Abstract
Objectives
It has been reported that occupational exposure to indium compounds, including indium-tin oxide, can induce pulmonary inflammation resulting in serious indium lung disease. However, whether there is an early effect of indium exposure on inflammatory factor expression remains unclear.
Methods
Twenty indium-tin oxide processing workers and 15 healthy volunteers were recruited to measure serum indium levels, respiratory symptoms, pulmonary function, and serum inflammatory factor levels.
Results
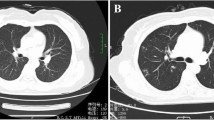
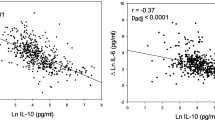
Although low serum indium was detected in workers, lung abnormalities were not increased, compared with healthy population. However, serum G-CSF, IL-4, IL-5, TNF-alpha, and TNF-beta levels were significantly increased, while IL-16 and TIMP-1 were obviously down-regulated in indium-tin oxide processing workers. These inflammatory factor levels showed a significant correlation with serum indium levels.
Conclusions
Basing on our findings, we speculate that low serum indium levels may induce inflammatory responses, which may be an adaptive response or may cause lung diseases. Therefore, further experiments or follow-up is needed. However, better safeguard procedures and indium exposure reduction should be considered in ITO industry.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu S, Hodgson G, Katz M, Dunn AR (2002) Evaluation of role of G-CSF in the production, survival, and release of neutrophils from bone marrow into circulation. Blood 100:854–861
Bomhard EM (2016) The toxicology of indium tin oxide. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 45:282–294
Chonan T, Taguchi O, Omae K (2007) Interstitial pulmonary disorders in indium-processing workers. Eur Respir J 29:317–324
Cummings KJ, Nakano M, Omae K, Takeuchi K, Chonan T, Xiao YL, Harley RA, Roggli VL, Hebisawa A, Tallaksen RJ, Trapnell BC, Day GA, Saito R, Stanton ML, Suarthana E, Kreiss K (2012) Indium lung disease. Chest 141:1512–1521
Cummings KJ, Virji MA, Park JY, Stanton ML, Edwards NT, Trapnell BC, Carey B, Stefaniak AB, Kreiss K (2016) Respirable indium exposures, plasma indium, and respiratory health among indium-tin oxide (ITO) workers. Am J Ind Med 59(7):522–531
Deckers J, Branco Madeira F, Hammad H (2013) Innate immune cells in asthma. Trends Immunol 34:540–547
Desai D, Brightling C (2010) TNF-alpha antagonism in severe asthma? Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 4:193–200
Finlay GA, O'Driscoll LR, Russell KJ, D'Arcy EM, Masterson JB, FitzGerald MX, O'CONNOR CM (1997) Matrix metalloproteinase expression and production by alveolar macrophages in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:240–247
Garcia H, Salter-Cid L, Stein-Streilein J (1992) Persistent interleukin-2 activity and molecular evidence for expression of lymphotoxin in the hapten-immune model for pulmonary interstitial fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6:22–28
Haugen J, Chandyo RK, Brokstad KA, Mathisen M, Ulak M, Basnet S, Valentiner-Branth P, Strand TA (2015) Cytokine concentrations in plasma from children with severe and non-severe community acquired pneumonia. PLoS ONE 10:e0138978
Homma T, Ueno T, Sekizawa K, Hirata M (2003) Interstitial pneumonia developed in a worker dealing with particles containing indium-tin oxide. J Occu Health 45:129–137
Hsu YT, Su TY, Liao HY, Kuo YC, Liou SH (2019) O5D.4 Exposure profiles of workers in indium-tin oxide powder manufacturing, target manufacturing and recycling factories in Taiwan. Occup Environ Med 76:A48
Josyula AB, Poplin GS, Kurzius-Spencer M, McClellen HE, Kopplin MJ, Stürup S, Lantz RC, Burgessa JL (2006) Environmental arsenic exposure and sputum metalloproteinase concentrations. Environ Res 102:283–290
Kumari S, Pasparakis M (2017) Epithelial cell death and inflammation in skin. Curr Top MicrobiolImmunol 403:77–93
Liao YH, Hwang LH, Kao JS, YiiH SJ, Lin SF, Lin CH, Lin YC, Aw TC (2006) Lipid peroxidation in workers exposed to aluminium, gallium, indium, arsenic, and antimony in the optoelectronic industry. J Occup Environ Med 48:789–793
Lison D, Laloy J, Corazzari I, Muller J, Rabolli V, Panin N, Huaux F, Fenoglio I, Fubini B (2009) Sintered indium-tin-oxide (ITO) particles: a new pneumotoxic entity. Toxicol Sci 108:472–481
Little FF, Cruikshank WW (2004) Interleukin-16 and peptide derivatives as immunomodulatory therapy in allergic lung disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther 4:837–846
Ministry of Health, Labor, Welfare (2010) Technical guidelines for preventing health impairment of workers engaged in the indium in oxide handling process. Government of Japan, Tokyo
Mohamed HS, Meguid MM (2017) Effect of nebulized budesonide on respiratory mechanics and oxygenation in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome: randomized controlled study. Saudi J Anaesth 11:9–14
Nagano K, Gotoh K, Kasai T, Aiso S, Nishizawa T, Ohnishi M, Ikawa N, Eitaki Y, Yamada K, Arito H, Fukushima Sh (2011a) Two- and 13-week inhalation toxicities of indium-tin oxide and indium oxide in rats. J Occup Health 53:51–63
Nagano K, Nishizawa T, Eitaki Y, Ohnishi M, Noguchi T, Arito H, Fukushima Sh (2011b) Pulmonary toxicity in mice by 2- and 13-week inhalation exposures to indium-tin oxide and indium oxide aerosols. J Occup Health 53:234–239
Nagano K, Nishizawa T, Umeda Y, Kasai T, Noguchi T, Gotoh K, Ikawa N, Eitaki Y, Kawasumi Y, Yamauchi T, Arito H, Fukushima S (2011c) Inhalation carcinogenicity and chronic toxicity of indium-tin oxide in rats and mice. J Occup Health 53:175–187
Nakano M, Omae K, Tanaka A, Hirata M, Michikawa T, Kikuchi Y, Yoshioka N, Nishiwaki Y, Chonan T (2009) Causal relationship between indium compound inhalation and effects on the lungs. J Occup Health 51:513–521
Olivas-Calderón E, Recio-Vega R, Gandolfi AJ, Lantz RC, González-Cortes T, Gonzalez-De Alba C, Froines JR, Espinosa-Fematt JA (2015) Lung inflammation biomarkers and lung function in children chronically exposed to arsenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 287:161–167
Omae K, Nakano M, Tanaka A, Hirata M, Hamaguchi T, Chonan T (2011) Indium lung-case reports and epidemiology. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 84:471–477
Tabei Y, Sonoda A, Nakajima Y, Biju V, Makita Y, Yoshida Y, Horie M (2016) Intracellular accumulation of indium ions released from nanoparticles induces oxidative stress, proinflammatory response and DNA damage. J Biochem 159:225–237
Tanaka H, Miyazaki N, Oashi K, Tanaka S, Ohmichi M, Abe S (2000) Sputum matrix metalloproteinase-9: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 ratio in acute asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105:900–905
Tanaka A, Hirata M, Homma T, Kiyohara Y (2010) Chronic pulmonary toxicity study of indium-tin oxide and indium oxide following intratracheal instillations into the lungs of hamsters. J Occup Health 52:14–22
Wu WT, Chung YT, Liao HY, Lai CH, Chen CY, Lee LH, Chen CJ, Liou SH (2014) 0061 Epidemiological study of lung inflammation and oxidative damage in indium tin oxide workers. Occup Environ Med 71:A66
Yang L, Sturgeon RE, Mester MJ (2010) Metrological triangle for measurements of isotope amount ratios of silver, indium, and antimony using multicollector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: the 21st century Harvard method. Anal Chem 82(21):8978–8982
Zhang-Hoover J, Finn P, Stein-Streilein J (2005) Modulation of ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and hyperreactivity by tolerogenic APC. J Immunol 175:7117–7124
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the participants, occupational physicians.
Funding
This study was financed by Natural Science Foundation of China (81473014) and Basic Research Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan (JCY20150403094740974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Y-JP. Performed the experiments: Y-JP, Z-WJ, and F-J. Analyzed the data: Y-JP and Z-WJ. Wrote the paper: Y-JP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Disclaimer
None.
Institution and ethics approval and informed consent
This study was performed in Department of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient enrolled in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhang, W. & Feng, J. Low serum indium levels induce expression disorders of some inflammatory factors. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 94, 23–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-020-01553-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-020-01553-2