Abstract
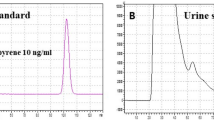
An analytical method was developed for the determination of free and conjugated PGME-α in urine. The method involves a solid-phase extraction on LC-18 columns and a GC/FID analysis after derivatization with trimethysilylimidazole. The assay was linear (least-squares regression coefficient 0.996), specific, reproducible (intraassay variability 10%, interassay variability 10%), and allowed a high level of PGME recovery (more than 90%). The assay was applied to the analysis of urine samples from three workers who were occupationally exposed to PGME to estimate their exposure. The highest value of PGME concentration in urine was 7.78 mg/l. Air concentrations of PGME ranged between 20 and 40 ppm. A statistically significant correlation was found between measurements of external exposure and PGME in urine. An important fraction of PGME in urine was found to be conjugated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 July 1999 / Accepted: 27 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devanthéry, A., Dentan, A., Berode, M. et al. Propylene glycol monomethyl ether (PGME) occupational exposure . Int Arch Occup Environ Health 73, 311–315 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200000120
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200000120