Abstract
Background
Cellular apoptosis plays an important role in ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury during organ transplantation. Synthetic small interference RNA (siRNA) targeting apoptotic receptor Fas has proven effective to protect mice against hepatitis and renal I/R injury. The objective of this study is to investigate the silencing impact of Fas siRNA to alleviate I/R injury in rat liver transplantation.
Materials and methods
Rat hepatocytes (BRL cells) were transfected with three pairs of synthesized Fas siRNA; cells untreated and treated with GFP siRNA were taken as blank and siRNA control. The most effective Fas siRNA was chosen for in vivo experiments. Syngeneic orthotopic liver transplantation was performed in Fas siRNA group, siRNA control group, and blank control group of Sprague–Dawley rats. There were 25 pairs of rats in each group. siRNA transfection of donor rats was done with hydrodynamic injection method 48 h before liver procurement. Blood and liver samples were collected for evaluation of serum ALT levels, Fas protein and mRNA expression, and apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining, 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after liver transplantation.
Results
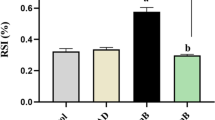
Fas siRNA2, which inhibited Fas gene expression much more than other siRNAs, was chosen for in vivo experiment. The serum ALT levels of Fas siRNA group were much less than those of blank and siRNA control groups 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after blood reperfusion, indicating diminishing ischemia-reperfusion injury. Donor livers in Fas siRNA group had substantially less cell apoptosis. The expression of Fas mRNA and protein was reduced dramatically in the Fas siRNA group compared with the other two groups.
Conclusion
Fas-mediated apoptosis play an important role in I/R injury of rat liver transplantation. Silencing Fas by hydrodynamic injection of siRNA holds therapeutic promise to limit I/R injury.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varotti G, Grazi GL, Vetrone G, Ercolani G, Cescon M, Del Gaudio M, Ravaioli M, Cavallari A, Pinna A (2005) Causes of early acute graft failure after liver transplantation: analysis of a 17-year single-centre experience. Clin Transplant 19(4):492–500
Jiang H, Meng F, Li J, Sun X (2005) Anti-apoptosis effects of oxymatrine protect the liver from warm ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. World J Surg 29(11):1397–1401
Cursio R, Filippa N, Miele C, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Van Obberghen E, Gugenheim J (2005) Fas ligand expression following normothermic liver ischemia-reperfusion. J Surg Res 125(1):30–36
Selzner M, Rudiger HA, Sindram D, Madden J, Clavien PA (2000) Mechanisms of ischemic injury are different in the steatotic and normal rat liver. Hepatology 32(6):1280–1288
Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, Adachi M, Nagata S (1997) Essential roles of the Fas ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nat Med 3(4):409–413
Yin XM, Ding WX (2003) Death receptor activation-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury. Curr Mol Med 3(6):491–508
Kasahara I, Saitoh K, Nakamura K (2000) Apoptosis in acute hepatic failure: histopathological study of human liver tissue using the TUNEL method and immunohistochemistry. J Med Dent Sci 47(3):167–175
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N, Min J, Chen J, Shankar P, Lieberman J (2003) RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med 9(3):347–351
Hamar P, Song E, Kokeny G, Chen A, Ouyang N, Lieberman J (2004) Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects mice against renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(41):14883–14888
Kamada N, Davies HS, Roser B (1981) Reversal of transplantation immunity by liver grafting. Nature 292(5826):840–842
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S, Marshall WS, Khvorova A (2004) Rational SiRNA design for RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 22(3):326–330
Hsieh AC, Bo R, Manola J, Vazquez F, Bare O, Khvorova A, Scaringe S, Sellers WR (2004) A library of SiRNA duplexes targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway: determinants of gene silencing for use in cell-based screens. Nucleic Acids Res 32(3):893–901
Zhang G, Gao X, Song YK, Vollmer R, Stolz DB, Gasiorowski JZ, Dean DA, Liu D (2004) Hydroporation as the mechanism of hydrodynamic delivery. Gene Ther 11(8):675–682
Ke B, Shen XD, Lassman CR, Gao F, Katori M, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2003) Interleukin-13 gene transfer protects rat livers from antigen-independent injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. Transplantation 75(8):1118–1123
Yang J, Jones SP, Suhara T, Greer JJ, Ware PD, Nguyen NP, Perlman H, Nelson DP, Lefer DJ, Walsh K (2003) Endothelial cell overexpression of Fas ligand attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in the heart. J Biol Chem 278(17):15185–15191
Jaeschke H (2002) Reperfusion injury after warm ischemia or cold storage of the liver: Role of apoptotic cell death. Transplant Proc 34(7):2656–2658
Wei ZZ, Xia SS (2004) Gamma-hydroxybutyrate protects the liver from warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 3(2):245–249
Zhang Y, Ye QF, Lu L, Xu XL, Ming YZ, Xiao JS (2005) Panax notoginseng saponins preconditioning protects rat liver grafts from ischemia/reperfusion injury via an antiapoptotic pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 4(2):207–212
Tannapfel A, Kohlhaw K, Ebelt J, Hauss J, Liebert U, Berr F, Wittekind C (1999) Apoptosis and the expression of Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) antigen in rejection and reinfection in liver allograft specimens. Transplantation 67(7):1079–1083
Cursio R, Filippa N, Miele C, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Van Obberghen E, Gugenheim J (2005) Fas ligand expression following normothermic liver ischemia-reperfusion. J Surg Res 125(1):30–36
Saxton NE, Barclay JL, Clouston AD, Fawcett J (2002) Cyclosporin A pretreatment in a rat model of warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Hepatol 36(2):241–247
Qiu J, Whalen MJ, Lowenstein P, Fiskum G, Fahy B, Darwish R, Aarabi B, Yuan J, Moskowitz MA (2002) Upregulation of the Fas receptor death-inducing signaling complex after traumatic brain injury in mice and humans. J Neurosci 22(9):3504–3511
Kossmehl P, Kurth E, Faramarzi S, Habighorst B, Shakibaei M, Wehland M, Kreutz R, Infanger M, Danser AH, Grosse J, Paul M, Grimm D (2006) Mechanisms of apoptosis after ischemia and reperfusion: role of the rennin–angiotensin system. Apoptosis 11(3):347–358
Zhao Y, Ding WX, Qian T, Watkins S, Lemasters JJ, Yin XM (2003) Bid activates multiple mitochondrial apoptotic mechanisms in primary hepatocytes after death receptor engagement. Gastroenterology 125(3):854–867
Schattenberg JM, Galle PR, Schuchmann M (2006) Apoptosis in liver disease. Liver Int 26(8):904–911
Feldmann G, Haouzi D, Moreau A, Durand-Schneider AM, Bringuier A, Berson A, Mansouri A, Fau D, Pessayre D (2000) Opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore causes matrix expansion and outer membrane rupture in Fas-mediated hepatic apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 31(3):674–683
Acknowledgment
The project was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China, 973 Program, No. 2003CB515507 and the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China, No. 20040558060.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, J.F., Lu, M.Q. et al. Alleviation of ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver transplantation by induction of small interference RNA targeting Fas. Langenbecks Arch Surg 392, 345–351 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-006-0142-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-006-0142-5