Abstract
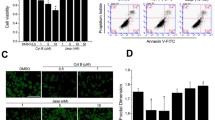
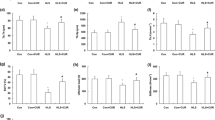
Destrin, also known as actin depolymerizing factor (ADF), is a member of the ADF/Cofilin/destrin superfamily that has the ability to rapidly depolymerize F-actin in a stoichiometric manner. Remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton through actin dynamics (assembly and disassembly of filamentous actin) is known to be essential for numerous basic biological processes including bone formation. The aim of current study was to elucidate whether destrin was involved in the progression of bone loss induced by modeled microgravity. We used the hindlimb suspension (HLS) mice model to simulate microgravity in vivo. Exposure to HLS in mice enhanced femur destrin expression. Destrin deletion in Dstn −/− mutant mice enhanced HLS-induced reduction of BMD, ultimate load, stiffness, trabecular thickness, trabecular number, and bone volume fraction in femur, but did not affect them under control static condition. The Rotary wall vessel bioreactor was used to model microgravity in vitro. Exposure to modeled microgravity in cultured 2T3 murine osteoblast precursor cells upregulated destrin expression. RNAi-mediated destrin knockdown enhanced the microgravity-induced reduction of osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation significantly. In conclusion, for the first time we demonstrated that destrin deletion enhances the bone loss in hindlimb suspended mice. Destrin may be a potential target for the prevention or management of microgravity-induced bone loss.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanc S, Normand S, Ritz P, Pachiaudi C, Vico L, Gharib C, Gauquelin-Koch G (1998) Energy and water metabolism, body composition, and hormonal changes induced by 42 days of enforced inactivity and simulated weightlessness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:4289–4297
Caillot-Augusseau A, Lafage-Proust MH, Soler C, Pernod J, Dubois F, Alexandre C (1998) Bone formation and resorption biological markers in osmonauts during and after a 180-day space flight (Euromir 95). Clin Chem 44:578–585
Carlier MF, Laurent V, Santolini J, Melki R, Didry D, Xia GX, Hong Y, Chua NH, Pantaloni D (1997) Actin depolymerizing factor (ADF/cofilin) enhances the rate of filament turnover: implication in actin-based motility. J Cell Biol 136:1307–1322
Carmeliet G, Vico L, Bouillon R (2001) Space flight: a challenge for normal bone homeostasis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 11:131–144
Chin YR, Toker A (2010) The actin-bundling protein palladin is an Akt1-specific substrate that regulates breast cancer cell migration. Mol Cell 38:333–344
Fowler JF Jr (1991) Physiological changes during spaceflight. Cutis 48:291–295
Galkin VE, Orlova A, Kudryashov DS, Solodukhin A, Reisler E, Schröder GF, Egelman EH (2011) Remodeling of actin filaments by ADF/cofilin proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20568–20572
Gershkovich PM, Gershkovich IuG, Buravkova LB (2011) Expression of cytoskeleton genes in culture of human mesenchymal stromal cells in different periods of simulating the effects of microgravity. Aviakosm Ekolog Med 45:39–41
Gershovich PM, Gershovich IuG, Buravkova LB (2009) Cytoskeleton structures and adhesion properties of human stromal precursors under conditions of simulated microgravity. Tsitologiia 51:896–904
Glotzer M (2010) Cytokinesis: integrating signaling, the cytoskeleton, and membranes to create new daughter cells. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:865
Guo D, Keightley A, Guthrie J, Veno PA, Harris SE, Bonewald LF (2010) Identification of osteocyte-selective proteins. Proteomics 10:3688–3698
Higuchi C, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa H, Itoh K (2009) Transient dynamic actin cytoskeletal change stimulates the osteoblastic differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab 27:158–167
Hughes-Fulford M (2003) Function of the cytoskeleton in gravisensing during spaceflight. Adv Space Res 32:1585–1593
Hughes-Fulford M, Lewis ML (1996) Effects of microgravity on osteoblast growth activation. Exp Cell Res 224:103–109
Katsumata T, Nakamura T, Ohnishi H, Sakurawa T (1995) Intermittent cyclical etidronate treatment maintains the mass, structure and the mechanical property of bone in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 10:921–931
Kuure S, Cebrian C, Machingo Q, Lu BC, Chi X, Hyink D, D’Agati V, Gurniak C, Witke W, Costantini F (2010) Actin depolymerizing factors cofilin1 and destrin are required for ureteric bud branching morphogenesis. PLoS Genet 6:e1001176
Le Beyec J, Xu R, Lee SY, Nelson CM, Rizki A, Alcaraz J, Bissell MJ (2007) Cell shape regulates global histone acetylation in human mammary epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 313:3066–3075
Makihira S, Kawahara Y, Yuge L, Mine Y, Nikawa H (2008) Impact of the microgravity environment in a 3-dimensional clinostat on osteoblast- and osteoclast-like cells. Cell Biol Int 32:1176–1181
McGough A, Pope B, Chiu W, Weeds A (1997) Cofilin changes the twist of F-actin: implications for actin filament dynamics and cellular function. J Cell Biol 138:771–781
Moran JL, Li Y, Hill AA, Mounts WM, Miller CP (2002) Gene expression changes during mouse skeletal myoblast differentiation revealed by transcriptional profiling. Physiol Genomics 10:103–111
Mseka T, Bamburg JR, Cramer LP (2007) ADF/cofilin family proteins control formation of oriented actin-filament bundles in the cell body to trigger fibroblast polarization. J Cell Sci 120:4332–4344
Nabavi N, Khandani A, Camirand A, Harrison RE (2011) Effects of microgravity on osteoclast bone resorption and osteoblast cytoskeletal organization and adhesion. Bone 49:965–974
Nadiminty N, Lou W, Lee SO, Mehraein-Ghomi F, Kirk JS, Conroy JM, Zhang H, Gao AC (2006) Prostate-specific antigen modulates genes involved in bone remodeling and induces osteoblast differentiation of human osteosarcoma cell line SaOS-2. Clin Cancer Res 12:1420–1430
Norvell SM, Ponik SM, Bowen DK, Gerard R, Pavalko FM (2004) Fluid shear stress induction of COX-2 protein and prostaglandin release in cultured MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts does not require intact microfilaments of microtubules. J Appl Physiol 96:957–966
Oganov VS, Skripnikova IA, Novikov VE, Bakulin AV, Kabitskaia OE, Murashko LM (2011) Characteristics of local human skeleton reactions to microgravity and drug treatment of osteoporosis in clinic. Aviakosm Ekolog Med 45:16–21
Pan Z, Yang J, Guo C, Shi D, Shen D, Zheng Q, Chen R, Xu Y, Xi Y, Wang J (2008) Effects of hindlimb unloading on ex vivo growth and osteogenic/adipogenic potentials of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Stem Cells Dev 17:795–804
Riggs BL, Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd (1998) A unitary model for involutional osteoporosis: estrogen deficiency causes both type I and type II osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and contributes to bone loss in aging men. J Bone Miner Res 13:763–773
Rösner H, Wassermann T, Möller W, Hanke W (2006) Effects of altered gravity on the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Protoplasma 229:225–234
Sakai D, Kii I, Nakagawa K, Matsumoto HN, Takahashi M, Yoshida S, Hosoya T, Takakuda K, Kudo A (2011) Remodeling of actin cytoskeleton in mouse periosteal cells under mechanical loading induces periosteal cell proliferation during bone formation. PLoS One 6:e24847
Serezani CH, Kane S, Medeiros AI, Cornett AM, Kim SH, Marques MM, Lee SP, Lewis C, Bourdonnay E, Ballinger MN, White ES, Peters-Golden M (2012) PTEN directly activates the actin depolymerization factor cofilin-1 during PGE2-mediated inhibition of phagocytosis of fungi. Sci Signal 5:ra12
Smith SM, Nillen JL, Leblanc A, Lipton A, Demers LM, Lane HW, Leach CS (1998) Collagen cross-link excretion during space flight and bed rest. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:3584–3591
Smith SM, Wastney ME, O’Brien KO, Morukov BV, Larina IM, Abrams SA, Davis-Street JE, Oganov V, Shackelford LC (2005) Bone markers, calcium metabolism, and calcium kinetics during extended-duration space flight on the mir space station. J Bone Miner Res 20:208–218
Uhthoff HK, Jaworski ZF (1978) Bone loss in response to long-term immobilisation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 60:420–429
Verdoni AM, Aoyama N, Ikeda A, Ikeda S (2008) Effect of destrin mutations on the gene expression profile in vivo. Physiol Genomics 34:9–21
Zayzafoon M, Gathings WE, Mcdonald JM (2004) Modeled microgravity inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and increases adipogenesis. Endocrinology 145:2421–2432
Zhang J, Ryder KD, Bethel JA, Ramirez R, Duncan RL (2006) PTH-induced actin depolymerization increases mechanosensitive channel activity to enhance mechanically stimulated Ca2+ signaling in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res 21:1729–1737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan A. Ward.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shuang, F., Sun, Y., Yang, HH. et al. Destrin deletion enhances the bone loss in hindlimb suspended mice. Eur J Appl Physiol 113, 403–410 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2451-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2451-4