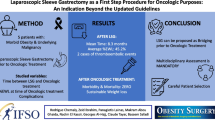
Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic hepatectomy has been used widely due to its advantages as a minimally invasive surgery. However, multicenter, large-scale, population-based laparoscopic caudate lobe resection (LCLR) versus open caudate lobe resection (OCLR) has rarely been reported. We assessed the feasibility and safety of LCLR compared with OCLR using meta-analysis.
Methods
Relevant literature was retrieved using PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, Ovid Medline, Web of Science, CNKI, and WanFang Med databases up to July 30th, 2020. Multiple parameters of feasibility and safety were compared between the treatment groups. Quality of studies was assessed with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). The data were analyzed by Review Manager 5.3. Results are expressed as odds ratio (OD) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) for fixed- and random-effects models.
Results
Seven studies with 237 patients were included in this meta-analysis. Compared with OCLR, the LCLR group had a lower intraoperative blood loss (MD − 180.84; 95% CI − 225.61 to − 136.07; P < 0.0001), shorter postoperative hospital stays (MD − 4.38; 95% CI − 7.07 to − 1.7; P = 0.001), shorter operative time (MD − 50.24; 95% CI − 78.57 to − 21.92; P = 0.0005), and lower rates in intraoperative blood transfusion (OR 0.12; P = 0.01). However, there were no statistically significant differences between LCLR and OCLR regarding hospital expenses (MD 0.92; P = 0.12), pedicle clamping (OR 1.57; P = 0.32), postoperative complications (OR 0.58; P = 0.15), bile leak (P = 0.88), ascites (P = 0.34), and incisional infection (P = 0.36).
Conclusions
LCLR has multiple advantages over OCLR, especially intraoperative blood loss and hospital stays. LCLR is a very useful technology and feasible choice in patients with caudate lobe lesions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Reich H, McGlynn F, DeCaprio J, Budin R (1991) Laparoscopic excision of benign liver lesions. Obstet Gynecol 78(5 Pt 2):956–958
Jin B, Chen MT, Fei YT, Du SD, Mao YL (2018) Safety and efficacy for laparoscopic versus open hepatectomy: a meta-analysis. Surg Oncol 27(2):A26–A34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2017.06.007
Yang TH, Chen JL, Lin YJ, Chao YJ, Shan YS, Hsu HP, Su ZM, Chou CC, Yen YT (2018) Laparoscopic surgery for large left lateral liver tumors: safety and oncologic outcomes. Surg Endosc 32(10):4314–4320
Ratti F, Barkhatov LI, Tomassini F, Cipriani F, Kazaryan AM, Edwin B, Abu Hilal M, Troisi RI, Aldrighetti L (2016) Learning curve of self-taught laparoscopic liver surgeons in left lateral sectionectomy: results from an international multi-institutional analysis on 245 cases. Surg Endosc 30(8):3618–3629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4665-0
Cho HD, Kim KH, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Moon DB, Ha TY, Song GW, Jung DH, Park GC, Lee SG (2018) Comparison of pure laparoscopic versus open left hemihepatectomy by multivariate analysis: a retrospective cohort study. Surg Endosc 32(2):643–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5714-7
Yin X, Luo D, Huang Y, Huang M (2019) Advantages of laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy: a metaanalysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(23):e15929. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015929
Peng L, Xiao J, Liu Z, Zhu J, Wan R, Xiao W, Li Y (2017) Laparoscopic left-sided hepatectomy for the treatment of hepatolithiasis: a comparative study with open approach. Int J Surg 40:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.02.068
Dagher I, Di Giuro G, Dubrez J, Lainas P, Smadja C, Franco D (2009) Laparoscopic versus open right hepatectomy: a comparative study. Am J Surg 198(2):173–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.09.015
Yu X, Luo D, Tang Y, Huang M, Huang Y (2019) Safety and feasibility of laparoscopy technology in right hemihepatectomy. Sci Rep 9(1):18809. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52694-5
Luo D, Xiong X, Xiong H, Liu H, Huang Y, Huang M (2020) The safety and feasibility of laparoscopic technology in right posterior sectionectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 30(2):169–172. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0000000000000772
Araki K, Fuks D, Nomi T, Ogiso S, Lozano RR, Kuwano H, Gayet B (2016) Feasibility of laparoscopic liver resection for caudate lobe: technical strategy and comparative analysis with anteroinferior and posterosuperior segments. Surg Endosc 30(10):4300–4306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4747-7
Chen KH, Jeng KS, Huang SH, Chu SH (2013) Laparoscopic caudate hepatectomy for cancer--an innovative approach to the no-man’s land. J Gastrointest Surg 17(3):522–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2115-z
Koh YX, Lee SY, Chiow AK, Kam JH, Goh BK, Chan CY (2017) Laparoscopic caudate lobe resection: navigating the technical challenge. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2:39. https://doi.org/10.21037/ales.2017.03.04
Ahanatha Pillai S, Sathyanesan J, Perumal S, Ulagendra Perumal S, Lakshmanan A, Ramaswami S, Ramasamy R, Palaniappan R, Rajagopal S (2013) Isolated caudate lobe resection: technical challenges. Ann Gastroenterol 26(2):150–155
Oh D, Kwon CH, Na BG, Lee KW, Cho WT, Lee SH (2016) Surgical techniques for totally laparoscopic caudate lobectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 26(9):689–692. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2016.0161
Ho KM, Han HS, Yoon YS, Cho JY, Choi YR, Jang JS, Kwon SU, Kim S, Choi JK (2017) Laparoscopic total caudate lobectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27(10):1074–1078. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2016.0459
Liu Z, Ding H, Xiong X, Huang Y (2018) Laparoscopic left lateral hepatic sectionectomy was expected to be the standard for the treatment of left hepatic lobe lesions: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(7):e9835
Cheung TT (2016) Technical notes on pure laparoscopic isolated caudate lobectomy for patient with liver cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:56. https://doi.org/10.21037/tgh.2016.06.06
Dulucq JL, Wintringer P, Stabilini C, Mahajna A (2006) Isolated laparoscopic resection of the hepatic caudate lobe: surgical technique and a report of 2 cases. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 16(1):32–35. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sle.0000202183.27042.63
Liu F, Wei Y, Li B (2019) Laparoscopic isolated total caudate lobectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma located in the paracaval portion of the cirrhotic liver. Ann Surg Oncol 26(9):2980. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07461-1
Goossen K, Tenckhoff S, Probst P, Grummich K, Mihaljevic AL, Büchler MW, Diener MK (2018) Optimal literature search for systematic reviews in surgery. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 403(1):119–129
Cota GF, de Sousa MR, Fereguetti TO, Rabello A (2013) Efficacy of anti-leishmania therapy in visceral leishmaniasis among HIV infected patients: a systematic review with indirect comparison. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7(5):e2195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002195
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Luo D, Wan X, Liu J, Tong T (2017) How to estimate the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, extremes or quartiles? Chin J Evid Based Med 17(11):1350–1356
Xu G, Tong J, Ji J, Wang H, Wu X’a, Jin B, Xu H, Lu X, Sang X, Mao Y, du S, Hong Z (2020) Laparoscopic caudate lobectomy: a multicenter, propensity score-matched report of safety, feasibility, and early outcomes. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07478-8
Ren’an J (2011) A clinical analysis of four cases of laparoscopic hepatic caudate lobectomy. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Luo L, Wu H, Huang J (2019) Experience of laparoscopic caudate lobe resection. Chin J Hepat Surg (Electron Ed) 8(4):311–314
Wang X (2019) Prognosis of laparoscopic hepatectomy vs open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in the caudate lobe. Dissertation, Fujian Medical University
Li Y, Zeng KN, Ruan DY et al (2019) Feasibility of laparoscopic isolated caudate lobe resection for rare hepatic mesenchymal neoplasms. World J Clin Cases 7(20):3194–3201. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3194
Jiang ZC (2019) Laparoscopic versus open surgery for hepatic caudate lobectomy: a retrospective study. Dissertation, Shandong University
Ding Z, Huang Y, Liu L, Xu B, Xiong H, Luo D, Huang M (2020) Comparative analysis of the safety and feasibility of laparoscopic versus open caudate lobe resection. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 405(6):737–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-01928-6
Uchida H, Iwashita Y, Tada K, Saga K, Takayama H, Hirashita T, Endo Y, Ohta M, Inomata M (2018) Laparoscopic liver resection in cirrhotic patients with specific reference to a difficulty scoring system. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 403(3):371–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-018-1671-4
Kasai M, Cipriani F, Gayet B, Aldrighetti L, Ratti F, Sarmiento JM, Scatton O, Kim KH, Dagher I, Topal B, Primrose J, Nomi T, Fuks D, Abu Hilal M (2018) Laparoscopic versus open major hepatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Surgery 163(5):985–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.01.020
Salloum C, Lahat E, Lim C, Doussot A, Osseis M, Compagnon P, Azoulay D (2016) Laparoscopic isolated resection of caudate lobe (segment 1): a safe and versatile technique. J Am Coll Surg 222(5):e61–e66
Jin B, Jiang Z, Hu S, du G, Shi B, Kong D, Yang J (2018) Surgical technique and clinical analysis of twelve cases of isolated laparoscopic resection of the hepatic caudate lobe. Biomed Res Int 2018:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5848309
Schemmer P, Friess H, Dervenis C, Schmidt J, Weitz J, Uhl W, Büchler MW (2007) The use of endo-GIA vascular staplers in liver surgery and their potential benefit: a review. Dig Surg 24(4):300–305. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103662
Kaneko H, Otsuka Y, Tsuchiya M, Tamura A, Katagiri T, Yamazaki K (2008) Application of devices for safe laparoscopic hepatectomy. HPB (Oxford) 10(4):219–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/13651820802166831
Azagra JS, Goergen M, Brondello S, Calmes MO, Philippe P, Schmitz B (2009) Laparoscopic liver sectionectomy 2 and 3 (LLS 2 and 3): towards the “gold standard”. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 16(4):422–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0117-3
Morino M, Morra I, Rosso E, Miglietta C, Garrone C (2003) Laparoscopic vs open hepatic resection: a comparative study. Surg Endosc 17(12):1914–1918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9070-4
Morise Z, Kawabe N, Kawase J, Tomishige H, Nagata H, Ohshima H, Arakawa S, Yoshida R, Isetani M (2013) Pure laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma with chronic liver disease. World J Hepatol 5(9):487–495. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i9.487
Wu YH, Li XG, Zhang YM (2014) Comparison of laparoscopic versus open left hemihepatectomy for left-sided hepatolithiasis. Int J Med Sci 11(2):127–133. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.7516
Medbery RL, Chadid TS, Sweeney JF, Knechtle SJ, Kooby DA, Maithel SK, Lin E, Sarmiento JM (2014) Laparoscopic vs open right hepatectomy: a value-based analysis. J Am Coll Surg 218(5):929–939
Zhong FP, Zhang YJ, Liu Y, Zou SB (2017) Prognostic impact of surgical margin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(37):e8043
Lee SG, Hwang S, Jung JP, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ahn CS (2007) Outcome of patients with huge hepatocellular carcinoma after primary resection and treatment of recurrent lesions. Br J Surg 94(3):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.5622
Montorsi M, Santambrogio R, Bianchi P, Dapri G, Spinelli A, Podda M (2002) Perspectives and drawbacks of minimally invasive surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 49(43):56–61
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81760514), and Science and Technology Plan Project of Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission (no.20175203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: ZG Ding, YH, LP Liu, BR Xu, HX, DL Luo, MW Huang. Data collection: ZG Ding, YH, LP Liu, BR Xu. Data analysis: ZG Ding, YH. Data interpretation: ZG Ding, YH. Writing of manuscript: ZG Ding, YH, LP Liu, BR Xu. Creation of figures: ZG Ding, YH. Critical review of manuscript: YH, MW Huang. Revision of manuscript: ZG Ding, LP Liu, BR Xu. Final approval: ZG Ding, LP Liu, BR Xu, HX, DL Luo, MW Huang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Z., Liu, L., Xu, B. et al. Safety and feasibility for laparoscopic versus open caudate lobe resection: a meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 1307–1316 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02055-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02055-y