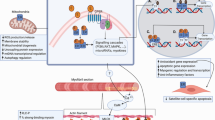
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effects of resistance training with or without transdermal estrogen therapy (ET) on satellite cell (SC) number and molecular markers for muscle hypertrophy in early postmenopausal women.
Methods
Using a double-blinded randomized controlled design, we allocated healthy, untrained postmenopausal women to perform 12 weeks of resistance training with placebo (PLC, n = 16) or ET (n = 15). Muscle biopsies obtained before and after the intervention, and two hours after the last training session were analyzed for fiber type, SC number and molecular markers for muscle hypertrophy and degradation (real-time PCR, western blotting).
Results
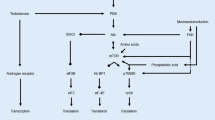
The analysis of SCs per Type I fiber showed a time x treatment interaction caused by a 47% decrease in PLC, and a 26% increase after ET after the training period. Also, SCs per Type II fiber area was lower after the intervention driven by a 57% decrease in PLC. Most molecular markers changed similarly in the two groups.
Conclusion
A decline in SC per muscle fiber was observed after the 12-week training period in postmenopausal women, which was counteracted when combined with use of transdermal ET.
Clinical trial registration number
nct03020953.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PLC:
-
Placebo
- ET:
-
Estrogen therapy
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- SC:
-
Satellite cell
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
References
Adams GR (2006) Satellite cell proliferation and skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 31(6):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1139/h06-053
Baltgalvis KA, Greising SM, Warren GL, Lowe DA (2010) Estrogen regulates estrogen receptors and antioxidant gene expression in mouse skeletal muscle. PLoS One 5(4):e10164. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010164
Bamman MM, Hill VJ, Adams GR, Haddad F, Wetzstein CJ, Gower BA, Ahmed A, Hunter GR (2003) Gender differences in resistance-training-induced myofiber hypertrophy among older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 58(2):108–116. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/58.2.b108
Bea JW, Zhao Q, Cauley JA, LaCroix AZ, Bassford T, Lewis CE, Jackson RD, Tylavsky FA, Chen Z (2011) Effect of hormone therapy on lean body mass, falls, and fractures: 6-year results from the Women’s Health Initiative hormone trials. Menopause (new York, NY) 18(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e3181e3aab1
Brzycki M (1993) Strength testing—predicting a one-rep max from reps-to-fatigue. J Phys Educ Recreat Dance 64:88–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/07303084.1993.10606684
Caldow MK, Thomas EE, Dale MJ, Tomkinson GR, Buckley JD, Cameron-Smith D (2015) Early myogenic responses to acute exercise before and after resistance training in young men. Physiol Reports. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12511
Collins BC, Arpke RW, Larson AA, Baumann CW, Xie N, Cabelka CA, Nash NL, Juppi HK, Laakkonen EK, Sipila S, Kovanen V, Spangenburg EE, Kyba M, Lowe DA (2019) Estrogen regulates the satellite cell compartment in females. Cell Rep 28(2):368-381.e366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.025
Dalgaard LB, Dalgas U, Andersen JL, Rossen NB, Moller AB, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Jorgensen JO, Kovanen V, Couppe C, Langberg H, Kjaer M, Hansen M (2019) Influence of oral contraceptive use on adaptations to resistance training. Front Physiol 10:824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00824
Dam TV, Dalgaard LB, Ringgaard S, Johansen FT, Bisgaard Bengtsen M, Mose M, Lauritsen KM, Ørtenblad N, Gravholt CH, Hansen M (2020) Transdermal estrogen therapy improves gains in skeletal muscle mass after 12 weeks of resistance training in early postmenopausal women. Front Physiol 11:596130. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.596130
Dam TV, Dalgaard LB, Thomsen CB, Hjortebjerg R, Ringgaard S, Johansen FT, Bengtsen MB, Mose M, Lauritsen KM, Søndergaard E, Gravholt CH, Hansen M (2021) Estrogen modulates metabolic risk profile after resistance training in early postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Menopause (new York, NY) 28(11):1214–1224. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0000000000001841
Dieli-Conwright CM, Spektor TM, Rice JC, Sattler FR, Schroeder ET (2009) Hormone therapy attenuates exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage in postmenopausal women. J Appl Physiol (1985) 107(3):853–858. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00404.2009
Dieli-Conwright CM, Spektor TM, Rice JC, Sattler FR, Schroeder ET (2010) Hormone replacement therapy and messenger RNA expression of estrogen receptor coregulators after exercise in postmenopausal women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(3):422–429. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181b7193f
Dieli-Conwright CM, Spektor TM, Rice JC, Sattler FR, Schroeder ET (2012) Hormone therapy and maximal eccentric exercise alters myostatin-related gene expression in postmenopausal women. J Strength Cond Res 26(5):1374–1382. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e318251083f
Doessing S, Holm L, Heinemeier KM, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Schjerling P, Qvortrup K, Larsen JO, Nielsen RH, Flyvbjerg A, Kjaer M (2010) GH and IGF1 levels are positively associated with musculotendinous collagen expression: experiments in acromegalic and GH deficiency patients. Eur J Endocrinol 163(6):853–862. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-10-0818
Dreyer HC, Blanco CE, Sattler FR, Schroeder ET, Wiswell RA (2006) Satellite cell numbers in young and older men 24 hours after eccentric exercise. Muscle Nerve 33(2):242–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20461
Edström E, Ulfhake B (2005) Sarcopenia is not due to lack of regenerative drive in senescent skeletal muscle. Aging Cell 4(2):65–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9728.2005.00145.x
Enns DL, Iqbal S, Tiidus PM (2008) Oestrogen receptors mediate oestrogen-induced increases in post-exercise rat skeletal muscle satellite cells. Acta Physiol (oxf) 194(1):81–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2008.01861.x
Epplein M, Reed SD, Voigt LF, Newton KM, Holt VL, Weiss NS (2008) Risk of complex and atypical endometrial hyperplasia in relation to anthropometric measures and reproductive history. Am J Epidemiol 168(6):563–576. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwn168
Evans W (1997) Functional and metabolic consequences of sarcopenia. J Nutr 127(5l):998s–1003s. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/127.5.998S
Fry CS, Lee JD, Jackson JR, Kirby TJ, Stasko SA, Liu H, Dupont-Versteegden EE, McCarthy JJ, Peterson CA (2014) Regulation of the muscle fiber microenvironment by activated satellite cells during hypertrophy. FASEB J 28(4):1654–1665. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-239426
Gallagher D, Visser M, De Meersman RE, Sepúlveda D, Baumgartner RN, Pierson RN, Harris T, Heymsfield SB (1997) Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: effects of age, gender, and ethnicity. J Appl Physiol (1985) 83(1):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1997.83.1.229
Hansen M, Skovgaard D, Reitelseder S, Holm L, Langbjerg H, Kjaer M (2012) Effects of estrogen replacement and lower androgen status on skeletal muscle collagen and myofibrillar protein synthesis in postmenopausal women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67(10):1005–1013. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls007
Harlow SD, Gass M, Hall JE, Lobo R, Maki P, Rebar RW, Sherman S, Sluss PM, de Villiers TJ, GroupSC (2012) Executive summary of the Stages of Reproductive Aging Workshop + 10: addressing the unfinished agenda of staging reproductive aging. Menopause (new York, NY) 19(4):387–395. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e31824d8f40
Herman-Montemayor JR, Hikida RS, Staron RS (2015) Early-phase satellite cell and myonuclear domain adaptations to slow-speed vs. traditional resistance training programs. J Strength Condition Res 29(11):3105–3114. https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000925
Hiller-Sturmhöfel S, Bartke A (1998) The endocrine system: an overview. Alcohol Health Res World 22(3):153–164
Hulmi JJ, Kovanen V, Selänne H, Kraemer WJ, Häkkinen K, Mero AA (2009) Acute and long-term effects of resistance exercise with or without protein ingestion on muscle hypertrophy and gene expression. Amino Acids 37(2):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0150-6
Juppi HK, Sipilä S, Cronin NJ, Karvinen S, Karppinen JE, Tammelin TH, Aukee P, Kovanen V, Kujala UM, Laakkonen EK (2020) Role of menopausal transition and physical activity in loss of lean and muscle mass: a follow-up study in middle-aged finish women. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051588
Kadi F, Charifi N, Denis C, Lexell J (2004a) Satellite cells and myonuclei in young and elderly women and men. Muscle Nerve 29(1):120–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.10510
Kadi F, Schjerling P, Andersen LL, Charifi N, Madsen JL, Christensen LR, Andersen JL (2004b) The effects of heavy resistance training and detraining on satellite cells in human skeletal muscles. J Physiol 558(Pt 3):1005–1012. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.065904
Kamanga-Sollo E, Thornton KJ, White ME, Dayton WR (2017) Role of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-1 in estradiol 17beta-induced alterations in protein synthesis and protein degradation rates in fused bovine satellite cell cultures. Domest Anim Endocrinol 58:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2016.09.002
Kamei Y, Miura S, Suzuki M, Kai Y, Mizukami J, Taniguchi T, Mochida K, Hata T, Matsuda J, Aburatani H, Nishino I, Ezaki O (2004) Skeletal muscle FOXO1 (FKHR) transgenic mice have less skeletal muscle mass, down-regulated Type I (slow twitch/red muscle) fiber genes, and impaired glycemic control. J Biol Chem 279(39):41114–41123. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M400674200
Kim JS, Kosek DJ, Petrella JK, Cross JM, Bamman MM (2005) Resting and load-induced levels of myogenic gene transcripts differ between older adults with demonstrable sarcopenia and young men and women. J Appl Physiol (1985) 99(6):2149–2158. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00513.2005
Kosek DJ, Kim JS, Petrella JK, Cross JM, Bamman MM (2006) Efficacy of 3 days/wk resistance training on myofiber hypertrophy and myogenic mechanisms in young vs. older adults. J Appl Physiol (1985) 101(2):531–544. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01474.2005
Larson AA, Baumann CW, Kyba M, Lowe DA (2020) Oestradiol affects skeletal muscle mass, strength and satellite cells following repeated injuries. Exp Physiol 105(10):1700–1707. https://doi.org/10.1113/ep088827
Léger B, Cartoni R, Praz M, Lamon S, Dériaz O, Crettenand A, Gobelet C, Rohmer P, Konzelmann M, Luthi F, Russell AP (2006) Akt signalling through GSK-3beta, mTOR and Foxo1 is involved in human skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. J Physiol 576(Pt 3):923–933. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116715
Lindle RS, Metter EJ, Lynch NA, Fleg JL, Fozard JL, Tobin J, Roy TA, Hurley BF (1997) Age and gender comparisons of muscle strength in 654 women and men aged 20–93 year. J Appl Physiol (bethesda, Md: 1985) 83(5):1581–1587. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1997.83.5.1581
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(− δδC(T)) method. Methods (san Diego, Calif) 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mackey AL, Esmarck B, Kadi F, Koskinen SO, Kongsgaard M, Sylvestersen A, Hansen JJ, Larsen G, Kjaer M (2007) Enhanced satellite cell proliferation with resistance training in elderly men and women. Scand J Med Sci Sports 17(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2006.00534.x
Mangan G, Iqbal S, Hubbard A, Hamilton V, Bombardier E, Tiidus PM (2015) Delay in post-ovariectomy estrogen replacement negates estrogen-induced augmentation of post-exercise muscle satellite cell proliferation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 93(11):945–951. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2015-0106
Moran AL, Nelson SA, Landisch RM, Warren GL, Lowe DA (2007) Estradiol replacement reverses ovariectomy-induced muscle contractile and myosin dysfunction in mature female mice. J Appl Physiol (1985) 102(4):1387–1393. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01305.2006
Murach KA, Fry CS, Kirby TJ, Jackson JR, Lee JD, White SH, Dupont-Versteegden EE, McCarthy JJ, Peterson CA (2018) Starring or supporting role? Satellite cells and skeletal muscle fiber size regulation. Physiology 33(1):26–38. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00019.2017
Oikawa SY, Holloway TM, Phillips SM (2019) The impact of step reduction on muscle health in aging: protein and exercise as countermeasures. Front Nutr 6:75. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00075
Oxfeldt M, Dalgaard LB, Risikesan J, Johansen FT, Hansen M (2020) Influence of fermented red clover extract on skeletal muscle in early postmenopausal women: a double-blinded cross-over study. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113587
Park YM, Pereira RI, Erickson CB, Swibas TA, Kang C, Van Pelt RE (2017) Time since menopause and skeletal muscle estrogen receptors, PGC-1alpha, and AMPK. Menopause (new York, NY) 24(7):815–823. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0000000000000829
Park YM, Jankowski CM, Ozemek C, Hildreth KL, Kohrt WM, Moreau KL (2020) Appendicular lean mass is lower in late compared with early perimenopausal women: potential role of FSH. J Appl Physiol (1985) 128(5):1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00315.2019
Petrella JK, Kim JS, Cross JM, Kosek DJ, Bamman MM (2006) Efficacy of myonuclear addition may explain differential myofiber growth among resistance-trained young and older men and women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291(5):E937-946. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00190.2006
Porter MM, Vandervoort AA, Lexell J (1995) Aging of human muscle: structure, function and adaptability. Scand J Med Sci Sports 5(3):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.1995.tb00026.x
Raguso CA, Kyle U, Kossovsky MP, Roynette C, Paoloni-Giacobino A, Hans D, Genton L, Pichard C (2006) A 3-year longitudinal study on body composition changes in the elderly: role of physical exercise. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh, Scotland) 25(4):573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2005.10.013
Ratamess NA, Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Maresh CM, Vanheest JL, Sharman MJ, Rubin MR, French DN, Vescovi JD, Silvestre R, Hatfield DL, Fleck SJ, Deschenes MR (2005) Androgen receptor content following heavy resistance exercise in men. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 93(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.10.019
Raue U, Slivka D, Jemiolo B, Hollon C, Trappe S (2006) Myogenic gene expression at rest and after a bout of resistance exercise in young (18–30 yr) and old (80–89 yr) women. J Appl Physiol (1985) 101(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01616.2005
Roth SM, Martel GF, Ivey FM, Lemmer JT, Tracy BL, Metter EJ, Hurley BF, Rogers MA (2001) Skeletal muscle satellite cell characteristics in young and older men and women after heavy resistance strength training. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56(6):B240-247. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/56.6.b240
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C, Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH, Goldberg AL (2004) Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 117(3):399–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00400-3
Sandri M, Lin J, Handschin C, Yang W, Arany ZP, Lecker SH, Goldberg AL, Spiegelman BM (2006) PGC-1alpha protects skeletal muscle from atrophy by suppressing FoxO3 action and atrophy-specific gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(44):16260–16265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607795103
Sieljacks P, Wang J, Groennebaek T, Rindom E, Jakobsgaard JE, Herskind J, Gravholt A, Moller AB, Musci RV, de Paoli FV, Hamilton KL, Miller BF, Vissing K (2019) Six weeks of low-load blood flow restricted and high-load resistance exercise training produce similar increases in cumulative myofibrillar protein synthesis and ribosomal biogenesis in healthy males. Front Physiol 10:649. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00649
Singh MA, Ding W, Manfredi TJ, Solares GS, O’Neill EF, Clements KM, Ryan ND, Kehayias JJ, Fielding RA, Evans WJ (1999) Insulin-like growth factor I in skeletal muscle after weight-lifting exercise in frail elders. Am J Physiol 277(1):E135-143. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1999.277.1.E135
Smith LR, Barton ER (2014) SMASH - semi-automatic muscle analysis using segmentation of histology: a MATLAB application. Skeletal Muscle 4:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/2044-5040-4-21
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F, Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2004) The IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription factors. Mol Cell 14(3):395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00211-4
Tiidus PM (2000) Estrogen and gender effects on muscle damage, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Can J Appl Physiol 25(4):274–287. https://doi.org/10.1139/h00-022
Tiidus PM (2005) Can oestrogen influence skeletal muscle damage, inflammation, and repair? Br J Sports Med 39(5):251–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2005.016881
Tiidus PM, Holden D, Bombardier E, Zajchowski S, Enns D, Belcastro A (2001) Estrogen effect on post-exercise skeletal muscle neutrophil infiltration and calpain activity. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 79(5):400–406
Verdijk LB, Koopman R, Schaart G, Meijer K, Savelberg HH, van Loon LJ (2007) Satellite cell content is specifically reduced in type II skeletal muscle fibers in the elderly. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292(1):E151-157. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00278.2006
Verdijk LB, Gleeson BG, Jonkers RA, Meijer K, Savelberg HH, Dendale P, van Loon LJ (2009a) Skeletal muscle hypertrophy following resistance training is accompanied by a fiber type-specific increase in satellite cell content in elderly men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(3):332–339. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gln050
Verdijk LB, Jonkers RA, Gleeson BG, Beelen M, Meijer K, Savelberg HH, Wodzig WK, Dendale P, van Loon LJ (2009b) Protein supplementation before and after exercise does not further augment skeletal muscle hypertrophy after resistance training in elderly men. Am J Clin Nutr 89(2):608–616. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.2662
Vitale G, Cesari M, Mari D (2016) Aging of the endocrine system and its potential impact on sarcopenia. Eur J Intern Med 35:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2016.07.017
Wiik A, Ekman M, Johansson O, Jansson E, Esbjornsson M (2009) Expression of both oestrogen receptor alpha and beta in human skeletal muscle tissue. Histochem Cell Biol 131(2):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0512-x
Yang Y, Creer A, Jemiolo B, Trappe S (2005) Time course of myogenic and metabolic gene expression in response to acute exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 98(5):1745–1752. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01185.2004
Zaldivar F, Wang-Rodriguez J, Nemet D, Schwindt C, Galassetti P, Mills PJ, Wilson LD, Cooper DM (2006) Constitutive pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine and growth factor response to exercise in leukocytes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 100(4):1124–1133. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00562.2005
Zammit PS, Partridge TA, Yablonka-Reuveni Z (2006) The skeletal muscle satellite cell: the stem cell that came in from the cold. J Histochem Cytochem 54(11):1177–1191. https://doi.org/10.1369/jhc.6R6995.2006
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants for their participation and devotion to this trial. We also thank the students involved in the execution of the intervention and the analysis (Line Noerregaard Olsen, Malene Andersen, Mathias Nordberg Jensen, Christian Bejlegaard Thomsen, Cecilie Jacobsen, Rikke Bach Nielsen, Caroline E. G. Frederiksen, Jens J. Frandsen, Lasse T. Taidal, Sara Malling Andersen and Francesca Alesci), and the laboratory technicians (Janni Mosgaard Jensen and Gitte Kaiser Hartvigsen) for their technical assistance during the experimental days and laboratory analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Augustinus Foundation (17-2075), Aarhus University Research Foundation (AUFF-E_2015_FLS-8-6), Hede Nielsen Foundation (unnumbered), A.P. Møller Foundation (17-L-0567), and Toyota Foundation, Denmark (KJ/BG-9659 F).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TVD, CHG and MH conceived and designed the study. TVD, FTJ, MBB, MM, KML and MH carried out the experiments. TVD, LBD and MH analyzed the samples and data. TVD, LBD and MH interpreted the results of the experiments. TVD, LBD and MH prepared the figures. TVD, LBD and MH drafted the manuscript. TVD, LBD, FTJ, MBB, MM, KML, CHG and MH edited and revised the manuscript. TVD, LBD, FTJ, MBB, MM, KML, CHG and MH approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
All participants gave written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Central Denmark Region Committee on Health Research Ethics approved the protocol (Journal No.: 1-10-72-234-16).
Additional information
Communicated by Kirsty Elliott-Sale.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dam, T.V., Dalgaard, L.B., Johansen, F.T. et al. Effects of transdermal estrogen therapy on satellite cell number and molecular markers for muscle hypertrophy in response to resistance training in early postmenopausal women. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 667–681 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05093-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05093-0