Abstract
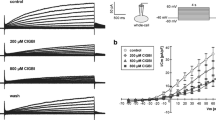
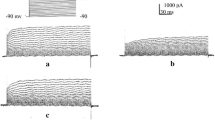
We have previously reported that Kv1.3 channel is expressed in Daudi cells. However, the present study demonstrates that Daudi cell cycle progression is not affected by margatoxin, a Kv1.3 channel blocker, but can be suppressed by tetraethylammonium (TEA) and 1-[(2-chlorophenyl) diphenylmethyl]-1H-pyrazole (TRAM-34), a selective blocker of intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (IK) channels. Our patch-clamp data indicate that Daudi cells express an IK channel because it has a unit conductance of about 30 pS, is voltage-independent, and can be activated by submicromolar Ca2+ and blocked by TRAM-34. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and activated this IK channel. Conversely, Rituximab, a human–mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody of CD20, significantly decreased [Ca2+]i and inhibited the channel. Furthermore, both FBS-induced IK channel expression and cell cycle progression were attenuated by the treatment with LY-294002, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor. These data together suggest that a growth factor(s) in FBS triggers cell cycle progression by elevating both IK channel activity via CD20 and IK channel expression on the cell surface via PI3K. Thus, elevated IK channel activity and expression may account, in part, for Daudi cell malignant growth and proliferation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avivi I, Robinson S, Goldstone A (2003) Clinical use of rituximab in haematological malignancies. Br J Cancer 89:1389–1394
Beck TW, Magnuson NS, Rapp UR (1995) Growth factor regulation of cell cycle progression and cell fate determination. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 194:291–303
Berridge MJ (1995) Calcium signalling and cell proliferation. BioEssays 17:491–500
Bloch M, Ousingsawat J, Simon R, Schraml P, Gasser TC, Mihatsch MJ, Kunzelmann K, Bubendorf L (2006) KCNMA1 gene amplification promotes tumor cell proliferation in human prostate cancer. Oncogene DOI 10.1038/sj.onc.1210036 (in press)
Bubien JK, Zhou LJ, Bell PD, Frizzell RA, Tedder TF (1993) Transfection of the CD20 cell surface molecule into ectopic cell types generates a Ca2+ conductance found constitutively in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol 121:1121–1132
Chang KL, Kamel OW, Arber DA, Horyd ID, Weiss LM (1995) Pathologic features of nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin’s disease in extranodal sites. Am J Surg Pathol 19:1313–1324
Coiret G, Borowiec AS, Mariot P, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Matifat F (2006) The antiestrogen tamoxifen activates BK channels and stimulates proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 71:843–851
Conforti L, Petrovic M, Mohammad D, Lee S, Ma Q, Barone S, Filipovich AH (2003) Hypoxia regulates expression and activity of Kv1.3 channels in T lymphocytes: a possible role in T cell proliferation. J Immunol 170:695–702
DeCoursey TE, Chandy KG, Gupta S, Cahalan MD (1984) Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis?. Nature 307:465–468
Fanger CM, Rauer H, Neben AL, Miller MJ, Rauer H, Wulff H, Rosa JC, Ganellin CR, Chandy KG, Cahalan MD (2001) Calcium-activated potassium channels sustain calcium signaling in T lymphocytes. Selective blockers and manipulated channel expression levels. J Biol Chem 276:12249–12256
Gallagher JD, Noelle RJ, McCann FV (1995) Mercury suppression of a potassium current in human B lymphocytes. Cell Signal 7:31–38
Gamper N, Fillon S, Huber SM, Feng Y, Kobayashi T, Cohen P, Lang F (2002) IGF-1 up-regulates K+ channels via PI3-kinase, PDK1 and SGK1. Pflugers Arch 443:625–634
Gongora R, Stephan RP, Zhang Z, Cooper MD (2001) An essential role for Daxx in the inhibition of B lymphopoiesis by type I interferons. Immunity 14:727–737
Grgic I, Eichler I, Heinau P, Si H, Brakemeier S, Hoyer J, Kohler R (2005) Selective blockade of the intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel suppresses proliferation of microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells and angiogenesis in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:704–709
Grimberg A (2003) Mechanisms by which IGF-I may promote cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2:630–635
Helms MN, Liu L, Liang YY, Al-Khalili O, Vandewalle A, Saxena S, Eaton DC, Ma HP (2005) Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate mediates aldosterone stimulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and interacts with γ-ENaC. J Biol Chem 280:40885–40891
Jager H, Dreker T, Buck A, Giehl K, Gress T, Grissmer S (2004) Blockage of intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels inhibit human pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 65:630–638
Jensen BS, Odum N, Jorgensen NK, Christophersen P, Olesen SP (1999) Inhibition of T cell proliferation by selective block of Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10917–10921
Ju YK, Wu MJ, Chaulet H, Marciniec T, Graham RM, Allen DG (2003) IGF-1 enhances a store-operated Ca2+ channel in skeletal muscle myoblasts: involvement of a CD20-like protein. J Cell Physiol 197:53–60
Kanzaki M, Nie L, Shibata H, Kojima I (1997) Activation of a calcium-permeable cation channel CD20 expressed in Balb/c 3T3 cells by insulin-like growth factor-I. J Biol Chem 272:4964–4969
Kanzaki M, Shibata H, Mogami H, Kojima I (1995) Expression of calcium-permeable cation channel CD20 accelerates progression through the G1 phase in Balb/c 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 270:13099–13104
Kojima I, Matsunaga H, Kurokawa K, Ogata E, Nishimoto I (1988) Calcium influx: an intracellular message of the mitogenic action of insulin-like growth factor-I. J Biol Chem 263:16561–16567
Kwon G, Marshall CA, Liu H, Pappan KL, Remedi MS, McDaniel ML (2006) Glucose-stimulated DNA synthesis through mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is regulated by KATP channels: effects on cell cycle progression in rodent islets. J Biol Chem 281:3261–3267
Liebau S, Propper C, Bockers T, Lehmann-Horn F, Storch A, Grissmer S, Wittekindt OH (2006) Selective blockage of Kv1.3 and Kv3.1 channels increases neural progenitor cell proliferation. J Neurochem 99:426–437
Lu X, Fein A, Feinstein MB, O’Rourke FA (1999) Antisense knock out of the inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate receptor GAP1(IP4BP) in the human erythroleukemia cell line leads to the appearance of intermediate conductance KCa channels that hyperpolarize the membrane and enhance calcium influx. J Gen Physiol 113:81–96
Ma H, Ling BN (1996) Luminal adenosine receptors regulate amiloride-sensitive Na channels in A6 distal nephron cells. Am J Physiol 270:F798–F805
Malhi H, Irani AN, Rajvanshi P, Suadicani SO, Spray DC, McDonald TV, Gupta S (2000) KATP channels regulate mitogenically induced proliferation in primary rat hepatocytes and human liver cell lines. Implications for liver growth control and potential therapeutic targeting. J Biol Chem 275:26050–26057
McCann FV, McCarthy DC, Noelle RJ (1990) Patch-clamp profile of ion channels in resting murine B lymphocytes. J Membr Biol 114:175–188
Nolan MK, Jankowska L, Prisco M, Xu S, Guvakova MA, Surmacz E (1997) Differential roles of IRS-1 and SHC signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 72:828–834
Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Roudbaraki M, Delcourt P, Ahidouch A, Joury N, Prevarskaya N (2004) Functional and molecular identification of intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in breast cancer cells: association with cell cycle progression. Am J Physiol 287:C125–C134
Pardo LA (2004) Voltage-gated potassium channels in cell proliferation. Physiology 19:285–292
Partiseti M, Choquet D, Diu A, Korn H (1992) Differential regulation of voltage- and calcium-activated potassium channels in human B lymphocytes. J Immunol 148:3361–3368
Press OW, Farr AG, Borroz KI, Anderson SK, Martin PJ (1989) Endocytosis and degradation of monoclonal antibodies targeting human B-cell malignancies. Cancer Res 49:4906–4912
Stiles CD, Capone GT, Scher CD, Antoniades HN, Van Wyk JJ, Pledger WJ (1979) Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1279–1283
Sutro JB, Vayuvegula BS, Gupta S, Cahalan MD (1989) Voltage-sensitive ion channels in human B lymphocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol 254:113–122
Tedder TF, Engel P (1994) CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today 15:450–454
Wilker E, Lu J, Rho O, Carbajal S, Beltran L, DiGiovanni J (2005) Role of PI3K/Akt signaling in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) skin tumor promotion. Mol Carcinog 44:137–145
Wonderlin WF, Strobl JS (1996) Potassium channels, proliferation and G1 progression. J Membr Biol 154:91–107
Wonderlin WF, Woodfork KA, Strobl JS (1995) Changes in membrane potential during the progression of MCF-7 human mammary tumor cells through the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol 165:177–185
Yamazaki D, Aoyama M, Ohya S, Muraki K, Asai K, Imaizumi Y (2006) Novel functions of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in enhanced cell proliferation by ATP in brain endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 281:38430–38439
Zhou ZH, Unlap MT, Li L, Ma H (2002) Incomplete inactivation of voltage-dependent potassium channels in human B lymphoma cells. J Membr Biol 188:97–105
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by DHHS, National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grant R01-DK067110 (to H.-P.M.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xu, YQ., Liang, YY. et al. An intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel mediates B lymphoma cell cycle progression induced by serum. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 454, 945–956 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0258-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0258-7