Abstract
Objective
Copper smelter workers are exposed to harmful chemical agents in dust and fumes which contain harmful metals such as copper and arsenic. These substances are known to be respiratory irritants.
Methods
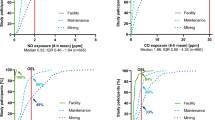
This study aimed at investigating the effect of occupational exposure to copper and arsenic on the respiratory system. A group of 75 male exposed workers, and 75 male administrative employees (control group) were recruited from a secondary copper smelting factory.
Full history, complete clinical examination, ventilatory function parameters (FVC, FEV1, FVC/FEV1 and FEF), and chest X-ray were done for both groups. Serum levels of ICAM-1 and IL8 (as markers of epithelial injury) were measured by ELISA. Serum copper and arsenic were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
Results
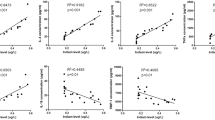
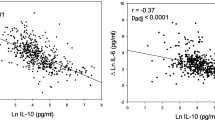
The exposed group was associated with increased respiratory symptoms, higher serum copper, arsenic, and ICAM-1and Il-8 as compared to the control group. There was a significant decrease in ventilatory parameters among the exposed group: 58.7% of the exposed group had restrictive lung impairment, 40% had obstructive impairment. In the exposed group a positive correlation between serum copper, arsenic and serum ICAM and IL8 was found. While a negative correlation was observed between both serum ICAM, IL8 and ventilatory parameters among the exposed group. Moreover, 36% of the exposed group had radiological infiltrates on chest X.ray.
Conclusion
Occupational exposure to copper and arsenic was associated with ventilatory and radiological impairment, with a corresponding increase in the serum level of ICAM-1 and IL8, which can be used as biomarkers for pulmonary impairment among copper smelter workers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) (1999) Threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents. Cincinnati
Backe EM, Lotz G, Tittelbach U et al (2002) Soluble intercellular adhesion molecules in the serum of subjects exposed to dust at different workplaces: correlation to airway symptoms, lung function, tobacco and dust exposure. Int J Hyg Environ Health 204:377–379. https://doi.org/10.1078/1438-4639-00111
Bat L, Bilgin S, Öztekin A (2017) Toxicity of copper on marine organisms from the Black Sea. J Coast Life Med 5:422–426. https://doi.org/10.12980/jclm.5.2017J7-119
Bittleman DB, Casale TB (1995) Interleukin-8 mediates interleukin-1 alpha-induced neutrophil transcellular migration. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 13:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.13.3.7654388
Brand P, Beilmann V, Thomas K et al (2019) the effects of exposure time on systemic inflammation in subjects with exposure to zinc- and copper-containing brazing fumes. J Occup Environ Med 61:806–811. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000001676
Chan YH (2003a) Biostatistics102: quantitative data—parametric and non-parametric tests. Singap Med J 44(8):391–396
Chan YH (2003b) Biostatistics 103: qualitative data—tests of independence. Singap Med J 44(10):498–503
Chan YH (2004) Biostatistics 201: linear regression analysis. Singap Med J 45(2):55–61
Cho WS, Duffin R, Poland CA et al (2010) Metal oxide nanoparticles induce unique inflammatory footprints in the lung: important implications for nanoparticle testing. Environ Health Perspect 118:1699–1706. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002201 (PMID:20729176)
Cook-Mills JM, Deem TL (2005) Active participation of endothelial cells in inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 77:4874–4895. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0904554
Cotes JE, Chinn DJ, Miller MR (2006) How individual diseases affect lung functions. Lung function: physiology measurement and application in medicine, 6th edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, pp 560–592
Dagli CE, Tanrikulu AC, Koksal N et al (2010) Interstitial lung disease in coppersmiths in high serum copper levels. Biol Trace Elem Res 137:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8566-8
Dikensoy O, Kervancioglu R, Ege I et al (2008) High prevalence of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases among Turkish tinners. J Occup Health 50(2):208–211. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.l7104
Ekosse G, de Jager L, van den Heever DJ (2005) The occurrences of chest pains and frequent coughing among residents living within the Selebi Phikwe Ni–Cu mine area, Botswana. Afr J Health Sci 12(1–2):37–48
El Safty A, Rashed L, Samir A et al (2014) Oxidative stress and arsenic exposure among copper smelters. J Adv Med Med Res 2955–2968. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261153144_Oxidative_stress_and_arsenic_exposure_among_copper_smelters
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2011) EPA results for copper and cancer. Available at: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0368_summary.pdf
Fogarty AW, Jones S, Britton JR et al (2007) Systemic inflammation and decline in lung function in a general population: a prospective study. Thorax 62:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2006.066969
Gerhardsson L, Brune D, Nordberg GF et al (1988) Multielemental assay of tissues of deceased smelter workers and controls. Sci Total Environ 74:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(88)90131-3
Gupta R (2007) Veterinary toxicology basic and clinical principles. Cyanogenic Plants 49:873–875
Hancox RJ, Poulton R, Greene JM et al (2007) Systemic inflammation and lung function in young adults. Thorax 62:1064–1068. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2006.076877
Jian Z, Guo H, Liu H et al (2020) Oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammatory responses involved in copperinduced pulmonary toxicity in mice. Aging (Albany NY) 12:16867–16886. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103585
Kelley J (1990) Cytokines of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:765–788. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.765
Khalil N, O’Connor RN, Unruh HW et al (1991) Increased production and immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-beta in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 5:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.155
Kony S, Zureik M, Driss F et al (2004) Association of bronchial hyperresponsiveness and lung function with C-reactive protein (CRP): a population based study. Thorax 59:892–896. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2003.015768
Kumar S, Khaliq F, Singh S et al (2016) Pulmonary functions, oxidative stress and DNA damage in workers of a copper processing industry. Int J Occup Environ Med (The IJOEM) 7(2):612–107. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijoem.2016.612
Lantz RC, Chau B, Sarihan P et al (2009) In utero and postnatal exposure to arsenic alters pulmonary structure and function. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 235:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.11.012
Lee JS, Shin JH, Choi BS (2015) Serum levels of IL-8 and ICAM-1 as biomarkers for progressive massive fibrosis in coal workers’ pneumoconiosis. J Korean Med Sci 30(2):140–144. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.2.140
Leite CE, Maboni LO, Cruz FF et al (2013) Involvement of purinergic system in inflammation and toxicity induced by copper in zebrafish larvae. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.08.001
Long G, Peng Y, Bradshaw D (2012) A review of copper–arsenic mineral removal from copper concentrates. Miner Eng 36(38):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.03.032
Marcisz C, Jonderko G, Wieczorek-Latka U et al (1998) The respiratory system of workers employed in the casting and processing of copper. Pneumonol Alergol Pol 66:433–439
Matteo R, Cattani S, Signorelli C (2018) Zinc exposure for female workers in a galvanizing plant in northern Italy. Intern J Occup Med and Env Health 31(1):113–124. https://doi.org/10.13075/ijomeh.1896.00878
Mattie MD, McElwee MK, Freedman JH (2008) Mechanism of copper-activated transcription: activation of AP-1, and the JNK/SAPK and p38 signal transduction pathways. J Mol Biol 383:1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.080
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V et al (2005) ATS/ERS Task Force. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26:319–338
Moynier F, Vance D, Fujii T et al (2017) The isotope geochemistry of zinc and copper. Mineral Geochem 82:543–600. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2017.82.13
Mukaida N (2003) Pathophysiological roles of interleukin-8/CXCL8 in pulmonary diseases. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284(4):L566-577. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00233.2002
Munday SW (2019) Arsenic. In: Nelson LS, Howland MA, Lewin NA (eds) Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies, 11th edn. McGraw-Hill Education, pp 1237–1250
Nafees AA, Kazi A, Fatmi Z et al (2011) Lung function decrement with arsenic exposure to drinking groundwater along River Indus: a comparative cross-sectional study. Environ Geochem Health 33:203–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9333-7
Nelson LS (2019) Copper. In: Nelson LS, Howland MA, Lewin NA (eds) Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies, 11th edn. McGraw-Hill Education, pp 1283–1291
Orfanos SE, Mavrommati I, Korovesi I et al (2004) Pulmonary endothelium in acute lung injury: from basic science to the critically ill. Intensive Care Med 30:1702–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-004-2370-x
Parvez F, Chen Y, Brandt-Rauf PW et al (2010) A prospective study of respiratory symptoms associated with chronic arsenic exposure in Bangladesh: findings from the Health Effects of Arsenic Longitudinal Study (HEALS). Thorax 65:528–533. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2009.119347
Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V et al (2005) Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J 26(5):948–968. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.05.00035205
Pereira TC, Campos MM, Bogo MR (2016) Copper toxicology, oxidative stress and inflammation using zebrafish as experimental model. J Appl Toxicol 36:876–885. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3303
Petrick JS, Blachere FM, Selmin O et al (2009) Inorganic arsenic as a developmental toxicant: in utero exposure and alterations in the developing rat lungs. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:583–591. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200800019
Roberts SM, James RC, Williams PL (2015) Principles of toxicology: environmental and industrial applications, 3rd edn. Wiley-Interscience
Shouman AE, Ahmed WS, El Hosseini DM et al (2018) Health impact of exposure to copper and zinc among workers in a metal die casting foundry in 10th Ramadan city. Egypt J Occup Med 42(3):383–398. https://doi.org/10.21608/EJOM.2018.12204
Smith AH, Marshall G, Yuan Y et al (2006) Increased mortality from lung cancer and bronchiectasis in young adults after exposure to arsenic in utero and in early childhood. Environ Health Perspect 114:1293–1296. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8832
Tockman MS, Pearson JD, Fleg JL et al (1995) Rapid decline in FEV1. A new risk factor for coronary heart disease mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:390–398. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.151.2.7842197
von Ehrenstein OS, Mazumder DN, Yuan Y et al (2005) Decrements in lung function related to arsenic in drinking water in West Bengal, India. Am J Epidemiol 162:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwi236
Warrell DA, Cox TM, Firth JD et al (2003) Oxford text book of medicine, 4th edn. Published by Oxford University Press, Oxford
Wolpe SD, Davatelis G, Sherry B et al (1988) Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med 167:570–581
Zubieta IX, Brown G, Cohen R et al (2009) Cananea copper mine: an international effort to improve hazardous working conditions in Mexico. Int J Occup Environ Health 15(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1179/107735209799449789
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the studied groups who generously agreed to participate and also the administrators of the factory who facilitated access to the study group.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work was carried out in collaboration between all authors. The authors MAR and MMF designed and performed the study and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. The author MAR managed the analyses of the study. The authors MAR and MMF designed the patient files and managed the literature searches. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fouad, M.M., Ramadan, M.A. Serum intracellular adhesion molecule-1 and interleukin-8 as predictors of pulmonary impairment among workers in secondary copper smelters. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 95, 365–375 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01770-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01770-3