate cells dependent on calcium entry and sodium-driven bile uptake. J Physiol 594:6147–6164
Ferdek PE, Jakubowska MA (2017) Biology of pancreatic stellate cells-more than just pancreatic cancer. Pflugers Arch
Haanes KA, Schwab A, Novak I (2012) The P2X7 receptor supports both life and death in fibrogenic pancreatic stellate cells. PLoS One 7:e51164
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Haugk B (2010) Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia-can we detect early pancreatic cancer? Histopathology 57:503–514
Hill C, Wurfel A, Heger J, Meyering B, Schluter KD, Weber M, Ferdinandy P, Aronheim A, Schulz R, Euler G (2013) Inhibition of AP-1 signaling by JDP2 overexpression protects cardiomyocytes against hypertrophy and apoptosis induction. Cardiovasc Res 99:121–128
Hofmann T, Obukhov AG, Schaefer M, Harteneck C, Gudermann T, Schultz G (1999) Direct activation of human TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels by diacylglycerol. Nature 397:259–263
Iyer SC, Kannan A, Gopal A, Devaraj N, Halagowder D (2015) Receptor channel TRPC6 orchestrate the activation of human hepatic stellate cell under hypoxia condition. Exp Cell Res 336:66–75
Jakubowska MA, Ferdek PE, Gerasimenko OV, Gerasimenko JV, Petersen OH (2016) Nitric oxide signals are interlinked with calcium signals in normal pancreatic stellate cells upon oxidative stress and inflammation. Open Biol 6
Johnsen IK, Slawik M, Shapiro I, Hartmann MF, Wudy SA, Looyenga BD, Hammer GD, Reincke M, Beuschlein F (2006) Gonadectomy in mice of the inbred strain CE/J induces proliferation of sub-capsular adrenal cells expressing gonadal marker genes. J Endocrinol 190:47–57
Koong AC, Mehta VK, Le QT, Fisher GA, Terris DJ, Brown JM, Bastidas AJ, Vierra M (2000) Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:919–922
Li S, Wang J, Wei Y, Liu Y, Ding X, Dong B, Xu Y, Wang Y (2015) Crucial role of TRPC6 in maintaining the stability of HIF-1alpha in glioma cells under hypoxia. J Cell Sci 128:3317–3329
Lindemann O, Umlauf D, Frank S, Schimmelpfennig S, Bertrand J, Pap T, Hanley PJ, Fabian A, Dietrich A, Schwab A (2013) TRPC6 regulates CXCR2-mediated chemotaxis of murine neutrophils. J Immunol 190:5496–5505
Liu X, Cheng KT, Bandyopadhyay BC, Pani B, Dietrich A, Paria BC, Swaim WD, Beech D, Yildrim E, Singh BB, Birnbaumer L, Ambudkar IS (2007) Attenuation of store-operated Ca2+ current impairs salivary gland fluid secretion in TRPC1−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:17542–17547
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔ CT Method. Methods 25:402–408
Lunardi S, Muschel RJ, Brunner TB (2014) The stromal compartments in pancreatic cancer: are there any therapeutic targets? Cancer Lett 343:147–155
Masamune A, Shimosegawa T (2015) Pancreatic stellate cells: a dynamic player of the intercellular communication in pancreatic cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 39(Suppl 1):S98–103
Nielsen N, Lindemann O, Schwab A (2014) TRP channels and STIM/ORAI proteins: sensors and effectors of cancer and stroma cell migration. Br J Pharmacol 171:5524–5540
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM (2014) Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 74:2913–2921
Raykov Z, Grekova SP, Bour G, Lehn JM, Giese NA, Nicolau C, Aprahamian M (2014) Myo-inositol trispyrophosphate-mediated hypoxia reversion controls pancreatic cancer in rodents and enhances gemcitabine efficacy. Int J Cancer 134:2572–2582
Rebours V, Albuquerque M, Sauvanet A, Ruszniewski P, Levy P, Paradis V, Bedossa P, Couvelard A (2013) Hypoxia pathways and cellular stress activate pancreatic stellate cells: development of an organotypic culture model of thick slices of normal human pancreas. PLoS One 8:e76229
Sada M, Ohuchida K, Horioka K, Okumura T, Moriyama T, Miyasaka Y, Ohtsuka T, Mizumoto K, Oda Y, Nakamura M (2016) Hypoxic stellate cells of pancreatic cancer stroma regulate extracellular matrix fiber organization and cancer cell motility. Cancer Lett 372:210–218
Stock C, Gassner B, Hauck CR, Arnold H, Mally S, Eble JA, Dieterich P, Schwab A (2005) Migration of human melanoma cells depends on extracellular pH and Na+/H+ exchange. J Physiol 567:225–238
Storch U, Forst AL, Philipp M, Gudermann T, Mederos y Schnitzler M (2012) Transient receptor potential channel 1 (TRPC1) reduces calcium permeability in heteromeric channel complexes. J Biol Chem 287:3530–3540
Storck H, Hild B, Schimmelpfennig S, Sargin S, Nielsen N, Zaccagnino A, Budde T, Novak I, Kalthoff H, Schwab A (2017) Ion channels in control of pancreatic stellate cell migration. Oncotarget 8:769–784
Varga-Szabo D, Authi KS, Braun A, Bender M, Ambily A, Hassock SR, Gudermann T, Dietrich A, Nieswandt B (2008) Store-operated Ca2+ entry in platelets occurs independently of transient receptor potential (TRP) C1. Pflugers Arch 457:377–387
Watanabe S, Nagashio Y, Asaumi H, Nomiyama Y, Taguchi M, Tashiro M, Kihara Y, Nakamura H, Otsuki M (2004) Pressure activates rat pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G1175–G1181
Weissmann N, Dietrich A, Fuchs B, Kalwa H, Ay M, Dumitrascu R, Olschewski A, Storch U, Mederos y Schnitzler M, Ghofrani HA, Schermuly RT, Pinkenburg O, Seeger W, Grimminger F, Gudermann T (2006) Classical transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) is essential for hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and alveolar gas exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19093–19098
Weissmann N, Sydykov A, Kalwa H, Storch U, Fuchs B, Mederos y Schnitzler M, Brandes RP, Grimminger F, Meissner M, Freichel M, Offermanns S, Veit F, Pak O, Krause KH, Schermuly RT, Brewer AC, Schmidt HH, Seeger W, Shah AM, Gudermann T, Ghofrani HA, Dietrich A (2012) Activation of TRPC6 channels is essential for lung ischaemia-reperfusion induced oedema in mice. Nat Commun 3:649
Won JH, Zhang Y, Ji B, Logsdon CD, Yule DI (2011) Phenotypic changes in mouse pancreatic stellate cell Ca2+ signaling events following activation in culture and in a disease model of pancreatitis. Mol Biol Cell 22:421–436
Zhou X, Ye Y, Sun Y, Li X, Wang W, Privratsky B, Tan S, Zhou Z, Huang C, Wei YQ, Birnbaumer L, Singh BB, Wu M (2015) Transient receptor potential channel 1 deficiency impairs host defense and proinflammatory responses to bacterial infection by regulating protein kinase C alpha signaling. Mol Cell Biol 35:2729–2739
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Marie Curie Initial Training Network IonTraC (FP7-PEOPLE-2011-ITN grant agreement no. 289648) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Cells-in-Motion Cluster of Excellence (EXC 1003—CiM), University of Münster, Germany, and DFG SCHW 407/17-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
At the time of the project SC and IK were employees of Bayer Pharma AG. It did not impact the study design nor data interpretation. Other authors do not have a conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, N., Kondratska, K., Ruck, T. et al. TRPC6 channels modulate the response of pancreatic stellate cells to hypoxia. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 469, 1567–1577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2057-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2057-0