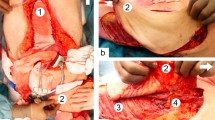
Abstract
Background and purpose
Despite their ubiquitous presence, easy availability and diverse possibilities, falciform ligament and hepatic round ligament have been used less frequently than their potential dictates. This article aims to comprehensively review the applications of hepatic round ligament/falciform ligament flap and graft in abdominal surgery and assess their utility and efficacy.
Methods
Medical literature/indexing databases were searched, using internet search engines, for pertinent articles and analysed.
Results
The studied flap and graft have found utility predominantly in the management of diaphragmatic hernias, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, peptic perforations, biliary reconstruction, venous reconstruction, post-operative pancreatic fistula, post-pancreatectomy haemorrhage, hepatic cyst cavity obliteration, liver bleed, sternal dehiscence, splenectomy, reinforcement of aortic stump, feeding access, diagnostic/therapeutic access into portal system, composite tissue allo-transplant and ventriculo-peritoneal shunting where they have exhibited the desired efficacy.
Conclusions
Hepatic round ligament/falciform ligament flap and graft are versatile and have multifarious applications in abdominal surgery with some novel and unique uses in hepatopancreaticobiliary surgery including liver transplantation. Their evident efficacy needs wider adoption to realise their true potential.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Articles used for the review were obtained from the internet.
Change history
08 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02134-8
References
Strode JE (1950) Utilization of the round and falciform ligament as a peritonealizing structure in surgery of the upper abdomen. Ann Surg 131:581–583
Bills D, Moore S (2009) The falciform ligament and the ligementum teres: friend or foe. ANZ J Surg 79:678–680
Li XP, Xu DC, Tan HY et al (2004) Anatomical study on the morphology and blood supply of the falciform ligament and its clinical significance. Surg Radiol Anat 26:106–109
Ying DJ, Ho GT, Cai JX (1997) Anatomic bases of the vascularised hepatic teres ligament flap. Surg Radiol Anat 19:293–294
Tesch C, Bruns DH, Holstein AF (1990) Open lymphatics in the falciform ligament of the human liver. Langenbeck's Arch Chir 375:130–134
Banerjee JK, Bharathi RS, Rao PP (2017) Buttressing hepaticojejunostomies with hepatic round ligament flap may be beneficial. Pol Przegl Chir 89:7–10
Varga G, Cseks L, Kalmar K et al (2004) Prevention of recurrence by reinforcement of hiatal closure using ligamentum teres in laparoscopic repair of large hiatal hernias. Surg Endosc 18:1051–1053
Facciuto ME, Davalos MIR, Singh MK et al (2009) Recanalized umbilical vein conduit for meso-Rex bypass in extrahepatic portal vein reconstruction. Surgery 145:406–410
Dokmak S, Aussilhou B, Sauvanet A et al (2015) Parietal peritoneum as an autologous substitute for venous reconstruction in hepatopancreatobiliary surgery. Ann Surg 262:366–371
Rudolph H, Neser F, Berger M, Bosse- Landgraf J (2016) Reconstruction of the bile duct with umbilical vein after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Zentralbl Chir 141:609–615
Goossen K, Tenchoff S, Probst P et al (2018) Optimal literature for systematic reviews in surgery. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 403:119–129
Varga G, Cseks L, Kalmar K et al (2008) Laparoscopic repair of large hiatal hernia with teres ligament: mid term follow up. Surg Endosc 22:881–884
Park AE, Hoogerboord CM, Sutton E (2012) Use of the falciform ligament flap for closure of the esophageal hiatus in giant paraesophageal hernia. J Gastrointest Surg 16:1417–1421
Laird R, Brody F, Harr JN et al (2015) Laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernias with a falciform ligament buttress. J Gastrointest Surg 19:1223–1228
Grossman RA, Brody F, Schoolfield CS et al (2018) Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with falciform ligament buttress. J Gastrointest Surg 22:1144–1151
Kaplan K, Gokler C, Aydin MC et al (2018) Falciform ligament instead of mesh for mini-laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair. LESS 25:125–127
El-Kordy M, Attia SG, Mohamed IA et al (2018) Falciform ligament plug in laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair. J Adv Pharm Educ Res 8:73–78
Rau HG, Schardey HM, Lange V (1994) Laparoscopic repair of a Morgagni hernia. Surg Endosc 8:1439–1442
Donati M (2008) Surgical treatment of a Morgagni-Larrey’s hernia. A report of a case. ANZ J Surg 78:317–318
Pironi D, Palazzini G, Arcieri S et al (2008) Laparoscopic diagnosis and treatment of diaphragmatic Morgagni hernia. Case report and review of literature. Ann Ital Chir 79:29–36
Flores R (2019) Robotic repair of Morgagni hernia. SSAT Abstracts 565:S-1403
Allaeys M, Venken R, Vanhulle A et al (2016) Laparoscopic repair of an iatrogenic intrapericardial diaphragmatic hernia using the falciform ligament flap. Acta Chir Belg 116:251–255
Palot JP, Delattre JF, Plet H et al (1989) Cardiopexy using the umbilical ligament of the liver in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Resuls of experience with 100 cases. J Chir 126:13–23
Flament JB, Plet H, Palot JP et al (1991) Cardiopexy using the hepatic ligament in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux. Apropos 200 cases. Chirurgie 117:214–223
Narbona- Arnau B, Lloris- Carsi JM, Calvo-Bermudez MA, Zaragoza C, Azcarraga F (1991) Cardiopexy with round (teres) ligament (‘sling approach’) in surgery for gastroesophageal reflux. Dig Surg 8:197–203
Nathanson LK, Shimi S, Cuschieri A (1991) Laparoscopic ligamentum teres (round ligament) cardiopexy. Br J Surg 78:947–951
Janssen IMC, Gouma DJ, Klementschitsch P et al (1993) Prospective randomised comparison of teres cardiopexy and Nissen fundoplication in the surgical therapy of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 80:875–878
Cuschieri A (1993) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery and repair of hiatal hernia. World J Surg 17:40–45
Meyer C, de Manzini N, Rohr S (1994) Prospective randomised comparison of teres cardiopexy and Nissen fundoplication in the therapy of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 81:153–154
Flament JB, Poloma L, Piet H, Palot JP, Delattre JF, Avisse C (May 1994) The Rampal procedure. In: Giuli R, GNJ T, TR DM, Galmiche JP (eds) The esophageal mucosa. Elsevier http://www.oeso.org/OESO/books/Vol_3_Eso_Mucosa/Articles/ART172.HTML
Valdovinos RG, Vigo JLC, Santillan EM et al (2015) Cardiopexy with ligamentum teres in patients with hiatal hernia and previous sleeve gastrectomy: an alternative treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Obes Surg 25:1539–1543
Blanc P, Epin A, Costanza C et al (2016) Laparoscopic cardiopexy with ligamentum teres in patient with late hiatal hernia after sleeve gastrectomy. Obesite 11:206–209
Al-Sabah S, Akrouf S, Alhadad M et al (2017) Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease and hiatal hernia post sleeve gastrectomy : cardiopexy with ligamentum teres. Surg Obes Relat Dis (12):2032–2036
Dambaev GT, Petlin GF, Solovyov MM et al (2017) Analysis of reconstructions cardioesophageal junction of the teres ligament in treatment hiatal hernias. Shape Memory Biomaterials and Implants in Medicine. KnE Mater Sci:219–226. https://doi.org/10.18502/kms.v2i1.800
Huang CK, Loo MBCL, Astudillo ES et al (2018) Sleeve gastrectomy with ligamentum teres cardiopexy. Obes Surg 28:2583–2584
Moon R, Kirkpatrick V, Teixeria A et al (2018) Laparoscopic repair of recurrent hiatal hernia with ligamentum teres cardiopexy. Surg Obes Relat Dis 14:S73–S75
Vilallonga R, Cordero CC, Alberti P et al (2019) Ligamentum teres cardiopexy as a late alternative for gastroesophageal reflux disease in a patient with previous reversal of gastric bypass to sleeve gastrectomy and hiatal hernia repair. Obes Surg 29:3765–3768
Hutopila LC, Copaescu C (2019) Laparoscopic Narbona-Arnau procedure to control the GERD after LSG – 3 years results of a prospective study. Surg Endosc 33(Suppl 2):485–781
Runkel A, Scheffel O, Marjanoviv G, Runkel N (2020) The new interest of bariatric surgeons in the old ligament teres hepatis. Obes Surg 30:4592–4598
Fry DE, Richardson JD, Flint LM (1978) Closure of an acute perforated peptic ulcer with the falciform ligament. Arch Surg 113:1209–1210
Jordan FT, Winkler JM, Hoshal VL Jr (1981) Falciform ligament closure of an acute perforated gastric ulcer. J Abdom Surg 23:109–110
Colstalat G, Dravet F, Noel P et al (1991) Coelioscopic treatment of perforated gasproduodenal ulcer using the ligament teres hepatis. Surg Endosc 5:154–155
Costalat G, Alquiler Y (1995) Combined laparoscopic and endoscopic treatment of gastroduodenal ulcer using the ligament teres hepatis. Surg Endosc 9:677–680
Munro WS, Bajwa F, Menzies D (1996) Laparoscopic repair of perforated duodenal ulcers with a falciform ligament patch. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 78:390–391
Naesgaard JM, Edwin B, Reiertsen O et al (1999) Laparoscopic and open operations in patients with perforated peptic ulcer. Eur J Surg 165:209–214
Shiryajev YN, Bernstein MA, Evstratov VD et al (2011) Closure of the perforated gastric ulcer using the round ligament of liver, pathologically changed due to ulcer penetration: report of a case. J Abdom Surg 53:16–19
Wijegoonewardene SI, Stein J, Cooke D et al (2012) Valentino’s syndrome a perforated peptic ulcer mimicking acute appendicitis. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr.03.2012.6015
Bingener J, Loomis EA, Gostout CJ et al (2013) Feasibility of NOTES omental plug repair of perforated peptic ulcers: Results from a clinical pilot trial. Surg Endosc 27:2201–2208
Boshnaq M, Thakrar A, Martini I et al (2016) Utilisation of the falciform ligament pedicle flap as an alternative approach for the repair of a perforated gastric ulcer. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-213025
Cahs H, Cetin M, Sahin S et al (2016) Marginal ulcer perforation repair with falciform ligament: Case report. CausaPedia 5:144–147
Allart K, Prevot F, Rebibo L et al (2018) Laparoscopic repair of a perforated duodenal uler: another use of a round ligament flap. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne 13:542–545
Olmez A, Cicek E, Aydin C et al (2019) Omentopexy versus falciformopexy for peptic ulcer perforation. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 25:580–584
Lewis WI (1996) Ligamentum teres not the ideal ulcer patch. Surg Endosc 10:697
Sain AHM (1996) Laparoscopic repair of perforated duodenal ulcers with a falciform ligament patch. Ann Surg 79:156–157
Stuker FJ (1990) Managing bile duct defects by pedicle ligament teres hepatis. Chirurg 61:600–602
Settaf A, Balafrej S (1993) Biliary surgery using the ligament teres. Technique for repairing loss of substance in the common bile duct. Ann Chir 47:529–533
Chang EG (2000) Repair of common bile duct injury with the round and falciform ligament after clip necrosis: Case report. JSLS 4:163–165
Kimura Y, Hirata K, Mukaiya M et al (2005) Biliary injury after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: end-to-end anastomosis covered with umbilical vein. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 12:269–271
Turegano-Fuentes F, Mercader-Cidoncha E, Perez-Diaz D, Sanz-Sanchez M, Jimnez-Gomez LM (2006) Use of round ligament in repair of extensive bile duct defects in Mirrizi syndrome type II. Cir Esp 79:379–381
Watabnabe M, Yamazaki K, Tsuchiya M et al (2007) Use of an opened umbilical vein patch for the reconstruction of the injured biliary tract. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 14:270–275
Zhang CH, Yang XY, Chen X et al (2011) A novel use for the round ligament of the liver in a complicated bile duct operation. ANZ J Surg 81:572–573
Sun DX, Tan XD, Gao F et al (2015) Use of an autologous liver round ligament flap zeros postoperative bile leak after curative resection of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0125977. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125977
Dokmak S, Aussilhou B, Ragot E et al (2017) Reconstruction of bile duct injury and defect with the round ligament. J Gastrointest Surg 21:1540–1543
Irigoyen JA, Cortes HH, Trujillo AT et al (2019) Round ligament repair of the bile duct as treatment of bile duct injuries: Case report. Arq Bras Cir Dig 32:e1443
Bratucu E, Ungureanu FD, Ungurianu L (2000) Drainage of the common bile duct by the axial transomphalic exztraperitoneal route. Dig Surg 17:348–353
Madge OLP, Daha C, Bratucu E (2012) The use of axial drainage in biliary surgery. Int J Biol Biomed Eng 6:141–148
Kuroda Y, Tanioka Y, Ku Y et al (1996) Centrifugal pump assisted venous bypass between the superior mesenteric vein and the umbilical vein during portal vein resection. Surg Today 26:762–764
Suzuki Y, Yoshida I, Ku Y et al (2004) Safety of portal vein resection using centrifugal pump assisted venous bypass between the superior mesenteric vein and the umbilical vein. Hepatogastroenterol 51:1183–1186
Yamanaka N, Yasui C, Yamanaka J et al (2000) Recycled use of reopened umbilical vein for venous reconstruction in hepatopancreatobiliary surgery. J Am Coll Surg 190:497–501
Miyazaki M, Ito H, Kimura F et al (2004) Hepatic vein reconstruction using autologous vein graft for resection of advanced hepatobiliary malignancy. Hepatogastroenterol 51:1581–1585
Lee KW, Lee DS, Lee JW et al (2004) Interposition vein graft in living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 36:2261–2262
Chen QP, Ou K, Guan QH et al (2006) Feasibility study on reconstruction of portal vein/ superior mesenteric vein using ligament teres hepatis. Shandong Med J 46:7–8
Soejima Y, Shimada M, Suehiro T et al (2006) Reconstruction of the middle hepatic vein tributaries using the recipient’s recanalized umbilical vein in right lobe living donor liver transplantation. Surgery 139:442–445
Mergental H, Gouw ASH, Sloof MJH et al (2007) Venous outflow reconstruction with surgically reopened obliterated umbilical vein in Domino liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 13:769–772
Singh A, Soin AS, Kakodkar R et al (2007) Recanalized umbilical vein as a conduit for anterior sector venous outflow reconstruction in right lobe grafts. Surgery 141:830
Kilic M, Aydin U, Sozbilen M et al (2007) Comparison between allogenic and autologous vascular conduits in the drainage of anterior sector in right living donor liver transplantation. Transpl Int 20:697–701
Ikegami T, Shimada M, Imura S et al (2008) Beneficial use of the round ligament as a patch graft for vena cava reconstruction. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 15:581–584
Sakamoto S, Kasahara M, Shigeta T et al (2010) Feasibility of using the grafts umbilical vein as patch graft for hepatic vein reconstruction in paediatric living donor liver transplantation. Transpl Int 23:436–437
Gonzales-Pinto IM, Miyar A, Gracia-Bernando C et al (2009) Portoumbilical anastomosis as a simple method of transient portosystemic shunt during liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 41:996–997
Krebs-Schmitt D, Briem-Richter A, Grabhorn E et al (2009) Effectiveness of Rex shunt in children with portal hypertension following liver transplantation or with primary portal hypertension. Pediatr Transplant 13:540–544
Sanada Y, Mizuta K, Kawano Y et al (2009) Living donor liver transplantation for congenital absence of the portal vein. Transplant Proc 41:4214–4219
Sato Y, Oya H, Yamamato S et al (2010) Method of spontaneous constriction and closure of portocaval shunt using a ligament teres hepatis in small for size graft liver transplantation. Transplantation 19:1200–1203
Sharif K, Mckiernan P, de Goyet JDV (2010) Mesoportal bypass for extra hepatic portal vein obstruction in children: close to a cure for most. J Pediatr Surg 45:272–276
Pomposelli JJ, Akooad M, Khwaja K et al (2012) Evolution of anterior segment reconstruction after live donor adult liver transplantation: a single centre experience. Clin Transpl 26:470–475
Chen CL, Yap AQ, Concejero AM, Liu CY (2012) All in one sleeve patch graft venoplasty for multiple hepatic vein reconstruction in living donor liver transplantation. HPB 14:274–278
Shinkai M, Ohhama Y, Honda S et al (2011) Recanalized umbilical vein as a conduit for mesenterico/porto- Rex bypass for patients with extra hepatic portal vein obstruction. Pediatr Surg Int 27:315–319
Gunasekaran G, Mosna LC, Savino JA (2013) Portomesenteric reconstruction using an umbilical vein patch during pancreatoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure). J Am Coll Surg 217:e9–e11
Ikegami T, Wang H, Imai D et al (2013) Pathological analysis of opened round ligaments as venous patch grafts in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 19:1245–1251
Rochon C, Steiner PA, Sharma J et al (2013) The utility of recanalized umbilical vein graft to the hepato-pancreato- biliary surgeon. Surg Innov 20:126–133
Toshima T, Ikegami T, Matsumoto Y et al (2014) One step venous reconstruction using the donor’s round ligament in right lobe living donor liver transplantation. Surg Today 45:522–525
Kamei H, Onishi Y, Ogawa K et al (2014) Living donor liver transplantation using a right liver graft with additional vein reconstruction for patient with situs inversus. Am J Transplant 14:1453–1458
Dokmak S (2015) Pancreatoduodenectomy with reconstruction of the mesentricoportal vein by the parietal peritoneum: ‘Safi Dokmak vascular graft’. Ann Surg Oncol Suppl 3:S343–S344. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4635-8
Dokmak S, Cherif R, Duquesne I et al (2016) Laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy with reconstruction of the portal vein with the parietal peritoneum. Ann Surg Oncol 23:2664
Sananda Y, Sakuma Y, Sasanuma H et al (2016) Immunohistochemical evaluation for outflow reconstruction using opened round ligament in living donor right posterior sector graft liver transplantation: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 22:7851–7856
Shinkai M, Mochizuki K, Kitagawa N et al (2016) Usefulness of a recanalized umbilical vein for vascular reconstruction in pediatric hepatic surgery. Pediatr Surg Int 32:553–558
Urshashi T, Ihara Y, Sanada Y et al (2016) Recanalized umbilico-caval anastomosis as a temporary portosystemic in pediatric living donor liver transplantation: the crossed fingers method. Clin Transpl 30:1425–1432
Takahashi M, Saiura A, Takahashi Y (2017) The usefulness of patch repair using the repermeabilized umbilical vein of the round ligament for hepatobiliary malignancies. World J Surg 41:2813–2816
Zhiying Y, Haidong T, Xiaolei L et al (2017) The falciform ligament as a graft for portal superior mesenteric vein reconstruction in pancreatectomy. J Surg Res 218:226–231
Shao Y, Yan S, Zhang AY et al (2018) Autologous falciform ligament graft as a substitute for mesentricoportal vein reconstruction in pancreatoduodenectomy. Int J Surg 52:159–162
Herrero E, Galofre M, Camps J et al (2018) Autologous graft of falciform ligament for vascular reconstruction in pancreatic surgery. HPB 20(S2):S656–S657
Malinka T, Klein F, Denke T et al (2018) The falciform ligament for mesenteric and portal vein reconstruction in local advanced pancreatic tumors: a surgical guide and single centre experience. HPB Surg:2943879. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2943879
Cai Y, Li Y, Gao P, Wang X, Peng B (2018) Laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy with major venous resection and reconstruction with repassed round ligament: a case report. Ann Transl Med 6:213
Wei Q, Chen QP, Guan QH et al (2019) Repair of the portal vein using a hepatic ligament teres patch for laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy: a case report. World J Clin Cases 7:2879–2887
Stuben BO, Heumann A, Sturznickel J et al (2019) Successful use of the recanalized remnant umbilical vein as a patch graft for venous reconstruction in abdominal surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 23:1227–1231
Toshima T, Yoshizumi T, Shimokawa M et al (2019) Feasilbility of all- in- one venoplasty with a venous cuff using an opened round ligament for the right lobe graft in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 25:171–175
Galfore-Recansens M, Fonollosa EH, Lasa JC, Garcia-Domingo MI, Andorra EC (2019) Autlogous falciform ligament graft for vascular reconstruction in pancreatic cancer surgery. Cir Esp 97:54–61
van Leeuwen OB, Fujiyoshi M, Ubbink R et al (2019) Ex situ machine perfusion of human donor livers via the surgically reopened umbilical vein: a proof of concept. Transplantation 103:2130–2135
Hobeika C, Cauchy F, Soubrane O (2020) Case series of extended liver resection associated with inferior vena cava reconstruction using peritoneal patch. Int J Surg 80:6–11
Yoshiya S, Yomoharu T, Iseda N et al (2020) Anastomosis of the common hepatic artery and round ligament as portal vein arterialisation for hepatic artery occlusion after deceased donor liver transplantation:a case report. Transplant Proc 52:641–643
Zhu W, Song R, Cao X et al (2020) A comparison between the mechanical properties of the hepatic round ligament and the portal vein: a clinical implication on surgical reconstruction of the portal and superior mesenteric veins. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2020.1780427
Urahashi T, Katsuragawa H, Yamamoto M et al (2012) Transumbilical portal venous catheterization: a useful adjunct in left lobe living donor liver transplantation. Clin Transpl. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2012.01663.x
Michalski CW, Tramell O, Buchler MW, Hackert T (2017) Closure of pancreas stump after distal and segmental resection: suture, stapler, coverage or anastomosis? Chirurg 88:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00104-016-0301-3
Iannitti DA, Coburn NG, Somberg J et al (2006) Use of the round ligament of the liver to decrease pancreatic fistulas: a novel technique. J Am Coll Surg 203:857–864
Ferrone CR, Warsaw AL, Rattner DW et al (2008) Pancreatic fistula rate after 462 distal pancreatectomies: staplers do not decrease fistula rates. J Gastrointest Surg 12:1691–1698
Oida T, Mimatsu K, Kawasaki A et al (2009) Towards zero pancreatic leakage after pancreatoduodenectomy for soft pancreas in low volume pancreatic surgery centres. Hepatogastroenterol 56:886–890
Walters DM, Stokes JB, Adams RB et al (2011) Use of a falciform ligament pedicle flap to decrease pancreatic fistula after distal pancreatectomy. Pancreas 40:595–599
Hassenpflug M, Hartwig W, Strobel O et al (2012) Decrease in clinically relevant pancreatic fistula by coverage of the pancreatic remnant after distal pancreatectomy. Surgery 152:S164–S171
Wu CT, Xu WY, Liu L et al (2013) Ligamentum teres hepatis patch enhances the healing of pancreatic fistula after distal pancreatectomy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 12:651–655
Carter TI, Fong ZV, Hyslop T et al (2013) A dual institution randomised controlled trial of remnant closure after distal pancreatectomy: does the addition of a falciform patch and fibrin glue improve outcomes? J Gastrointest Surg 17:102–109
Hackert T, Lozanovski VJ, Werner J et al (2013) Teres hepatis ligament flap plasty to prevent pancreatic fistula after tumor enucleation. J Am Coll Surg 217:e29–e34
Lei P, Liu XM, Lu Y (2013) Clinical application of autologous falciform ligament patch in reinforced pancreatojejunostomy. J Xian Jiaotong Univ 34:125–127
Fujino Y, Sendo H, Oshikiri T, Sugimoto T, Tominaga M (2015) A novel surgical technique to prevent pancreatic fistula in distal pancreatectomy using a patch of the falciform ligament. Surg Today 45:44–49
Egeli T, Unek T, Ozbilgin M, Goztok M, Astarcioglu I (2016) A novel technique for managing pancreaticojejunal anastomotic leak after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Case Rep Surg. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5392923
Hasselpflug M, Hinz U, Strobel O et al (2016) Teres ligament patch reduces relevant morbidity after distal pancreatectomy (the DISCOVER randomised controlled trial ). Ann Surg 264:723–730
Mech K, Wysocki L, Guzel T et al (2016) Can round ligament of the liver patch decrease the rate and grade of postoperative pancreatic fistula? Pol Przegl Chirurg 88:63–67
Tillman LC, Herzog T, Uhl W et al (2017) Sealing with cyanoacrylate and a falciform patch cannot prevent postoperative pancreatic fistula. World J Surg 41:1601–1609
Zizzo M, Ugoletti L, Morni A et al (2018) Pancreatojejunostomy with or without reinforcement after pancreatoduodenectomy: surgical technique of ligament teres hepatis wrap around pancreatojejunostomy. World J Surg Oncol 18:181
Abe N, Sugiyama M, Yanagida O et al (2007) Wraping of skeletonized and divided vessels using the falciform ligament in distal pancreatectomy. Am J Surg 194:94–97
Sakamoto Y, Shimada K, Esaki M et al (2007) Wrapping the stump of the gastroduodenal artery using the falciform ligament during pancreatoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 204:334–336
Abe N, Sugiyama M, Suzuki Y et al (2009) Falciform ligament in pancreatoduodenectomy for protection of skeletonized and divided vessels. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 16:184–188
Mimatsu K, Oida T, Kano H et al (2011) Protection of major vessels and pancreatogastrostomy using the falciform ligament and greater omentum for preventing pancreatic fistula in soft pancreatic texture after pancreatoduodenectomy. Hepatogastroenterology 58:1782–1786
Nakatsuka H, Sawatsubashi T, Morioka N et al (2013) Use of the round ligament of the liver to prevent post pancreatectomy haemorrhage. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 40:1903–1905
Xu C, Yang X, Luo X et al (2014) Wrapping the gastroduodenal artery stump during pancreatoduodenectomy reduced the stump haemorrhage incidence after operation. Chin J Cancer Res 26:299–308
Ray S, Sanyal S, Ghatak S et al (2016) Falciform ligament flap for the protection of the gastroduodenal artery stump after pancreatoduodenectomy: a single centre experience. J Visc Surg 153:9–13
Mussle B, Wierick A, Distler M et al (2017) Falciform ligament wrap for prevention of gastroduodenal artery bleed after pancreatodudenctomy. J Surg Res 207:215–222
Magge D, Zenati M, Lutfi W et al (2018) Robotic pancreatoduodenectomy at an experienced institution is not associated with an increased risk of post pancreatectomy haemorrhage. HPB 20:448–455
Okada K, Murakami Y, Uemura K et al (2020) Flooring the major vessels with falciform ligament to prevent post pancreatectomy hemorrhage. World J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05637-5
Meng L, Gao P, Peng B (2020) Pedicled round ligament wraps the gastro-duodenal artery stump to prevent bleeding after laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy. J Sinchuan Univ 51:453–456. https://doi.org/10.12182/20200760602
Ozmen MM, Coskun F, Ziraman I (2006) Falciform ligament in the management of the residual cavity for liver hydatidosis: new surgical technique. World J Surg 30:1722–1728
Dirican A, Unal B, Ozgor D et al (2008) Perforated hepatic hydatid cyst into the peritoneum with mild symptoms. Case Rep Gastroenterol 2:439–443
Faulds JM, Scudamore CH (2010) Technical report of a novel surgical technique: laparoscopic cyst fenestration and falciform ligament pedicle graft for treatment of symptomatic simple hepatic cysts. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 20:857–861
Fujino Y, Ku Y, Suzuki Y et al (2001) Successful haemostasis of a ruptured liver tumour using flaps of gallbladder serosa and the falciform ligament. Eur J Surg 167:552–553
Narayansingh V, Ramdass (2009) Control of the bleeding gallbladder bed using a pedicled falciform ligament flap based on the left inferior phrenic artery and middle segment hepatic artery. Can J Surg 52:E203–E204
Nagarkatti SS, Pickens RC, Baker EH et al (2019) Robotic portal lymphadenectomy with segment 4B and 5 resection for gallbladder cancer. HPB 21(S1):S97
Levites HA, Phillips BT, Bilfinger TV et al (2014) Sternal wound reconstruction with falciform and omental flaps for chronic sternal osteomyelitis. Plast Reconst Surg Glob Open 2:e233
Nagahama T (2018) Secure tube gastrostomy using round ligament of liver flap for the patient after esophageal surgery. Clin Nutr 37:S313
Watanabe M, Etoh K, Nagai Y et al (2011) Feeding tube insertion through the round ligament of liver: a safe approach to placing a feeding tube for retrosternal gastric tube reconstruction after esophagectomy. J Am Coll Surg 213:e21–e22
Oya H, Koike M, Iwata et al (2015) Feeding duodenostomy decreases the incidence of mechanical obstruction after radical esophageal cancer surgery. World J Surg 39:1105–1110
Kawai R, Abe T, Uemura N et al (2017) Feeding catheter gastrostomy with the round ligament of the liver prevents mechanical bowel obstruction after esophagectomy. Dis Esophagus 30:1–8
Otake R, Okamura A, Kanamori J et al (2020) The optimal feeding enterostomy creation during esophagectomy to reduce the long term risk of small bowel obstruction. World J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05701-0
Andreasi V, Partelli S, Crippa S et al (2020) A systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of omental or falciform ligament wrapping during pancreaticoduodenectomy. HPB. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpb.2020.05.003
Tani M, Kawai M, Jirono S et al (2012) Use of omentum or falciform ligament does not decrease complications after pancreatoduodenectomy: nationwide survey of the Japanese society of pancreatic surgery. Surgery 151:183–191
Ramia J, de la Plaza R, Adel F et al (2014) Wrapping in pancreatic surgery: a systematic review. ANZ J Surg 84:921–924
Ungureanu FD, Ungurianu L, Hasias S et al (2004) The exztraperitoneal transomphalic drainage of the postoperative hydatid cavity through the transposed round ligament detached from the liver. Chirurgia 99:87–92
Ungureanu FD, Ungurianu L, Cucu S et al (2004) Extraperitonal transomphalic drainage of the post hydatid hepatic residual cavity by coelioscopic approach. Chirurgia 99:159–165
Marincas M, Bratucu E, Badarau A et al (2009) External drainage of the hepatic post hydatid remnant cavity. Chirurgia 104:151–157
Monden K, Sadamori H, Hioki M et al (2019) Useful technique for draining a large cystic tumour through the round ligament in laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy. Asian J Endosc Surg 12:237–241
Oida T, Mimatsu K, Kawasaki A, Kanou H, Kuboi Y, Amano S (2010) Fixation of the round ligament to the peritoneum and wrapping of the cut surface of the liver for prevention of early delayed gastric emptying after hepatic lateral segmentectomy. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 395:655–659
Agarwal S, Dorafshar AH, Harland RC et al (2010) Liver and vascularized posterior rectus sheath fascia composite tissue allo-transplantation. Am J Transplant 10:2712–2716
Ammori BJ (2020) Utilization of the falciform ligament to buttress the spleen transection staple line during laparoscopic partial splenectomy: a novel technique. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 30:e1–e3
Moulakakis KG, Koliakos N, Martikos G, Lazaris AM (2020) A technical tip of aortic stump reinforcement with plication of the falciform ligament of the liver. Ann Vasc Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2020.04.044
Pollard C, Gravante G, Webb MB et al (2011) Use of the recanalised umbilical vein for islet autotransplantation following total pancreatectomy. Pancreatology 11:233–239
Soyama A, Eguchi S, Takatsuki M et al (2011) Tumour throbectomy via a surgical reopened umbilical vein combined with right hepatectomy in a patient with hepatocellucar carcinoma. Dig Surg 28:222–225
Tamaki I, Kami K, Yamamoto E, Moromoto T (2014) Catheter-directed thrombolysis through the operatively recanalized umbilical vein for acute extensive portal vein thrombosis: report of a case. Clin J Gastroenterol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-014-0510-6
Derksen WJM, de Jong IEM, Buis CI et al (2020) Successful thrombectomy via a surgically reopened umbilical vein for extended portal vein thrombosis caused by portal vein embolozation prior to extended liver resection. Dig Surg 14:320–328
Shao Y, Li M, Sun JL et al (2011) A laparoscopic approach to ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement with a novel fixation method for distal shunt catheter in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 54:44–47
Svoboda SM, Park H, Naff N et al (2015) Preventing distal catheter obstruction in laparoscopic ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in adults: the falciform technique. J Laparoendosc Endosc Surg Tech 25:642–645
Stokes RB, Whetzel TP, Sommerhaug E et al (1998) Arterial vascular anatomy of the umbilicus. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:761–764
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study concept, design, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript and critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baskaran, V., Banerjee, J.K., Ghosh, S.R. et al. Applications of hepatic round ligament/falciform ligament flap and graft in abdominal surgery—a review of their utility and efficacy. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 1249–1281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02031-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02031-6