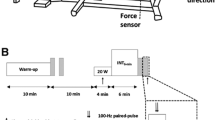
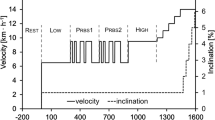
Abstract
Purpose
This study examined the impact of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage on the rate of adjustment in muscle deoxygenation and pulmonary O2 uptake (\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\)) kinetics during moderate exercise.
Methods
Fourteen males (25 ± 3 year; mean ± SD) completed three step transitions to 90 % θL before (Pre), 24 h (Post24) and 48 h after (Post48) eccentric exercise (100 eccentric leg-press repetitions with a load corresponding to 110 % of the participant’s concentric 1RM). Participants were separated into two groups: phase II \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) time constant (τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\)) ≤ 25 s (fast group; n = 7) or τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) > 25 s (slow group; n = 7). \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) and [HHb] responses were modeled as a mono-exponential.
Results
In both groups, isometric peak torque (0°/s) at Post24 was decreased compared to Pre (p < 0.05) and remained depressed at Post48 (p < 0.05). τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) was designed to be different (p < 0.05) at Pre between the Fast (τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\); 19 ± 4 s) and Slow (32 ± 6 s) groups. There were no differences among time points (τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\): Pre, 19 ± 4 s; Post24, 22 ± 3 s; Post48, 20 ± 4 s) in the Fast group. In Slow, there was a speeding (p < 0.05) from the Pre (32 ± 6 s) to the Post24 (25 ± 6) but not Post48 (31 ± 6), resulting in no difference (p > 0.05) between groups at Post24. This reduction of τ\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}} \,\) was concomitant with the abolishment (p < 0.05) of an overshoot in the [HHb]/\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) ratio.
Conclusion
We propose that the sped \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) kinetics observed in the Slow group coupled with an improved [HHb]/\(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}}}\) ratio suggest a better matching of local muscle O2 delivery to O2 utilization following eccentric contractions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1RM:
-
Repetition maximum
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CI95:
-
95 % confidence interval
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- CTD:
-
Calculated time delay
- DOMS:
-
Delayed-onset muscle soreness
- [HHb]:
-
Deoxyhemoglobin—measure of muscle deoxygenation concentration
- [HHb]bsl :
-
Baseline muscle deoxygenation
- [HHb]ss :
-
Steady state muscle deoxygenation
- MOD:
-
Moderate-intensity cycling corresponding to 90 % \(\hat{\theta }_{\text{L}}\)
- MVC:
-
Maximal voluntary contractions
- N2 :
-
Nitrogen
- NIRS:
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy
- O2 :
-
Oxygen
- PCO2 :
-
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- PO2 :
-
Partial pressure of oxygen
- POST24:
-
Post-training condition, 24 h following eccentric contractions
- POST48:
-
Post-training condition, 48 h following eccentric contractions
- PRE:
-
Pre training condition
- RPM:
-
Revolutions per minute
- SS:
-
Steady state
- TD:
-
Time delay
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
- \(\dot{V}{\text{CO}}_{ 2}\) :
-
Carbon dioxide output
- \(\dot{V}_{\text{E}}\) :
-
Pulmonary ventilation
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2}\) :
-
Oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{ 2 {\text{m}}}}\) :
-
Muscle oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{ 2 {\text{p}}}}\) :
-
Pulmonary oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{ 2 {\text{p}}\,{\text{amp}}}}\) :
-
Amplitude of the primary component of pulmonary oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}\,{\text{bsl}}}}\) :
-
Baseline pulmonary oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}\,{\text{Gain}}}}\) :
-
Fundamental gain of pulmonary oxygen uptake (\(\Delta\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2}\)/∆WR)
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}\,{\text{peak}}}}\) :
-
Maximal oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{{2{\text{p}}\,{\text{ss}}}}\) :
-
Steady-state pulmonary oxygen uptake
- WR:
-
Work rate
References
Babcock MA, Paterson DH, Cunningham DA, Dickinson JR (1994) Exercise on-transient gas exchange kinetics are slowed as a function of age. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26(4):440–446
Beaver WL, Lamarra N, Wasserman K (1981) Breath-by-breath measurement of true alveolar gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 51(6):1662–1675
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ (1986) A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 60(6):2020–2027
Bell C, Paterson DH, Kowalchuk JM, Padilla J, Cunningham DA (2001) A comparison of modelling techniques used to characterise oxygen uptake kinetics during the on-transient of exercise. Exp Physiol 86(5):667–676
Boushel R, Langberg H, Gemmer C, Olesen J, Crameri R, Scheede C, Sander M, Kjaer M (2002) Combined inhibition of nitric oxide and prostaglandins reduces human skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise. J Physiol 543(Pt 2):691–698
Burnley M, Jones AM, Carter H, Doust JH (2000) Effects of prior heavy exercise on phase II pulmonary oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. J Appl Physiol 89(4):1387–1396
Clarkson PM, Hubal MJ (2002) Exercise-induced muscle damage in humans. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 81(11 Suppl):S52–S69
Davies RC, Eston RG, Poole DC, Rowlands AV, DiMenna F, Wilkerson DP, Twist C, Jones AM (2008) Effect of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage on the dynamics of muscle oxygenation and pulmonary oxygen uptake. J Appl Physiol 105(5):1413–1421
DeLorey DS, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2003) Relationship between pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics and muscle deoxygenation during moderate-intensity exercise. J Appl Physiol 95(1):113–120
DeLorey DS, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2004) Effects of prior heavy-intensity exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake and muscle deoxygenation kinetics in young and older adult humans. J Appl Physiol 97(3):998–1005
DeLorey DS, Paterson DH, Kowalchuk JM (2007) Effects of ageing on muscle O2 utilization and muscle oxygenation during the transition to moderate-intensity exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab (Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme) 32(6):1251–1262
duManoir GR, DeLorey DS, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2010) Kinetics of VO2 limb blood flow and regional muscle deoxygenation in young adults during moderate intensity, knee-extension exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 108(3):607–617
Friden J, Lieber RL (2001) Eccentric exercise-induced injuries to contractile and cytoskeletal muscle fibre components. Acta Physiol Scand 171(3):321–326
Friden J, Sfakianos PN, Hargens AR, Akeson WH (1988) Residual muscular swelling after repetitive eccentric contractions. J Orthop Res 6(4):493–498
Gallagher EJ, Bijur PE, Latimer C, Silver W (2002) Reliability and validity of a visual analog scale for acute abdominal pain in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 20(4):287–290
Goto C, Higashi Y, Kimura M, Noma K, Hara K, Nakagawa K, Kawamura M, Chayama K, Yoshizumi M, Nara I (2003) Effect of different intensities of exercise on endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans: role of endothelium-dependent nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Circulation 108(5):530–535
Grassi B (2001) Regulation of oxygen consumption at exercise onset: is it really controversial? Exerc Sport Sci Rev 29(3):134–138
Grassi B, Poole DC, Richardson RS, Knight DR, Erickson BK, Wagner PD (1996) Muscle O2 uptake kinetics in humans: implications for metabolic control. J Appl Physiol 80(3):988–998
Grassi B, Gladden LB, Stary CM, Wagner PD, Hogan MC (1998) Peripheral O2 diffusion does not affect V(O2)on-kinetics in isolated insitu canine muscle. J Appl Physiol 85(4):1404–1412
Green DJ, Maiorana A, O’Driscoll G, Taylor R (2004) Effect of exercise training on endothelium-derived nitric oxide function in humans. J Physiol 561(Pt 1):1–25
Gurd BJ, Scheuermann BW, Paterson DH, Kowalchuk JM (2005) Prior heavy-intensity exercise speeds VO2 kinetics during moderate-intensity exercise in young adults. J Appl Physiol 98(4):1371–1378
Gurd BJ, Peters SJ, Heigenhauser GJ, LeBlanc PJ, Doherty TJ, Paterson DH, Kowalchuk JM (2006) Prior heavy exercise elevates pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and speeds O2 uptake kinetics during subsequent moderate-intensity exercise in healthy young adults. J Physiol 577(Pt 3):985–996
Haram PM, Adams V, Kemi OJ, Brubakk AO, Hambrecht R, Ellingsen O, Wisloff U (2006) Time-course of endothelial adaptation following acute and regular exercise. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 13(4):585–591
Howlett RA, Heigenhauser GJ, Hultman E, Hollidge-Horvat MG, Spriet LL (1999) Effects of dichloroacetate infusion on human skeletal muscle metabolism at the onset of exercise. Am J Physiol 277(1 Pt 1):E18–E25
Hughson RL (2009) Oxygen uptake kinetics: historical perspective and future directions. Appl Physiol Nutr Metabol (Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme) 34(5):840–850
Jamurtas AZ, Theocharis V, Tofas T, Tsiokanos A, Yfanti C, Paschalis V, Koutedakis Y, Nosaka K (2005) Comparison between leg and arm eccentric exercises of the same relative intensity on indices of muscle damage. Eur J Appl Physiol 95(2–3):179–185
Kano Y, Padilla DJ, Behnke BJ, Hageman KS, Musch TI, Poole DC (2005) Effects of eccentric exercise on microcirculation and microvascular oxygen pressures in rat spinotrapezius muscle. J Appl Physiol 99(4):1516–1522
Koga S, Poole DC, Ferreira LF, Whipp BJ, Kondo N, Saitoh T, Ohmae E, Barstow TJ (2007) Spatial heterogeneity of quadriceps muscle deoxygenation kinetics during cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 103(6):2049–2056
Laaksonen MS, Kivela R, Kyrolainen H, Sipila S, Selanne H, Lautamaki R, Nuutila P, Knuuti J, Kalliokoski KK, Komi PV (2006) Effects of exhaustive stretch-shortening cycle exercise on muscle blood flow during exercise. Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 186(4):261–270
Lamarra N, Whipp BJ, Ward SA, Wasserman K (1987) Effect of interbreath fluctuations on characterizing exercise gas exchange kinetics. J Appl Physiol 62(5):2003–2012
Lieber RL, Friden J (2002) Morphologic and mechanical basis of delayed-onset muscle soreness. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 10(1):67–73
Lieber RL, Thornell LE, Friden J (1996) Muscle cytoskeletal disruption occurs within the first 15 min of cyclic eccentric contraction. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda, Md: 1985) 80(1):278–284
Magalhaes J, Fraga M, Lumini-Oliveira J, Goncalves I, Costa M, Ferreira R, Oliveira PJ, Ascensao A (2013) Eccentric exercise transiently affects mice skeletal muscle mitochondrial function. Appl Physiol Nutr Metabol (Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme) 38(4):401–409
McHugh MP (2003) Recent advances in the understanding of the repeated bout effect: the protective effect against muscle damage from a single bout of eccentric exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13(2):88–97
McHugh MP, Tetro DT (2003) Changes in the relationship between joint angle and torque production associated with the repeated bout effect. J Sports Sci 21(11):927–932
Molina R, Denadai BS (2011) Muscle damage slows oxygen uptake kinetics during moderate-intensity exercise performed at high pedal rate. Appl Physiol Nutr Metabol (Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme) 36(6):848–855
Morgan DL (1990) New insights into the behavior of muscle during active lengthening. Biophys J 57(2):209–221
Murias JM, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2010) Speeding of VO2 kinetics with endurance training in old and young men is associated with improved matching of local O2 delivery to muscle O2 utilization. J Appl Physiol 108(4):913–922
Murias JM, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2011a) Speeding of VO2 kinetics in response to endurance-training in older and young women. Eur J Appl Physiol 111(2):235–243
Murias JM, Spencer MD, Delorey DS, Gurd BJ, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2011b) Speeding of VO2 kinetics during moderate-intensity exercise subsequent to heavy-intensity exercise is associated with improved local O2 distribution. J Appl Physiol 111(5):1410–1415
Murias JM, Spencer MD, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2011c) Influence of phase I duration on phase II VO2 kinetics parameter estimates in older and young adults. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301(1):R218–R224
Murias JM, Spencer MD, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2011d) Muscle deoxygenation to VO(2) relationship differs in young subjects with varying tauVO(2). Eur J Appl Physiol 111(12):3107–3118
Murias JM, Dey A, Campos OA, Estaki M, Hall KE, Melling CW, Noble EG (2013) High-intensity endurance training results in faster vessel-specific rate of vasorelaxation in type 1 diabetic rats. PLoS One 8(3):e59678
Murias JM, Spencer MD, Paterson DH (2014) The critical role of O2 provision in the dynamic adjustment of oxidative phosphorylation. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 42(1):4–11
Pizza FX, Koh TJ, McGregor SJ, Brooks SV (2002) Muscle inflammatory cells after passive stretches, isometric contractions, and lengthening contractions. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda, Md: 1985) 92(5):1873–1878
Poole DC, Musch TI (2010) Muscle microcirculatory O(2) exchange in health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 662:301–307
Poole DC, Ferreira LF, Behnke BJ, Barstow TJ, Jones AM (2007) The final frontier: oxygen flux into muscle at exercise onset. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 35(4):166–173
Poole DC, Barstow TJ, McDonough P, Jones AM (2008) Control of oxygen uptake during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(3):462–474
Rattray B, Thompson M, Ruell P, Caillaud C (2013) Specific training improves skeletal muscle mitochondrial calcium homeostasis after eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 113(2):427–436
Rossiter HB, Ward SA, Doyle VL, Howe FA, Griffiths JR, Whipp BJ (1999) Inferences from pulmonary O2 uptake with respect to intramuscular [phosphocreatine] kinetics during moderate exercise in humans. J Physiol 518(Pt 3):921–932
Rossiter HB, Ward SA, Howe FA, Wood DM, Kowalchuk JM, Griffiths JR, Whipp BJ (2003) Effects of dichloroacetate on VO2 and intramuscular 31P metabolite kinetics during high-intensity exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 95(3):1105–1115
Saxton JM, Donnelly AE (1996) Length-specific impairment of skeletal muscle contractile function after eccentric muscle actions in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 90(2):119–125
Sbriccoli P, Felici F, Rosponi A, Aliotta A, Castellano V, Mazza C, Bernardi M, Marchetti M (2001) Exercise induced muscle damage and recovery assessed by means of linear and non-linear sEMG analysis and ultrasonography. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 11(2):73–83
Scheuermann BW, Bell C, Paterson DH, Barstow TJ, Kowalchuk JM (2002) Oxygen uptake kinetics for moderate exercise are speeded in older humans by prior heavy exercise. J Appl Physiol 92(2):609–616
Schneider DA, Berwick JP, Sabapathy S, Minahan CL (2007) Delayed onset muscle soreness does not alter O2 uptake kinetics during heavy-intensity cycling in humans. Int J Sports Med 28(7):550–556
Sonobe T, Inagaki T, Poole DC, Kano Y (2008) Intracellular calcium accumulation following eccentric contractions in rat skeletal muscle in vivo: role of stretch-activated channels. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(4):R1329–R1337
Spencer MD, Murias JM, Lamb HP, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2011) Are the parameters of VO2, heart rate and muscle deoxygenation kinetics affected by serial moderate-intensity exercise transitions in a single day? Eur J Appl Physiol 111(4):591–600
Spencer MD, Murias JM, Grey TM, Paterson DH (2012) Regulation of VO(2) kinetics by O(2) delivery: insights from acute hypoxia and heavy-intensity priming exercise in young men. J Appl Physiol 112(6):1023–1032
Spriet LL, Heigenhauser GJ (2002) Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 30(2):91–95
Stamler JS, Loh E, Roddy MA, Currie KE, Creager MA (1994) Nitric oxide regulates basal systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance in healthy humans. Circulation 89(5):2035–2040
Stupka N, Tarnopolsky MA, Yardley NJ, Phillips SM (2001) Cellular adaptation to repeated eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J Appl Physiol 91(4):1669–1678
Warren GL, Ingalls CP, Lowe DA, Armstrong RB (2001) Excitation-contraction uncoupling: major role in contraction-induced muscle injury. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 29(2):82–87
Whipp BJ (1971) Rate constant for the kinetics of oxygen uptake during light exercise. J Appl Physiol 30(2):261–263
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the participants of this study and to acknowledge the technical assistance provided by Daniel Keir. This study was supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) research and equipment grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-René Lacour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nederveen, J.P., Major, B., Paterson, D.H. et al. Faster \(\dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2}\) kinetics after eccentric contractions is explained by better matching of O2 delivery to O2 utilization. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 2169–2181 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2937-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2937-3