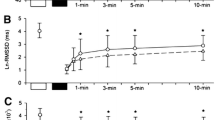
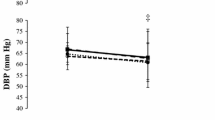
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of exercise-induced plasma volume expansion on post-exercise parasympathetic reactivation. Before (D0) and 2 days after (D+2) a supramaximal exercise session, 11 men (21.4 ± 2.6 years and BMI = 23.0 ± 1.4) performed 6-min of submaximal running where heart rate (HR) recovery (HRR) and HR variability (HRV) indices were calculated during the first 10 min of recovery. Relative plasma volume changes (∆PV) were calculated using changes in hematocrit and hemoglobin measured over consecutive mornings from D0 to D+2. Parasympathetic reactivation was evaluated through HRR and vagal-related indexes calculated during a stationary period of recovery. Compared with D0, ∆PV (+4.8%, P < 0.01) and all vagal-related HRV indices were significantly higher at D+2 (all P < 0.05). HRR was not different between trials. Changes in HRV indices, but not HRR, were related to ∆PV (all P < 0.01). HRR and HRV indices characterize distinct independent aspects of cardiac parasympathetic function, with HRV indices being more sensitive to changes in plasma volume than HRR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bainbridge FA (1915) The influence of venous filling upon the rate of the heart. J Physiol 50:65–84
Billman GE (2006) Cardiovascular variability is/is not an index of autonomic control of circulation. J Appl Physiol 101:684–685. (author reply 690-681). doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00562.2006
Billman GE, Dickey DT, Teoh KK, Stone HL (1981) Effects of central venous blood volume shifts on arterial baroreflex control of heart rate. Am J Physiol 241:H571–H575
Borresen J, Lambert MI (2007) Changes in heart rate recovery in response to acute changes in training load. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:503–511. doi:10.1007/s00421-007-0516-6
Borresen J, Lambert MI (2008) Autonomic control of heart rate during and after exercise : measurements and implications for monitoring training status. Sports Med 38:633–646. doi:10.2165/00007256-200838080-00002
Brandenberger G, Buchheit M, Ehrhart J, Simon C, Piquard F (2005) Is slow wave sleep an appropriate recording condition for heart rate variability analysis? Auton Neurosci 121:81–86. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2005.06.002
Buchheit M (2008a) The 30–15 intermittent fitness test: accuracy for individualizing interval training of young intermittent sport players. J Strength Cond Res 22:365–374
Buchheit M, Gindre C (2006) Cardiac parasympathetic regulation: respective associations with cardiorespiratory fitness and training load. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H451–H458. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00008.2006
Buchheit M, Laursen PB, Ahmaidi S (2007a) Parasympathetic reactivation after repeated sprint exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H133–H141. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00062.2007
Buchheit M, Papelier Y, Laursen PB, Ahmaidi S (2007b) Non-invasive assessment of cardiac parasympathetic function: post-exercise heart rate recovery or heart rate variability? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H8–H10. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00335.2007
Buchheit M, Al Haddad H, Leprêtre PM, Millet G, Newton M, Ahmaidi S (2008b) Cardiorespiratory and cardiac autonomic responses to 30–15 intermittent fitness test. J Strength Cond Res (in press)
Buchheit M, Millet GP, Parisy A, Pourchez S, Laursen PB, Ahmaidi S (2008c) Supramaximal training and post-exercise parasympathetic reactivation in adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:362–371
Coleridge HM, Coleridge JC, Dangel A, Kidd C, Luck JC, Sleight P (1973) Impulses in slowly conducting vagal fibers from afferent endings in the veins, atria, and arteries of dogs and cats. Circ Res 33:87–97
Convertino VA (1991) Blood volume: its adaptation to endurance training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:1338–1348. doi:10.1249/00005768-199112000-00004
Convertino VA (2003) Baroreflex-mediated heart rate and vascular resistance responses 24 h after maximal exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:970–977. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000069753.92706.DD
Dewland TA, Androne AS, Lee FA, Lampert RJ, Katz SD (2007) Effect of acetylcholinesterase inhibition with pyridostigmine on cardiac parasympathetic function in sedentary adults and trained athletes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H86–H92. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01339.2006
Furlan R, Guzzetti S, Crivellaro W, Dassi S, Tinelli M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A (1990) Continuous 24-h assessment of the neural regulation of systemic arterial pressure and RR variabilities in ambulant subjects. Circulation 81:537–547
Gamelin FX, Berthoin S, Bosquet L (2006) Validity of the polar S810 heart rate monitor to measure R–R intervals at rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:887–893. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000218135.79476.9c
Goforth HW Jr, Laurent D, Prusaczyk WK, Schneider KE, Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2003) Effects of depletion exercise and light training on muscle glycogen supercompensation in men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E1304–E1311
Goldberger JJ, Le FK, Lahiri M, Kannankeril PJ, Ng J, Kadish AH (2006) Assessment of parasympathetic reactivation after exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H2446–H2452. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01118.2005
Green HJ, Thomson JA, Ball ME, Hughson RL, Houston ME, Sharratt MT (1984) Alterations in blood volume following short-term supramaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 56:145–149
Hainsworth R (1991) Reflexes from the heart. Physiol Rev 71:617–658
Hautala AJ, Tulppo MP, Makikallio TH, Laukkanen R, Nissila S, Huikuri HV (2001) Changes in cardiac autonomic regulation after prolonged maximal exercise. Clin Physiol 21:238–245. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2281.2001.00309.x
Hautala AJ, Rankinen T, Kiviniemi AM, Makikallio TH, Huikuri HV, Bouchard C, Tulppo MP (2006) Heart rate recovery after maximal exercise is associated with acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene polymorphism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H459–H466. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01193.2005
Hooper SL, Mackinnon LT (1995) Monitoring overtraining in athletes. Recommendations. Sports Med 20:321–327. doi:10.2165/00007256-199520050-00003
Iwasaki K, Zhang R, Perhonen MA, Zuckerman JH, Levine BD (2004) Reduced baroreflex control of heart period after bed rest is normalized by acute plasma volume restoration. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R1256–R1262. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00613.2002
James DV, Barnes AJ, Lopes P, Wood DM (2002) Heart rate variability: response following a single bout of interval training. Int J Sports Med 23:247–251. doi:10.1055/s-2002-29077
Kannankeril PJ, Le FK, Kadish AH, Goldberger JJ (2004) Parasympathetic effects on heart rate recovery after exercise. J Investig Med 52:394–401. doi:10.2310/6650.2004.00611
Lundvall J, Lindgren P (1998) F-cell shift and protein loss strongly affect validity of PV reductions indicated by Hb/Hct and plasma proteins. J Appl Physiol 84:822–829
Miyamoto T, Kawada T, Takaki H, Inagaki M, Yanagiya Y, Jin Y, Sugimachi M, Sunagawa K (2003) High plasma norepinephrine attenuates the dynamic heart rate response to vagal stimulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H2412–H2418
Miyamoto T, Kawada T, Yanagiya Y, Inagaki M, Takaki H, Sugimachi M, Sunagawa K (2004) Cardiac sympathetic nerve stimulation does not attenuate dynamic vagal control of heart rate via alpha-adrenergic mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H860–H865. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00752.2003
Mourot L, Bouhaddi M, Tordi N, Rouillon JD, Regnard J (2004) Short- and long-term effects of a single bout of exercise on heart rate variability: comparison between constant and interval training exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 92:508–517. doi:10.1007/s00421-004-1119-0
Niewiadomski W, Gasiorowska A, Krauss B, Mroz A, Cybulski G (2007) Suppression of heart rate variability after supramaximal exertion. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 27:309–319. doi:10.1111/j.1475-097X.2007.00753.x
Ozyener F, Rossiter HB, Ward SA, Whipp BJ (2001) Influence of exercise intensity on the on- and off-transient kinetics of pulmonary oxygen uptake in humans. J Physiol 533:891–902. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00891.x
Perini R, Orizio C, Comande A, Castellano M, Beschi M, Veicsteinas A (1989) Plasma norepinephrine and heart rate dynamics during recovery from submaximal exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 58:879–883. doi:10.1007/BF02332222
Pyne DB, Boston T, Martin DT, Logan A (2000) Evaluation of the lactate pro blood lactate analyser. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:112–116. doi:10.1007/s004210050659
Richardson RS, Verstraete D, Johnson SC, Luetkemeier MJ, Stray-Gundersen J (1996) Evidence of a secondary hypervolemia in trained man following acute high intensity exercise. Int J Sports Med 17:243–247. doi:10.1055/s-2007-972840
Sagnol M, Claustre J, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM, Fellmann N, Coudert J, Peyrin L (1990) Plasma free and sulphated catecholamines after ultra-long exercise and recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 60:91–97. doi:10.1007/BF00846027
Spinelli L, Petretta M, Marciano F, Testa G, Rao MA, Volpe M, Bonaduce D (1999) Cardiac autonomic responses to volume overload in normal subjects and in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol 277:H1361–H1368
Strauss MB, Davis RK, Rosenbaum JD, Rossmeisl EC (1951) Water diuresis produced during recumbency by the intravenous infusion of isotonic saline solution. J Clin Invest 30:862–868. doi:10.1172/JCI102501
Sugawara J, Murakami H, Maeda S, Kuno S, Matsuda M (2001) Change in post-exercise vagal reactivation with exercise training and detraining in young men. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:259–263. doi:10.1007/s004210100443
Takahashi T, Okada A, Saitoh T, Hayano J, Miyamoto Y (2000) Difference in human cardiovascular response between upright and supine recovery from upright cycle exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 81:233–239. doi:10.1007/s004210050036
Task Force (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task force of the european society of cardiology and the north American society of pacing and electrophysiology. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Trujillo-Ortiz A, Hernandez-Walls R (2003) Mauspher: Mauchly’s sphericity tests. A MATLAB file [WWW document]. http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/loadFile.do?objectId=3694&objectType=FILE
Uusitalo AL, Uusitalo AJ, Rusko HK (2000) Heart rate and blood pressure variability during heavy training and overtraining in the female athlete. Int J Sports Med 21:45–53. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8853
Vatner SF, Boettcher DH, Heyndrickx GR, McRitchie RJ (1975) Reduced baroreflex sensitivity with volume loading in conscious dogs. Circ Res 37:236–242
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Foult for his assistance with blood sample analysis, Irmant Cadjjiov for his helpful comments during preparation of the manuscript and Veronique Bach for her helpful remarks on statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchheit, M., Laursen, P.B., Al Haddad, H. et al. Exercise-induced plasma volume expansion and post-exercise parasympathetic reactivation. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 471–481 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0925-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0925-1