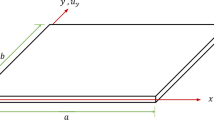
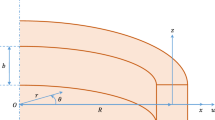
Abstract
As a main source of energy dissipation, thermoelastic damping (TED) cannot be ignored in designing resonators with high-quality factor. However, due to the size-dependent effect and the thermal relaxation, the TED models formulated in the classical theory are no longer able to accurately estimate the energy dissipation in the micro-/nano-resonators. To fill theses gaps, the present work aims at developing a new TED model for micro-plate resonators based on the modified couple stress theory incorporating memory-dependent derivative heat conduction model. The corresponding governing equations are derived, and the analytical solution for the TED is obtained. In order to discover the variation law of TED of micro-plate resonators, the numerical results corresponding to different materials and different theories are illustrated and compared. In calculation, the effects of the material parameters, the boundary conditions, the length scale parameters and the length on the peak value as well as the critical thickness of TED are further studied. It is expected that this novel model may provide a theoretical basis for designing high-performance micro-plate resonators under complex working conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, X., Bhushan, B., Takashima, K., Baek, C.W., Kim, Y.K.: Mechanical characterization of micro/nanoscale structures for MEMS/NEMS applications using nanoindentation techniques. Ultramicroscopy 97(1), 481–494 (2003)
Eom, K., Kwon, T.Y., Yoon, D.S., Lee, H.L., Kim, T.S.: Dynamical response of nanomechanical resonators to biomolecular interactions. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 76(11), 113408 (2007)
Lee, I., Lee, J.: Measurement uncertainties in resonant characteristics of MEMS resonators. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 27(2), 491 (2013)
Pelesko, J.A., Bernstein, D.H.: Modeling Mems and Nems. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2002)
Ciminelli, C., Dell’Olio, F., Armenise, M.N.: High-Q spiral resonator for optical gyroscope applications: numerical and experimental investigation. IEEE Photonics J. 4(5), 1844–1854 (2012)
Lin, L.W., Howe, R.T., Pisano, A.P.: Microelectromechanical filters for signal processing. Micro Electron. Mech. Syst. 7(3), 286–294 (1992)
Ekinci, K.L., Roukes, M.L.: Nanoelectromechanical systems. Science 76(6), 25–30 (2005)
Beek, J.V., Puers, R.: A review of MEMS oscillators for frequency reference and timing applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 22(1), 013001 (2012)
Duwel, A., Gorman, J., Weinstein, M., Borenstein, J., Ward, P.: Experimental study of thermoelastic damping in MEMS gyros. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 15(1), 70–75 (2003)
Zener, C.: Internal friction in solids II: general theory of thermoelastic internal friction. Phys. Today 47(2), 117–118 (1938)
Lifshitz, R., Roukes, M.L.: Thermoelastic damping in micro- and nano mechanical systems. Phys. Rev. B 61(8), 5600–5609 (2000)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I.: Modeling and simulations of thermoelastic damping in microplates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14(12), 1711–1717 (2004)
Sun, Y.X., Saka, M.: Thermoelastic damping in micro-scale circular plate resonators. J. Sound Vib. 329(3), 328–337 (2010)
Fang, Y.M., Li, P., Wang, Z.: Thermoelastic damping in the axisymmetric vibration of circular microplate resonators with two-dimensional heat conduction. J. Therm. Stress. 36(8), 830–850 (2013)
Fang, Y.M., Li, P., Zhou, H.Y.: Thermoelastic damping in rectangular microplate resonators with three-dimensional heat conduction. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 133, 578–589 (2017)
Zuo, W.L., Li, P., Zhang, J.R.: Analytical modeling of thermoelastic damping in bilayered microplate resonators. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 106, 128–137 (2016)
Eringen, A.C.: Nonlocal Continuum Field Theories. Springer, New York (2002)
Aifantis, E.C.: Gradient deformation models at nano, micro, and macro scales. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 121(2), 189–202 (1999)
Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Lam, D.C.C., Tong, P.: Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39(10), 2731–2743 (2002)
Tsiatas, G.C.: A new Kirchhoff plate model based on a modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46(13), 2757–2764 (2009)
Zhong, Z.Y., Zhang, W.M., Meng, G., Wang, M.Y.: Thermoelastic damping in the size-dependent microplate resonators based on modified couple stress theory. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 24(2), 431–445 (2015)
Segovia, F.J., Piazza, G.: Analytical and numerical methods to model anchor losses in 65-MHz AlN contour mode resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 25, 459–468 (2016)
Maxwell, J.C.: On the dynamical theory of gases. Phil. Mag. 157, 49–88 (1972)
Cattaneo, C.: A form of heat conduction equation which eliminates the paradox of instantaneous propagation. C. R. Phys. 247, 431–433 (1958)
Vernotte, P.M., Hebd, C.R.: Paradoxes in the continuous theory of the heat conduction. C. R. Phys. 246, 3154–3155 (1958)
Tzou, D.Y.: A unified field approach for heat conduction from macro-to-micro-scales. J. Heat Transf. 117(1), 8–16 (1995)
Choudhuri, S.K.: On a thermoelastic three-phase-lag model. J. Therm. Stress. 30(3), 231–238 (2007)
Lord, H.W., Shulman, Y.A.: A generalized dynamical theory of thermoelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 15(5), 299–309 (2007)
Green, A.E., Lindsay, K.A.: Thermoelasticity. J. Elast. 2(1), 1–7 (1972)
Yu, Y.J., Hu, W., Tian, X.G.: A novel generalized thermoelasticity model based on memory-dependent derivative. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 81, 123–134 (2014)
Zhou, H.Y., Li, P.: Thermoelastic damping in micro-and nanobeam resonators with non-Fourier heat conduction. IEEE Sens. J. 17(21), 6966–6977 (2017)
Guo, X., Yi, Y.B., Pourkamali, S.: A finite element analysis of thermoelastic damping in vented MEMS beam resonators. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 74, 73–82 (2013)
Zhou, H.Y., Shao, D.F., Song, X.R., Li, P.: Three-dimensional thermoelastic damping models for rectangular micro/nanoplate resonators with nonlocal-single-phase-lagging effect of heat conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 196, 123271 (2022)
Wang, Y.W., Chen, J., Zheng, R.Y., Li, X.F.: Thermoelastic damping in circular microplate resonators based on fractional dual-phase-lag model and couple stress theory. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 201, 123570 (2023)
Borjalilou, V., Asghari, M., Bagheri, E.: Small-scale thermoelastic damping in micro-beams utilizing the modified couple stress theory and the dual-phase-lag model. J. Therm. Stress. 42(7), 1–14 (2019)
Bhagwan, S., Harendra, K., Santwana, M.: Analysis of size effects on thermoelastic damping in the Kirchhoff’s plate resonator under Moore–Gibson–Thompson thermoelasticity. Thin-Walled Struct. 180, 109793 (2022)
Kakhki, E.K., Hosseini, S.M., Tahani, M.: An analytical solution for thermoelastic damping in a micro-beam based on generalized theory of thermoelasticity and modified couple stress theory. Appl. Math. Model. 40(4), 3164–3174 (2016)
Gu, B.D., He, T.H., Ma, Y.B.: Thermoelastic damping analysis in micro-beam resonators considering nonlocal strain gradient based on dual-phase-lag model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 180, 121771 (2021)
Stephen, T.: Theory of Plates and Shells. McGraw-Hill, New York (1959)
Dym, C.L., Shames, I.H.: Solid mechanics: a variational approach. Heidelberg Dordrecht, London (1980)
Li, P., Fang, Y.M., Hu, R.F.: Thermoelastic damping in rectangular and circular microplate resonators. J. Sound Vib. 331(3), 721–733 (2012)
Zhong, Z.Y., Zhang, W.M., Meng, G.: Thermoelastic damping in the size-dependent microplate resonators based on modified couple stress theory. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 24(2), 431–445 (2015)
Chakraverty, S., Pradhan, K.K.: Free vibration of functionally graded thin rectangular plates resting on Winkler elastic foundation with general boundary conditions using Rayleigh–Ritz method. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 6(4), 1450043 (2014)
Shi, S.H., He, T.H., Jin, F.: Thermoelastic damping analysis of size-dependent nano-resonators considering dual-phase-lag heat conduction model and surface effect. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 170(6), 120977 (2021)
Borjalilou, V., Asghari, M.: Small-scale analysis of plates with thermoelastic damping based on the modified couple stress theory and the dual-phase-lag heat conduction model. Acta Mech. 229, 3869–3884 (2018)
Babaei, A., Noorani, M.S., Ghanbari, A.: Temperature-dependent free vibration analysis of functionally graded micro-beams based on the modified couple stress theory. Microsyst Technol 23, 4599–4610 (2017)
Babaei, A., Rahmani, A.: On dynamic-vibration analysis of temperature-dependent Timoshenko microbeam possessing mutable nonclassical length scale parameter. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 27(16), 1451–1458 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11972176, 12062011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the data have no conflicting interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., He, T. Investigation on thermoelastic damping of micro-plate resonators based on the modified couple stress theory incorporating the memory-dependent derivative heat transfer model. Arch Appl Mech 93, 3495–3509 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-023-02450-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-023-02450-z