Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated the effects of different rest interval strategies during high-intensity interval resistance training (HIRT) on cardiorespiratory, perceptual, and enjoyment responses among trained young men.
Methods
Sixteen men experienced with HIRT underwent cardiopulmonary exercise testing and were familiarized with the exercises and HIRT protocol. On the subsequent three visits, interspaced 48–72 h, participants performed HIRT sessions with different rest intervals in a randomized order: 10 s and 30 s fixed rest intervals (FRI-10 and FRI-30), and self-selected rest interval (SSRI). Oxygen uptake (VO2), heart rate (HR), and recovery perception (Total Quality Recovery Scale) were measured during HIRT, while enjoyment responses (Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale) were assessed immediately after the sessions.
Results
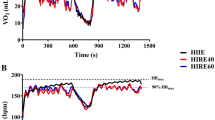
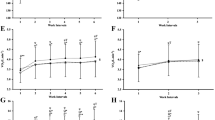
The VO2 during exercise was greater in FRI-10 than FRI-30 (55% VO2max and 47% VO2max, respectively, p = 0.01), while no difference occurred between SSRI and bouts performed with fixed intervals (52% VO2max vs. FRI, p > 0.05). HR, excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), recovery perception, and enjoyment responses were similar across conditions (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
Exercise intensity was not affected by the rest interval strategy. High exercise intensity was maintained in sessions performed with FRI or SSRI, without negative repercussions on the duration of training sessions and enjoyment responses after exercise sessions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data from this study are not publicly available but some data might be available upon reasonable request made to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- ACSM:
-
American College of Sports Medicine
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CPET:
-
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- EPOC:
-
Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption
- FRI:
-
Fixed rest interval
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HIIT:
-
High-intensity interval training
- HRmax :
-
Maximum HR
- VO2peak :
-
Maximum oxygen uptake
- MICT:
-
Moderate-intensity continuous training
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen uptake
- PACES:
-
Physical activity enjoyment scale
- SSRI:
-
Self-selected rest intervals
- TQR:
-
Total Quality Recovery Scale
References
American College of Sports Medicine (2018) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, Tenth. Wolters Kluwer Health, Philadelphia
Bornath DPD, Kenno KA (2022) Physiological responses to increasing battling rope weight during two 3-week high-intensity interval training programs. J Strength Cond Res 36:352–358. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000003470
Bouaziz W, Malgoyre A, Schmitt E et al (2020) Effect of high-intensity interval training and continuous endurance training on peak oxygen uptake among seniors aged 65 or older: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Clin Pract 74:e13490. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.13490
Buckley S, Knapp K, Lackie A et al (2015) Multimodal high-intensity interval training increases muscle function and metabolic performance in females. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 40:1157–1162. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2015-0238
Compher C, Frankenfield D, Keim N, Roth-Yousey L (2006) Best practice methods to apply to measurement of resting metabolic rate in adults: a systematic review. J Am Diet Assoc 106:881–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2006.02.009
Cunha FA, Midgley AW, Monteiro W et al (2013) How long does it take to achieve steady state for an accurate assessment of resting VO2 in healthy men? Eur J Appl Physiol 113:1441–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2571-x
Fidalgo A, Joi S, Lattari E et al (2022) Influence of HIIRT with fixed and self-selected recovery intervals on physiological, affective, and enjoyment responses. Res Q Exerc Sport. https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.2022.2042463
García-Hermoso A, Cerrillo-Urbina AJ, Herrera-Valenzuela T et al (2016) Is high-intensity interval training more effective on improving cardiometabolic risk and aerobic capacity than other forms of exercise in overweight and obese youth? A meta-analysis. Obes Rev 17:531–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12395
Heisz JJ, Tejada MG, Paolucci EM, Muir C (2016) Enjoyment for high-intensity interval exercise increases during the first six weeks of training: implications for promoting exercise adherence in sedentary adults. PLoS ONE 11:e0168534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168534
Hendker A, Eils E (2021) A group-based 8-week functional interval-type outdoor training program improves physical performance in recreationally active adults. Front Sport Act Living 3:627853. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspor.2021.627853
Howley ET, Bassett DR, Welch HG (1995) Criteria for maximal oxygen uptake: review and commentary. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:1292–1301
Kendzierski D, DeCarlo KJ (1991) Physical activity enjoyment scale: two validation studies. J Sport Exerc Psychol 13:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.13.1.50
Kenttä G, Hassmén P (1998) Overtraining and recovery. Sports Med 26:1–16. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199826010-00001
Laursen P, Buchheit M (2019) Science and application of high-intensity interval training: solutions to the programming puzzle. Human Kinetics, Cham
Lu Y, Wiltshire HD, Baker JS et al (2023) The effect of Tabata-style functional high-intensity interval training on cardiometabolic health and physical activity in female university students. Front Physiol 14:264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1095315
MacInnis MJ, Gibala MJ (2017) Physiological adaptations to interval training and the role of exercise intensity. J Physiol 595:2915–2930. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp273196
Mann T, Lamberts RP, Lambert MI (2013) Methods of prescribing relative exercise intensity: physiological and practical considerations. Sports Med 43:613–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0045-x
Matthews CE, Heil DP, Freedson PS, Pastides H (1999) Classification of cardiorespiratory fitness without exercise testing. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:486–493. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-199903000-00019
McEwan G, Arthur R, Phillips SM et al (2018) Interval running with self-selected recovery: physiology, performance, and perception. Eur J Sport Sci 18:1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2018.1472811
McRae G, Payne A, Zelt JG et al (2012) Extremely low volume, whole-body aerobic-resistance training improves aerobic fitness and muscular endurance in females. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37:1124–1131. https://doi.org/10.1139/h2012-093
Milanović Z, Sporiš G, Weston M (2015) Effectiveness of high-intensity interval training (HIT) and continuous endurance training for VO2max improvements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. Sport Med 45:1469–1481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-015-0365-0
Myers TR, Schneider MG, Schmale MS, Hazell TJ (2015) Whole-body aerobic resistance training circuit improves aerobic fitness and muscle strength in sedentary young females. J Strength Cond Res 29:1592–1600. https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000790
Nuñez TP, Amorim FT, Beltz NM et al (2020) Metabolic effects of two high-intensity circuit training protocols: Does sequence matter? J Exerc Sci Fit 18:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesf.2019.08.001
Ozaki H, Loenneke JP, Thiebaud RS, Abe T (2013) Resistance training induced increase in VO2max in young and older subjects. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act 10:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11556-013-0120-1
Schoenmakers PPJM, Reed KE (2019) The effects of recovery duration on physiological and perceptual responses of trained runners during four self-paced HIIT sessions. J Sci Med Sport 22:462–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2018.09.230
Seiler S, Hetlelid KJ (2005) The impact of rest duration on work intensity and RPE during interval training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:1601–1607. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000177560.18014.d8
Shi Q, Tong TK, Sun S et al (2018) Influence of recovery duration during 6-s sprint interval exercise on time spent at high rates of oxygen uptake. J Exerc Sci Fit 16:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesf.2018.01.001
Smilios I, Myrkos A, Zafeiridis A et al (2018) The effects of recovery duration during high-intensity interval exercise on time spent at high rates of oxygen consumption, oxygen kinetics, and blood lactate. J Strength Cond Res 32:2183–2189. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001904
Sousa FAB, Vasque RE, Gobatto CA (2017) Anaerobic metabolism during short all-out efforts in tethered running: comparison of energy expenditure and mechanical parameters between different sprint durations for testing. PLoS ONE 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179378
Sperlich B, Wallmann-Sperlich B, Zinner C et al (2017) Functional high-intensity circuit training improves body composition, peak oxygen uptake, strength, and alters certain dimensions of quality of life in overweight women. Front Physiol 8:172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00172
Sultana RN, Sabag A, Keating SE, Johnson NA (2019) The effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med 49:1687–1721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-019-01167-w
Tabata I, Nishimura K, Kouzaki M et al (1996) Effects of moderate-intensity endurance and high-intensity intermittent training on anaerobic capacity and VO2 max. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:1327–1330. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-199610000-00018
Thum JS, Parsons G, Whittle T, Astorino TA (2017) High-intensity interval training elicits higher enjoyment than moderate intensity continuous exercise. PLoS ONE 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166299
Warr-di Piero D, Valverde-Esteve T, Redondo-Castán JC et al (2018) Effects of work-interval duration and sport specificity on blood lactate concentration, heart rate and perceptual responses during high intensity interval training. PLoS ONE 13:e0200690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200690
Weir JBdV (1949) New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 109:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AF and WM were involved in the conception and design of the research; AF, RP, GMR, and LMS collected the data; PF, BRRO, and WM analyzed the data; AF, PF, and WM drafted the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript and approved its submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Research Ethics Committee of Salgado de Oliveira University (CAAE: 08275619.6.0000.5289).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by William J. Kraemer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fidalgo, A., Farinatti, P., Matos-Santos, L. et al. Self-selected or fixed: is there an optimal rest interval for controlling intensity in high-intensity interval resistance training?. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 2307–2316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05246-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05246-9