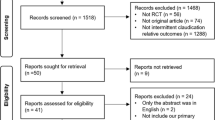
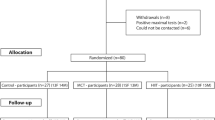
Abstract
Purpose
Investigate whether a single bout of mixed circuit training (MCT) can elicit changes in arterial stiffness in patients with chronic stroke. Second, to assess the between-day reproducibility of post-MCT arterial stiffness measurements.
Methods
Seven participants (58 ± 12 years) performed a non-exercise control session (CTL) and two bouts of MCT on separate days in a randomized counterbalanced order. The MCT involved 3 sets of 15 repetition maximum for 10 exercises, with each set separated by 45-s of walking. Brachial-radial pulse wave velocity (br-PWV), radial artery compliance (AC) and reflection index (RI1,2) were assessed 10 min before and 60 min after CTL and MCT. Ambulatory arterial stiffness index (AASI) was calculated from 24-h recovery ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Results
Compared to CTL, after 60 min of recovery from the 1st and 2nd bouts of MCT, lower values were observed for br-PWV (mean diff = − 3.9 and − 3.7 m/s, respectively, P < 0.01; ICC2,1 = 0.75) and RI1,2 (mean diff = − 16.1 and − 16.0%, respectively, P < 0.05; ICC2,1 = 0.83) concomitant with higher AC (mean diff = 1.2 and 1.0 × 10–6 cm5/dyna, respectively, P < 0.01; ICC2,1 = 0.40). The 24-h AASI was reduced after bouts of MCT vs. CTL (1st and 2nd bouts of MCT vs. CTL: mean diff = − 0.32 and − 0.29 units, respectively, P < 0.001; ICC2,1 = 0.64).
Conclusion
A single bout of MCT reduces arterial stiffness during laboratory (60 min) and ambulatory (24 h) recovery phases in patients with chronic stroke with moderate-to-high reproducibility.
Trial registration: Ensaiosclinicos.gov.br identifier RBR-5dn5zd.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AASI:
-
Ambulatory arterial stiffness index
- AC:
-
Arterial compliance
- AIx:
-
Augmentation index
- AIx@75:
-
Heart rate-corrected augmentation index
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- br-PWV:
-
Brachial-radial pulse wave velocity
- CTL:
-
Non-exercise control session
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- MCT:
-
Mixed circuit training
- RI1,2 :
-
Reflection index
- RPE:
-
Rating of perceived exertion
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen uptake
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen uptake
- %VO2R:
-
Percentage of oxygen uptake reserve
- WRmax :
-
Maximal work rate
References
Ashor AW, Lara J, Siervo M, Celis-Morales C, Mathers JC (2014) Effects of exercise modalities on arterial stiffness and wave reflection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 9(10):e110034. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110034
Bernardes WL, Montenegro RA, Monteiro WD, de Almeida FR, Massaferri R, Farinatti P (2018) Optimizing a treadmill ramp protocol to evaluate aerobic capacity of hemiparetic post-stroke patients. J Strength Cond Res 32(3):876–884. https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000002297
Billinger SA, Arena R, Bernhardt J, Eng JJ, Franklin BA, Johnson CM, MacKay-Lyons M, Macko RF, Mead GE, Roth EJ, Shaughnessy M, Tang A (2014) Physical activity and exercise recommendations for stroke survivors: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 45(8):2532–2553. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000022
Boesby L, Thijs L, Elung-Jensen T, Strandgaard S, Kamper AL (2012) Ambulatory arterial stiffness index in chronic kidney disease stage 2–5. Reproducibility and relationship with pulse wave parameters and kidney function. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 72(4):304–312. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365513.2012.682164
Cavalcante JL, Lima JAC, Redheuil A, Al-Mallah MH (2011) Aortic stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol 57(14):1511–1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.017
Chen Y, Shen F, Liu J, Yang GY (2017) Arterial stiffness and stroke: de-stiffening strategy, a therapeutic target for stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2(2):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2016-000045
Cheung YF (2010) Arterial stiffness in the young: assessment, determinants, and implications. Korean Circ J 40(4):153–162. https://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2010.40.4.153
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, Pratt M, Ekelund U, Yngve A, Sallis JF, Oja P (2003) International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1381–1395. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.Mss.0000078924.61453.Fb
Cunha FA, Midgley AW, Monteiro W, Freire R, Lima T, Farinatti PT (2013) How long does it take to achieve steady state for an accurate assessment of resting VO2 in healthy men? Eur J Appl Physiol 113(6):1441–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2571-x
Dechering DG, van der Steen MS, Adiyaman A, Thijs L, Deinum J, Li Y, Dolan E, Akkermans RP, Richart T, Hansen TW, Kikuya M, Wang J, O’Brien E, Thien T, Staessen JA (2008) Reproducibility of the ambulatory arterial stiffness index in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 26(10):1993–2000. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e328309ee4c
Dias-Santos EG, Farah BQ, Germano-Soares AH, Correia MA, Souza AA, Hora JEJ, Ritti-Dias RM, Andrade-Lima A (2021) Effects of exercise mode on arterial stiffness in symptomatic peripheral artery disease patients: a randomized crossover clinical trial. Ann Vasc Surg 74:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2020.12.049
Dolan E, Li Y, Thijs L, McCormack P, Staessen JA, O’Brien E, Stanton A (2006a) Ambulatory arterial stiffness index: rationale and methodology. Blood Press Monit 11(2):103–105. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mbp.0000200478.19046.dd
Dolan E, Thijs L, Li Y, Atkins N, McCormack P, McClory S, O’Brien E, Staessen JA, Stanton AV (2006b) Ambulatory arterial stiffness index as a predictor of cardiovascular mortality in the Dublin Outcome Study. Hypertension 47(3):365–370. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000200699.74641.c5
Ferreira AS, Santos MA, Barbosa Filho J, Cordovil I, Souza MN (2004) Determination of radial artery compliance can increase the diagnostic power of pulse wave velocity measurement. Physiol Meas 25(1):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/25/1/004
Ferreira AS, Filho JB, Souza MN (2006) Simplified distributed-parameter model of brachial-radial arteries for noninvasive determination of mechanical characteristics of vessel. In: Conference proceedings: annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, vol 1, pp 1814–1817. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2006.26010
Fetics B, Nevo E, Chen CH, Kass DA (1999) Parametric model derivation of transfer function for noninvasive estimation of aortic pressure by radial tonometry. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46(6):698–706. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.764946
Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J (1998) Calibration of the computer science and applications. Inc Accelerometer Med Sci Sports Exerc 30(5):777–781
Gąsecki D, Rojek A, Kwarciany M, Kowalczyk K, Boutouyrie P, Nyka W, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K (2012) Pulse wave velocity is associated with early clinical outcome after ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis 225(2):348–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.024
Halliwill JR, Buck TM, Lacewell AN, Romero SA (2013) Postexercise hypotension and sustained postexercise vasodilatation: what happens after we exercise? Exp Physiol 98(1):7–18. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2011.058065
Joyner MJ (2000) Effect of exercise on arterial compliance. Circulation 102(11):1214–1215. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.11.1214
Jurik R, Żebrowska A, Stastny P (2021) Effect of an acute resistance training bout and long-term resistance training program on arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med 10(16):3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163492
Karamanoglu M, O’Rourke MF, Avolio AP, Kelly RP (1993) An analysis of the relationship between central aortic and peripheral upper limb pressure waves in man. Eur Heart J 14(2):160–167. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/14.2.160
Laugesen E, Hansen KW, Knudsen ST, Erlandsen M, Ebbehøj E, Poulsen PL (2010) Reproducibility of the ambulatory arterial stiffness index in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Blood Press Monit 15(1):18–22. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBP.0b013e32833531f9
Lee YH, Park SH, Yoon ES, Lee CD, Wee SO, Fernhall B, Jae SY (2015) Effects of combined aerobic and resistance exercise on central arterial stiffness and gait velocity in patients with chronic poststroke hemiparesis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 94(9):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1097/phm.0000000000000233
Lee JY, Kwon S, Kim WS, Hahn SJ, Park J, Paik NJ (2018) Feasibility, reliability, and validity of using accelerometers to measure physical activities of patients with stroke during inpatient rehabilitation. PLoS ONE 13(12):e0209607. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209607
Li Y, Wang JG, Dolan E, Gao PJ, Guo HF, Nawrot T, Stanton AV, Zhu DL, O’Brien E, Staessen JA (2006) Ambulatory arterial stiffness index derived from 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension 47(3):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000200695.34024.4c
Lim J, Pearman ME, Park W, Alkatan M, Machin DR, Tanaka H (2015) Impact of blood pressure perturbations on arterial stiffness. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 309(12):R1540–R1545. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00368.2015
Lopes S, Afreixo V, Teixeira M, Garcia C, Leitão C, Gouveia M, Figueiredo D, Alves AJ, Polonia J, Oliveira J, Mesquita-Bastos J, Ribeiro F (2020) Exercise training reduces arterial stiffness in adults with hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000002619
Maki T, Quagliato E, Cacho E, Paz L, Nascimento N, Inoue M, Viana M (2006) Estudo de confiabilidade da aplicação da escala de Fugl-Meyer no Brasil. Braz J Phys Ther 10(2):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-35552006000200007
Matsudo S, Araújo T, Matsudo V, Andrade D, Andrade E, Oliveira LC, Braggion G (2012) Questionário internacional de atividade física (IPAQ): estudo de validade e reprodutibilidade no Brasil. Rev Bras Ativ Fís Saúde 6(2):5–18. https://doi.org/10.12820/rbafs.v.6n2p5-18
Michaelides AP, Soulis D, Antoniades C, Antonopoulos AS, Miliou A, Ioakeimidis N, Chatzistamatiou E, Bakogiannis C, Marinou K, Liakos C, Stefanadis C (2011) Exercise duration as a determinant of vascular function and antioxidant balance in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart 97(10):832–837. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2010.209080
Midgley AW, Carroll S, Marchant D, McNaughton LR, Siegler J (2009) Evaluation of true maximal oxygen uptake based on a novel set of standardized criteria. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 34(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1139/H08-146
Mikael LR, Paiva AMG, Gomes MM, Sousa ALL, Jardim P, Vitorino PVO, Euzébio MB, Sousa WM, Barroso WKS (2017) Vascular aging and arterial stiffness. Arq Bras Cardiol 109(3):253–258. https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.20170091
Miyamoto ST, Lombardi Junior I, Berg KO, Ramos LR, Natour J (2004) Brazilian version of the Berg balance scale. Braz J Med Biol Res 37(9):1411–1421. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x2004000900017
Nichols WW, Denardo SJ, Wilkinson IB, McEniery CM, Cockcroft J, O’Rourke MF (2008) Effects of arterial stiffness, pulse wave velocity, and wave reflections on the central aortic pressure waveform. J Clin Hypertens (greenwich) 10(4):295–303
Noguchi KS, Moncion K, Wiley E, MacDonald MJ, Richardson J, Roig M, Tang A (2021) Prolonged elevation of arterial stiffness following peak aerobic exercise in individuals with chronic stroke. Front Physiol 12:666171. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.666171
Nottin S, Walther G, Vinet A, Dauzat M, Beck L, Messner-Pellenc P, Obert P (2006) Reproducibility of automated pulse wave velocity measurement during exercise. Running head: pulse wave velocity during exercise. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 99(6):564–568
O’Rourke MF, Staessen JA, Vlachopoulos C, Duprez D, GéE P (2002) Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am J Hypertens 15(5):426–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-7061(01)02319-6
O’Brien E, Coats A, Owens P, Petrie J, Padfield PL, Littler WA, de Swiet M, Mee F (2000) Use and interpretation of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: recommendations of the British hypertension society. BMJ 320(7242):1128–1134
Papaioannou TG, Protogerou AD, Stergiopulos N, Vardoulis O, Stefanadis C, Safar M, Blacher J (2014) Total arterial compliance estimated by a novel method and all-cause mortality in the elderly: the PROTEGER study. Age (dordr) 36(3):9661–9661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9661-0
Perissiou M, Bailey TG, Windsor M, Leicht AS, Golledge J, Askew CD (2019) Reliability of arterial stiffness indices at rest and following a single bout of moderate-intensity exercise in older adults. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 39(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12537
Pierce DR, Doma K, Leicht AS (2018) Acute effects of exercise mode on arterial stiffness and wave reflection in healthy young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Physiol 9:73. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00073
Riebe D, Ehrman JK, Liguori G, Magal M, Medicine ACoS (2018) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 10th edn. Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia
Saco-Ledo G, Valenzuela PL, Ramírez-Jiménez M, Morales JS, Castillo-García A, Blumenthal JA, Ruilope LM, Lucia A (2021) Acute aerobic exercise induces short-term reductions in ambulatory blood pressure in patients with hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 78(6):1844–1858. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.121.18099
Saeed S, Waje-Andreassen U, Fromm A, Øygarden H, Kokorina MV, Naess H, Gerdts E (2014) Early vascular aging in young and middle-aged ischemic stroke patients: the Norwegian Stroke in the Young Study. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112814. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112814
Sardeli AV, Gáspari AF, Chacon-Mikahil MP (2018) Acute, short-, and long-term effects of different types of exercise in central arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 58(6):923–932. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0022-4707.17.07486-2
Schillaci G, Pucci G, Mannarino MR, Pirro M, Parati G (2009) Determinants of the ambulatory arterial stiffness index regression line. Hypertension 53 (5):e33; author reply e34. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.109.130591
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D, the CG, (2010) CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Trials 11(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-11-32
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86(2):420–428
Takatori K, Matsumoto D, Okada Y, Nakamura J, Shomoto K (2012) Effect of intensive rehabilitation on physical function and arterial function in community-dwelling chronic stroke survivors. Top Stroke Rehabil 19(5):377–383. https://doi.org/10.1310/tsr1905-377
Tang A, Eng JJ, Krassioukov AV, Madden KM, Mohammadi A, Tsang MY, Tsang TS (2014) Exercise-induced changes in cardiovascular function after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Stroke 9(7):883–889. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijs.12156
Townsend RR, Wilkinson IB, Schiffrin EL, Avolio AP, Chirinos JA, Cockcroft JR, Heffernan KS, Lakatta EG, McEniery CM, Mitchell GF, Najjar SS, Nichols WW, Urbina EM, Weber T (2015) Recommendations for Improving and Standardizing Vascular Research on Arterial Stiffness: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 66(3):698–722. https://doi.org/10.1161/hyp.0000000000000033
Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo D, Serio A, D’Aguanno G, Pinto A, Licata G (2010) Arterial stiffness indexes in acute ischemic stroke: relationship with stroke subtype. Atherosclerosis 211(1):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.02.010
van Sloten TT, Sedaghat S, Laurent S, London GM, Pannier B, Ikram MA, Kavousi M, Mattace-Raso F, Franco OH, Boutouyrie P, Stehouwer CDA (2015) Carotid stiffness is associated with incident stroke: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 66(19):2116–2125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.888
Acknowledgements
We thank all our volunteers for their efforts in participating in this study. We also thank Paulo Couto for his excellent technical assistance with experiment procedures.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported by the Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for the Research Support in Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ, E-26/202.705/2019 and E-26/211.210/2021 [271104], recipient FAC; E-26/110.450/2012 recipient ASF), by the Brazilian Council for Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq, 403206/2021–9, recipient FAC), and by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES, Finance Code 001, recipient ASF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ACM and FAC were involved in the study conception, design and management, data interpretation and analysis, literature search, and drafting of the manuscript. ACM, GFF and VABC were involved in the recruitment of participants, data collection, and manuscript preparation. ASF, AWM, NSLS, JB, and SB provided considerable intellectual input in the writing of the manuscript. FAC was the principal investigator supervising all the experimental procedures and the manuscript preparation, as well as lab resources and financial support for the project. All authors read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest that relates to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Fischetti.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Michalski, A.C., Ferreira, A.S., Midgley, A.W. et al. Mixed circuit training acutely reduces arterial stiffness in patients with chronic stroke: a crossover randomized controlled trial. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 121–134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05061-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05061-8