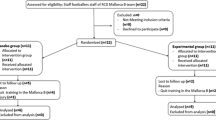
Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the effect of the racemic β-hydroxybutyrate precursor, R,S-1,3-butanediol (BD), on T-cell-related cytokine gene expression within stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) following prolonged, strenuous exercise.
Methods
A repeated-measures, randomised, crossover study was conducted in nine healthy, trained male cyclists (age, 26.7 ± 5.2 years; VO2peak, 63.9 ± 2.5 mL kg−1 min−1). Participants ingested 0.35 g kg−1 of BD or placebo 30 min before and 60 min during 85 min of steady-state (SS) exercise, which preceded a ~ 30 min time-trial (TT) (7 kJ kg−1). Blood samples were collected at pre-supplement, pre-exercise, post-SS, post-TT and 1-h post-TT. Whole blood cultures were stimulated with Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) for 24 h to determine T-cell-related interleukin (IL)-4, IL-10 and interferon (IFN)-γ mRNA expression within isolated PBMCs in vitro.
Results
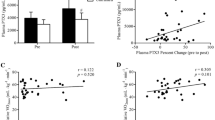
Serum cortisol, total circulating leukocyte and lymphocyte, and T-cell subset concentrations were similar between trials during exercise and recovery (all p > 0.05). BD ingestion increased T-cell-related IFN-γ mRNA expression compared with placebo throughout exercise and recovery (p = 0.011); however, IL-4 and IL-10 mRNA expression and the IFN-γ/IL-4 mRNA expression ratio were unaltered (all p > 0.05).
Conclusion
Acute hyperketonaemia appears to transiently amplify the initiation of the pro-inflammatory T-cell-related IFN-γ response to an immune challenge in vitro during and following prolonged, strenuous exercise; suggesting enhanced type-1 T-cell immunity at the gene level.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AcAc:
-
Acetoacetate
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- β2-MG:
-
β2-Microglobulin
- BD:
-
R,S-1,3-Butanediol
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- cDNA:
-
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- D-βHB:
-
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate
- ES:
-
Effect size
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- K2EDTA:
-
Dipotassium ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid
- KB:
-
Ketone body
- kJ:
-
Kilojoules
- mRNA:
-
Messenger ribonucleic acid
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PLA:
-
Placebo
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
- SEB:
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B
- SS:
-
Steady-state
- T-cell:
-
T-lymphocyte
- TT:
-
Time-trial
- URTS:
-
Upper respiratory tract symptom
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen uptake
- VO2peak :
-
Peak oxygen uptake
- VT2 :
-
Second ventilatory threshold
- W max :
-
Maximal wattage
References
Agarwal SK, Marshall GD (1998) Glucocorticoid-induced type 1/type 2 cytokine alterations in humans: a model for stress-related immune dysfunction. J Interf Cytokine Res 18:1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.1998.18.1059
Ardawi MSM, Newsholme EA (1984) Metabolism of ketone bodies, oleate and glucose in lymphocytes of the rat. Biochem J 221:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2210255
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ (1986) A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 60:2020–2027
Bermon S, Castell LM, Calder PC et al (2017) Consensus statement: immunonutrition and exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev 23:8–50
Bishop NC, Walker GJ, Bowley LA et al (2005) Lymphocyte responses to influenza and tetanus toxoid in vitro following intensive exercise and carbohydrate ingestion on consecutive days. J Appl Physiol 99:1327–1335. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00038.2005
Boeuf P, Vigan-Womas I, Jublot D et al (2005) CyProQuant-PCR: a real time RT-PCR technique for profiling human cytokines, based on external RNA standards, readily automatable for clinical use. BMC Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2172-6-5
Campbell JP, Riddell NE, Burns VE et al (2009) Acute exercise mobilises CD8+ T lymphocytes exhibiting an effector-memory phenotype. Brain Behav Immun 23:767–775
Choi YW, Kotzin B, Herron L et al (1989) Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin “superantigens” with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:8941–8945. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941
Clifford T, Wood MJ, Stocks P et al (2017) T-regulatory cells exhibit a biphasic response to prolonged endurance exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:1727–1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3667-0
Cox PJ, Kirk T, Ashmore T et al (2016) Nutritional ketosis alters fuel preference and thereby endurance performance in athletes. Cell Metab 24:256–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.07.010
Curi R, Williams JF, Newsholme EA (1989) Formation of ketone-bodies by resting lymphocytes. Int J Biochem 21:1133–1136
Davison G, Kehaya C, Diment BC, Walsh NP (2015) Carbohydrate supplementation does not blunt the prolonged exercise-induced reduction of in vivo immunity. Eur J Nutr 55:1583–1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0977-z
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Diment BC, Fortes MB, Edwards JP et al (2015) Exercise intensity and duration effects on in vivo immunity. Med Sci Sport Exerc 47:1390–1398. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000562
Elenkov IJ (2004) Glucocorticoids and the Th1/Th2 balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1024:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1321.010/full
Evans M, Egan B (2018) Intermittent running and cognitive performance after ketone ester ingestion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 50:2330–2338. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001700
Evans M, McSwiney FT, Brady AJ, Egan B (2019) No benefit of ingestion of a ketone monoester supplement on 10-km running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002065
Fabbri M (2003) T lymphocytes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:1004–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(03)00037-2
Fox CJ, Hammerman PS, Thompson CB (2005) Fuel feeds function: energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nat Rev Immunol 5:844–852. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1710
Gjevestad GO, Holven KB, Ulven SM (2015) Effects of exercise on gene expression of inflammatory markers in human peripheral blood cells: a systematic review. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep 9:34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12170-015-0463-4
Gleeson M, Bishop NC (2005) The T cell and NK cell immune response to exercise. Ann Transpl 10:44–49
Green KJ, Croaker SJ, Rowbottom DG (2003) Carbohydrate supplementation and exercise-induced changes in T-lymphocyte function. J Appl Physiol 95:1216–1223. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00179.2003
Grievink HW, Luisman T, Kluft C et al (2016) Comparison of three isolation techniques for human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: cell recovery and viability, population composition, and cell functionality. Biopreserv Biobank 14:410–415. https://doi.org/10.1089/bio.2015.0104
Hermann C, von Aulock S, Graf K, Hartung T (2003) A model of human whole blood lymphokine release for in vitro and ex vivo use. J Immunol Methods 275:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1759(03)00003-6
Holdsworth DA, Cox PJ, Kirk T et al (2017) A Ketone ester drink increases postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 49:1789–1795. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001292
Hopkins WG (2006) Spreadsheets for analysis of controlled trials, with adjustment for a predictor. Sportscience 10:46–50
Hopkins WG, Marshall SW, Batterham AM, Hanin J (2009) Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31818cb278
Keaney LC, Kilding AE, Merien F, Dulson DK (2019) Keeping athletes healthy at the 2020 Tokyo summer games: considerations and illness prevention strategies. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00426
Kidd P (2003) Th1/Th2 balance: the hypothesis, its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Altern Med Rev 8:223–246
Lancaster GI (2006) Methods of assessing immune function. In: Gleeson M (ed) Immune function in sport and exercise. Elsevier, UK, pp 45–65
Lancaster GI, Halson SL, Khan Q et al (2004) Effects of acute exhaustive exercise and chronic exercise training on type 1 and type 2 T lymphocytes. Exerc Immunol Rev 10:91–106
Lancaster GI, Khan Q, Drysdale PT et al (2005) Effect of prolonged exercise and carbohydrate ingestion on type 1 and type 2 T lymphocyte distribution and intracellular cytokine production in humans. J Appl Physiol 98:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00754.2004
LaVoy EC, Hussain M, Reed J et al (2017) T-cell redeployment and intracellular cytokine expression following exercise: effects of exercise intensity and cytomegalovirus infection. Physiol Rep 5:e13070. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13070
Leckey JJ, Ross ML, Quod M et al (2017) Ketone diester ingestion impairs time-trial performance in professional cyclists. Front Physiol 8:806. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00806
Li H, Llera A, Malchiodi EL, Mariuzza RA (1999) The structural basis of T cell activation by superantigens. Annu Rev Immunol 17:435–466. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.435
Maciolek JA, Pasternak JA, Wilson HL (2014) Metabolism of activated T lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol 27:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2014.01.006
Natarajan K, Li H, Mariuzza RA, Margulies DH (1999) MHC class I molecules, structure and function. Rev Immunogenet 1:32–46
Neudorf H, Durrer C, Myette-Cote E et al (2019) Oral ketone supplementation acutely increases markers of nlrp3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201801171
Newsholme P, Curi R, Gordon S, Newsholme EA (1986) Metabolism of glucose, glutamine, long-chain fatty acids and ketone bodies by murine macrophages. Biochem J 239:121–125
O’Malley T, Myette-Cote E, Durrer C, Little JP (2017) Nutritional ketone salts increase fat oxidation but impair high-intensity exercise performance in healthy adult males. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 42:1031–1035. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0641
O'Rourke AM, Rider CC (1989) Glucose, glutamine and ketone body utilisation by resting and concanavalin A activated rat splenic lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1010:342–345
Palmer CS, Ostrowski M, Balderson B et al (2015) Glucose metabolism regulates T cell activation, differentiation, and functions. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00001
Peake JM, Neubauer O, Walsh NP, Simpson RJ (2016) Recovery of the immune system after exercise. J Appl Physiol 122:1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00622.2016
Piccirillo CA (2008) Regulatory T cells in health and disease. Cytokine 43:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.469
Poffé C, Ramaekers M, Van Thienen R, Hespel P (2019) Ketone ester supplementation blunts overreaching symptoms during endurance training overload. J Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP277831
Raysmith BP, Drew MK (2016) Performance success or failure is influenced by weeks lost to injury and illness in elite Australian track and field athletes: a 5-year prospective study. J Sci Med Sport 19:778–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2015.12.515
Rodger S, Plews D, Laursen P, Driller M (2017) Oral β-hydroxybutyrate salt fails to improve 4-minute cycling performance following submaximal exercise. J Sci Cycl 6:26–31
Rooney BV, Bigley AB, LaVoy EC et al (2018) Lymphocytes and monocytes egress peripheral blood within minutes after cessation of steady state exercise: a detailed temporal analysis of leukocyte extravasation. Physiol Behav 194:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.06.008
Salicru AN, Sams CF, Marshall GD (2007) Cooperative effects of corticosteroids and catecholamines upon immune deviation of the type-1/type-2 cytokine balance in favor of type-2 expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Brain Behav Immun 21:913–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2007.02.006
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Shaw DM, Merien F, Braakhuis A, Dulson D (2018) T-cells and their cytokine production: the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of strenuous exercise. Cytokine 104:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.10.001
Shaw DM, Merien F, Braakhuis A et al (2019) The Effect of 1,3-butanediol on cycling time-trial performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 29:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0284
Steensberg A, Toft AD, Bruunsgaard H et al (2001) Strenuous exercise decreases the percentage of type 1 T cells in the circulation. J Appl Physiol 91:1708–1712
Svendsen IS, Gleeson M, Haugen TA, Tønnessen E (2015) Effect of an intense period of competition on race performance and self-reported illness in elite cross-country skiers. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25:846–853. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12452
Vandoorne T, De Smet S, Ramaekers M et al (2017) Intake of a ketone ester drink during recovery from exercise promotes mTORC1 signalling but not glycogen resynthesis in human muscle. Front Physiol 8:310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00310/full
Youm Y-H, Nguyen KY, Grant RW et al (2015) The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med 21:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3804
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants for their effort, cooperation and humour.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by DS, FM, AB and DD; data were collected by DS; data interpretation and manuscript preparation were undertaken by DS, FM, AB, LK and DD. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Klaas R. Westerterp.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaw, D.M., Merien, F., Braakhuis, A. et al. Acute hyperketonaemia alters T-cell-related cytokine gene expression within stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells following prolonged exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 120, 191–202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04263-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04263-x