Abstract
Purpose
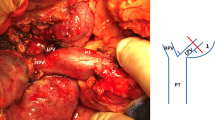
Temporary portal decompression (TPD) during liver transplantation (LT) remains a divisive technical issue in the liver transplant community. In this video-based article, we show the technical details of the different techniques used for TPD during LT.
Methods
An early portal section, before liver mobilization, should be preferred in order to achieve hepatectomy of a totally devascularized liver. Portal decompression can be achieved through direct right portocaval shunts and indirect portosystemic shunts (i.e., mesentericosaphenous and portosaphenous shunts).
Results
The preference for direct portocaval or indirect portosystemic shunts is tailored on patients and anatomical characteristics. Each of these three techniques presents specific indications, limitations, and advantages.
Conclusion
TPD during LT can be achieved through different techniques that aim to facilitate the recipient hepatectomy, reduce the blood loss, and maintain hemodynamic stability.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Tzakis AG, Reyes J, Nour B, Marino IR, Todo S, Starzl TE (1993) Temporary end to side portacaval shunt in orthotopic hepatic transplantation in humans. Surg Gynecol Obstet 176:180–182
Belghiti J, Noun R, Sauvanet A (1995) Temporary portocaval anastomosis with preservation of caval flow during orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Surg 169:277–279
Czigany Z, Scherer MN, Pratschke J, Guba M, Nadalin S, Mehrabi A, Berlakovich G, Rogiers X, Pirenne J, Lerut J, Mathe Z, Dutkowski P, Ericzon BG, Malagó M, Heaton N, Schöning W, Bednarsch J, Neumann UP, Lurje G (2019) Technical aspects of orthotopic liver transplantation-a survey-based study within the eurotransplant, Swisstransplant, Scandiatransplant, and British Transplantation Society Networks. J Gastrointest Surg 23:529–537
Kluger MD, Memeo R, Laurent A, Tayar C, Cherqui D (2011) Survey of adult liver transplantation techniques (SALT): an international study of current practices in deceased donor liver transplantation. HPB (Oxford) 13:692–698
Hoffmann K, Weigand MA, Hillebrand N, Buchler MW, Schmidt J, Schemmer P (2009) Is veno-venous bypass still needed during liver transplantation? A review of the literature. Clin Transplant 23:1–8
Pratschke S, Rauch A, Albertsmeier M, Rentsch M, Kirschneck M, Andrassy J, Thomas M, Hartwig W, Figueras J, del Rio Martin J, de Ruvo N, Werner J, Guba M, Weniger M, Angele MK (2016) Temporary intraoperative porto-caval shunts in piggy-back liver transplantation reduce intraoperative blood loss and improve postoperative transaminases and renal function: a meta-analysis. World J Surg 40:2988–2998
Faitot F, Addeo P, Besch C, Michard B, Oncioiu C, Ellero B, Woehl-Jaeglé ML, Bachellier P (2019) Passive mesenterico-saphenous shunt: an alternative to portocaval anastomosis for tailored portal decompression during liver transplantation. Surgery 165:970–977
Pratschke S, Meimarakis G, Bruns CJ, Kaspar M, Prix N, Zachoval R, Guba M, Jauch KW, Loehe F, Angele MK (2013) Temporary intraoperative porto-caval shunt: useless or beneficial in piggy back liver transplantation? Transpl Int 26:90–98
Addeo P, Locicero A, Faitot F, Bachellier P (2019) Temporary Right Portocaval Shunt During Piggyback Liver Transplantation. World J Surg 43:2612–2615
Lerut J, Ciccarelli O, Roggen F, Laterre PF??, Danse E, Goffette P, Aunac S, Carlier M, de Kock M, van Obbergh L, Veyckemans F, Guerrieri C, Reding R, Otte JB (2003) Cavocaval adult liver transplantation and retransplantation without venovenous bypass and without portocaval shunting: a prospective feasibility study in adult liver transplantation. Transplantation 75:1740–1745
Lerut JP, Molle G, Donataccio M et al (1997) Cavocaval liver transplantation without venovenous bypass and without temporary portocaval shunting: the ideal technique for adult liver grafting? Transpl Int 10:171–179
Figueras J, Llado L, Ramos E et al (2001) Temporary portocaval shunt during liver transplantation with vena cava preservation. Results of a prospective randomized study. Liver Transpl 7:904–911
Ghinolfi D, Marti J, Rodriguez-Laiz G et al (2011) The beneficial impact of temporary porto-caval shunt in orthotopic liver transplantation: a single center analysis. Transpl Int 24:243–250
Nacif LS, Zanini LY, Costa Dos Santos JP et al (2020) Intraoperative temporary portocaval shunt in liver transplant. Transplant Proc
Rayar M, Levi Sandri GB, Cusumano C, Locher C, Houssel-Debry P, Camus C, Lombard N, Desfourneaux V, Lakehal M, Meunier B, Sulpice L, Boudjema K (2017) Benefits of temporary portocaval shunt during orthotopic liver transplantation with vena cava preservation: A propensity score analysis. Liver Transpl 23:174–183
Panaro F, Boisset G, Chanques G, Guiu B, Herrero A, Bouyabrine H, Pageaux GP, Boudjema K, Navarro F (2016) Vena cava encirclement predicts difficult native hepatectomy. Liver Transpl 22:906–913
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work: PA, OJ, AT, CS, FF, and PB. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work: PA, OJ, AT, CS, FF, and PB. Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content and final approval of the version to be published: PA, OJ, AT, CS, FF, and PB. Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved: PA, OJ, AT, CS, FF, and PB
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Addeo, P., Julliard, O., Terrone, A. et al. Temporary portal decompression during liver transplantation: a video review of the different techniques. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 227–231 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-01991-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-01991-z