Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether pancreatic steatosis (PS) is associated with the risk of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) after radical gastrectomy, and if so, to investigate whether pre-assessment by diagnostic imaging can mitigate the risk.
Methods
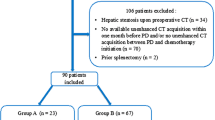
The clinical records of 276 patients with cStage I gastric cancer who underwent laparoscopic gastrectomy with D1 + lymphadenectomy between 2012 and 2015 were reviewed. In the first phase up to July 2013 (n = 138), PS was classified from computed tomography (CT) findings into type S (superficial fat deposition) or type D (diffuse fatty replacement) and examined for association with POPF. In the second phase (n = 138), the preoperative CT assessment of PS was routinized. Separate samples from pancreatoduodenectomy consistent with each type were histologically examined.
Results
In the first phase, the incidence of POPF was significantly higher in group S, but not in group D, compared with normal pancreas (16.3% and 9.1% vs. 3.6%, respectively; P = 0.03). The drain amylase level was lowest in group D, reflecting exocrine insufficiency. Histologically, the loose connective-tissue space between the fat infiltrating the pancreas and the peripancreatic fat containing the lymph nodes was unclear in type D but conserved in type S. In the second phase, surgery was performed with more intention on accurately tracing the dissection plane and significantly lowered incidence of POPF in Group S (16.3% to 2.1%; P = 0.047).
Conclusion
Peripancreatic lymphadenectomy is more challenging and likely to cause POPF in patients with PS. However, the risk may be reduced using appropriate dissection techniques based on the CT pre-assessment findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the medical data including participants’ personal data.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Kung CH, Lindblad M, Nilsson M, Rouvelas I, Kumagai K, Lundell L, Tsai JA (2014) Postoperative pancreatic fistula formation according to ISGPF criteria after D2 gastrectomy in Western patients. Gastric Cancer 17:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-013-0307-1
Degiuli M, Sasako M, Ponti A, Italian Gastric Cancer Study Group (2010) Morbidity and mortality in the Italian Gastric Cancer Study Group randomized clinical trial of D1 versus D2 resection for gastric cancer. Br J Surg 97:643–649. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6936
Yu HW, Jung DH, Son SY, Lee CM, Lee JH, Ahn SH, Park DJ, Kim HH (2013) Risk factors of postoperative pancreatic fistula in curative gastric cancer surgery. J Gastric Cancer 13:179–184. https://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2013.13.3.179
Uchida Y, Masui T, Nakano K, Yago A, Sato A, Nagai K, Anazawa T, Takaori K, Tabata Y, Uemoto S (2019) Clinical and experimental studies of intraperitoneal lipolysis and the development of clinically relevant pancreatic fistula after pancreatic surgery. Br J Surg 106:616–625. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.11075
Tsujiura M, Hiki N, Ohashi M, Nunobe S, Kumagi K, Ida S, Okumura Y, Sano T, Yamaguchi T (2017) “Pancreas-compressionless gastrectomy”: a novel laparoscopic approach for suprapancreatic lymph node dissection. Ann Surg Oncol 24:3331–3337. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-5974-4
Fujita T, Ohta M, Ozaki Y, Takahashi Y, Miyazaki S, Harada T, Iino I, Kikuchi H, Hiramatsu Y, Kamiya K, Konno H (2015) Collateral thermal damage to the pancreas by ultrasonic instruments during lymph node dissection in laparoscopic gastrectomy. Asian J Endosc Surg 8:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/ases.12177
Ida S, Hiki N, Ishizawa T, Kuriki Y, Kamiya M, Urano Y, Nakamura T, Tsuda Y, Kano Y, Kumagai K, Nunobe S, Ohashi M, Sano T (2018) Pancreatic compression during lymph node dissection in laparoscopic gastrectomy: possible cause of pancreatic leakage. J Gastric Cancer 18:134–141. https://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e15
Washio M, Yamashita K, Niihara M, Hosoda K, Hiki N (2020) Postoperative pancreatic fistula after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg E-pub. https://doi.org/10.1002/ags3.12398
Engström K, Engström KG (2010) Hazards with electrocautery-induced decomposition of fatty acids–in view of lipid embolization. Scand Cardiovasc J 44:307–312. https://doi.org/10.3109/14017431.2010.491553
Okura Y, Shinohara H, Shindoh J, Haruta S, Ueno M, Sakai Y, Udagawa H (2016) A new scoring system using preoperative factors and contour mapping for predicting postoperative complications of laparoscopic gastrectomy. Dig Surg 33:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1159/000442028
Tanaka K, Miyashiro I, Yano M, Kishi K, Motoori M, Seki Y, Noura S, Ohue M, Yamada T, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O (2009) Accumulation of excess visceral fat is a risk factor for pancreatic fistula formation after total gastrectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 16:1520–1525. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0391-y
Van Herpen NA, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB (2008) Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol Behav 94:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.11.049
van Geenen EJ, Smits MM, Schreuder TC, van der Peet DL, Bloemena E, Mulder CJ (2010) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is related to nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease. Pancreas 39:1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181f6fce2
Smits MM, van Geenen EJ (2011) The clinical significance of pancreatic steatosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.4
Paul J, Shihaz AVH (2020) Pancreatic steatosis: a new diagnosis and therapeutic challenging in gastroenterology. Arq Gastroenterol 57:216–220. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-2803.202000000-27
Pezzilli R, Calculli L (2014) Pancreatic steatosis: is it related to either obesity or diabetes mellitus? World J Diabetes 5:415–419. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.415
Lee SE, Jang JY, Lim CS, Kang MJ, Kim SH, Kim MA, Kim SW (2010) Measurement of pancreatic fat by magnetic resonance imaging: predicting the occurrence of pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann Surg 251:932–936. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d65483
Mathur A, Pitt HA, Marine M, Saxena R, Schmidt CM, Howard TJ, Nakeeb A, Zyromski NJ, Lillemoe KD (2007) Fatty pancreas: a factor in postoperative pancreatic fistula. Ann Surg 246:1058–1064. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e31814a6906
Shinohara H, Kurahashi Y, Ishida Y (2021) Gastric equivalent of the ‘Holy Plane’ to standardize the surgical concept of stomach cancer to mesogastric excision: updating Jamieson and Dobson’s historic schema. Gastric Cancer 24:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-020-01142-9
Shinohara H, Kurahashi Y, Haruta S, Ishida Y, Sasako M (2018) Universalization of the operative strategy by systematic mesogastric excision for stomach cancer with that for total mesorectal excision and complete mesocolic excision colorectal counterparts. Ann Gastroenterol Surg 2:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/ags3.12048
Stecco C, Sfriso MM, Porzionato A, Rambaldo A, Albertin G, Macchi V, De Caro R (2017) Microscopic anatomy of the visceral fasciae. J Anat 231:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12617
Shinohara H, Haruta S, Ohkura Y, Udagawa H, Sakai Y (2015) Tracing dissectable layers of mesenteries overcomes embryologic restrictions when performing infrapyloric lymphadenectomy in laparoscopic gastric cancer surgery. J Am Coll Surg 220:e81–e87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.02.037
Shibazaki S, Suda K, Nakauchi M, Nakamura T, Kadoya S, Kikuchi K, Inaba K, Uyama I (2018) Outermost layer-oriented medial approach for infrapyloric nodal dissection in laparoscopic distal gastrectomy. Surg Endosc 32:2137–2148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6111-6
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae
Kumamoto T, Kurahashi Y, Haruta S, Niwa H, Nakanishi Y, Ozawa R, Okumura K, Ishida Y, Shinohara H (2019) Laparoscopic modified lymphadenectomy in gastric cancer surgery using systematic mesogastric excision: a novel technique based on a concept. Langenbecks Arch Surg 404:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-019-01770-5
Kumamoto T, Kurahashi Y, Niwa H, Nakanishi Y, Ozawa R, Okumura K, Ishida Y, Shinohara H (2020) Laparoscopic suprapancreatic lymph node dissection using a systematic mesogastric excision concept for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 27:529–531. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07700-5
Shinohara H, Kurahashi Y, Kanaya S, Haruta S, Ueno M, Udagawa H, Sakai Y (2013) Topographic anatomy and laparoscopic technique for dissection of no. 6 infrapyloric lymph nodes in gastric cancer surgery. Gastric Cancer 16:615–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-012-0229-3
Katz DS, Hines J, Math KR, Nardi PM, Mindelzun RE, Lane MJ (1999) Using CT to reveal fat-containing abnormalities of the pancreas. Am J Roentgenol 172:393–396. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.172.2.9930790
Soyer P, Spelle L, Pelage JP, Dufresne AC, Rondeau Y, Gouhiri M, Scherrer A, Rymer R (1999) Cystic fibrosis in adolescents and adults: fatty replacement of the pancreas—CT evaluation and functional correlation. Radiology 210:611–615. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.210.3.r99mr08611
Matsumoto S, Mori H, Kiyake H, Takaki H, Maeda T, Yamada Y, Oga M (1995) Uneven fatty replacement of the pancreas: evaluation with CT. Radiology 194:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.194.2.7824726
Kawamoto S, Siegelman SS, Bluemke DA, Hruban RH, Fishman EK (2009) Focal fatty infiltration in the head of the pancreas: evaluation with multidetector computed tomography with multiplanar reformation imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0b013e31815cff0d
Bassi C, Marchegiani G, Dervenis C, Sarr M, Abu Hilal M, Adham M, Allen P, Andersson R, Asbun HJ, Besselink MG, Conlon K, Del Chiaro M, Falconi M, Fernandez-Cruz L, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Fingerhut A, Friess H, Gouma DJ, Hackert T, Izbicki J, Lillemoe KD, Neoptolemos JP, Olah A, Schulick R, Shrikhande SV, Takada T, Takaori K, Traverso W, Vollmer CR, Wolfgang CL, Yeo CJ, Salvia R, Buchler M, International Study Group on Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) (2017) The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 Years After. Surgery 161:584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.014
Pinnick KE, Collins SC, Londos C, Gauguier D, Clark A, Fielding BA (2008) Pancreatic ectopic fat is characterized by adipocyte infiltration and altered lipid composition. Obesity 16:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2007.110
Ozbulbul NI, Yurdakul M, Tola M (2010) Does the visceral fat tissue show better correlation with the fatty replacement of the pancreas than with BMI? Eur J Med 42:24–27. https://doi.org/10.5152/eajm.2010.08
Bi Y, Wang JL, Li ML, Zhou J, Sun XL (2019) The association between pancreas steatosis and metabolic sysndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 35:e3142–e3153. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3142
Unger RH, Orci L (2002) Lipoapoptosis: its mechanism and its diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1585:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00342-6
Marks WM, Filly RA, Callen PW (1980) Ultrasonic evaluation of normal pancreatic echogenicity and its relationship to fat deposition. Radiology 137:475–479. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.137.2.7433680
Patel K, Trivedi RN, Durgampudi C, Noel P, Cline RA, Delany JP, Navina S, Singh VP (2015) Lipolysis of visceral adipocyte triglyceride by pancreatic lipases converts mild acute pancreatitis to severe pancreatitis independent of necrosis and inflammation. Am J Pathol 185:808–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.11.019
Noel P, Patel K, Durgampudi C et al (2016) Peripancreatic fat necrosis worsens acute pancreatitis independent of pancreatic necrosis via unsaturated fatty acids increased in human pancreatic necrosis collections. Gut 65:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308043
Hiki N, Honda M, Etoh T, Yoshida K, Kodera Y, Kakeji Y, Kumamaru H, Miyata H, Yamashita Y, Inomata M, Konno H, Seto Y, Kitano S (2018) Higher incidence of pancreatic fistula in laparoscopic gastrectomy. Real-world evidence from a nationwide prospective cohort study. Gastric Cancer 21:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-017-0764-z
Kawaguchi Y, Cooper B, Gannon M, Ray M, MacDonald RJ, Wright CV (2002) The role of the transcriptional regulator Ptf1a in converting intestinal to pancreatic progenitors. Nat Genet 32:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng959
Sadler TW, Langman J (2019) Langman’s medical embryology, 14th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Maruyama K, Okabayashi K, Kinoshita T (1987) Progress in gastric cancer surgery in Japan and its limits of radicality. World J Surg 11:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01655804
Tushuizen ME, Bunck MC, Pouwels PJ, Bontemps S, van Waesberghe JH, Schindhelm RK, Mari A, Heine RJ, Diamant M (2007) Pancreatic fat content and beta-cell function in men with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:2916–2921. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-0326
van Raalte DH, van der Zijl NJ, Diamant M (2010) Pancreatic steatosis in humans: cause or marker of lipotoxicity? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833aa1ef
Lee Y, Lingvay I, Szczepaniak LS, Ravazzola M, Orci L, Unger RH (2010) Pancreatic steatosis: harbinger of type 2 diabetes in obese rodents. Int J Obes (Lond) 34:396–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.245
Lingvay I, Esser V, Legendre JL, Price AL, Wertz KM, Adams-Huet B, Zhang S, Unger RH, Szczepaniak LS (2009) Noninvasive quantification of pancreatic fat in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4070–4076. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-0584
Tahtacı M, Algın O, Karakan T, Yürekli ÖT, Alışık M, Köseoğlu H, Metin MR, Bolat AD, Erel O, Ersoy O (2018) Can pancreatic steatosis affect exocrine functions of pancreas? Turk J Gastroenterol 29:588–594. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2018.17696
Wu WC, Wang CY (2013) Association between non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease (NAFPD) and the metabolic syndrome: case-control retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 12:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-12-77
Suliburk JW, Buck QM, Pirko CJ, Massarweh NN, Barshes NR, Singh H, Rosengart TK (2019) Analysis of human performance deficiencies associated with surgical adverse events. JAMA Netw Open 2:e198067. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.806
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Ken Motoori at the Department of Radiology, Tsudanuma General Hospital, for specialist evaluation of the CT classification used in this study; Caryn Jones at ThinkSCIENCE for professional editing and language revision; and all the young surgeons at Toranomon Hospital for their assistance in surgical specimen handling.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI Grant Number 19H03735). The sponsor had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, manuscript preparation, or publication decisions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: Kobayashi N and Shinohara H; acquisition of data: Kobayashi N and Haruta S; analysis and interpretation of data: Kobayashi N and Shinohara H; drafting of manuscript: Shinohara H; critical revision of manuscript: Udagawa H and Ueno M.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects for participation in and publication of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, N., Shinohara, H., Haruta, S. et al. Reducing the risk of postoperative pancreatic fistula in radical gastrectomy: pre-assessment with computed tomography for the diagnosis of pancreatic steatosis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407, 587–596 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02337-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02337-z



