Abstract
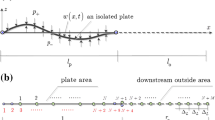
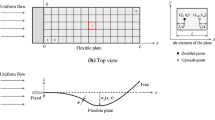
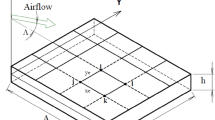
This paper aims at the static instability of a thin, flexible plate loaded by low-speed airflow in the wall effect. The present plate model has the flow impinging on its leading and free edge and is called an inverted cantilevered plate. A theoretical continuum model is first established, which mathematically presents such an instability problem as a mathematical function approximation problem within the framework of differential operators. The mirror image method considers the wall’s effect on fluids. The fluid force is presented as a Possio integral equation composed of Hilbert and Tricomi operators. We bring no approximation at the first equation level, and the derived instability equation is on the continuum. A convergent numerical scheme based on the Weierstrass theorem and the least square method is proposed to solve the instability equation. The results show that the current analysis strategy successfully predicts the plate instability in the wall effect compared with other theoretical and experimental studies. The confinement of the wall plays a destabilizing effect, and the critical flow velocity significantly decreases as the confinement is increased; however, the plate instability modes are not sensitive to wall confinement. The plate instability modes are close to the plate’s first natural ones and not sensitive to the channel character parameters. This conclusion allows further theoretical exploration of an approximation of the instability boundary from the obtained instability equation, a five-second scaling relation. The present plate aeroelasticity model on the continuum and its solution approximation may provide a new idea and essential reference for other instability problems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dowell, E.H.: Aeroelasticity of Plates and Shells. Noordhoff International Publishing, Leyden (1975)
Paidoussis, M.P.: Fluid-Structure Interactions. Slender Structures and Axial Flow, vol. 2, 1st edn. Elsevier Academic Press, London (2004)
Dowell, E.H.: Nonlinear oscillations of a fluttering plate II. AIAA J. 5, 1856–1862 (1967). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1967-13
Algazin, S.D., Kijko, I.A.: Aeroelastic vibrations and stability of plates and shells, vol. 25. Walter de Gruyter GmbH and Co KG (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110338379.20
Li, P., Yang, Y.R., Xu, W.: Nonlinear dynamics analysis of a two-dimensional thin panel with an external forcing in incompressible subsonic flow. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1251–1267 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0162-8
Li, P., Zhang, D.C., Li, Z.W., et al.: Bifurcations and post-critical behaviors of a nonlinear curved plate in subsonic airflow. Arch. Appl. Mech. 89(2), 343–362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-018-1471-x
Li, P., Li, Z.W., Liu, S., et al.: Non-linear limit cycle flutter of a plate with Hertzian contact in axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 81, 131–160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2018.04.014
Li, P., Li, Z.W., Dai, C.D., et al.: On the non-linear dynmics of a forced plate with boundary conditions correction in subsonic flow. Appl. Math. Model. 64, 15–46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.07.012
Zhang, D.C., Li, P., Zhu, Y.Z., et al.: Aeroleastic instability of an inverted cantilevered plate with cracks in axial subsonic airflow. Appl. Math. Model. 107, 782–801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2022.03.019
Guo, C.Q., Païdoussis, M.P.: Stability of rectangular plates with free side-edges in two-dimensional inviscid channel flow. J. Appl. Mech. 67(1), 171–176 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.321143
Watanabe, Y., Suzuki, S., Sugihara, M., et al.: A experimental study of paper flutter. J. Fluids Struct. 16, 529–542 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jfls.2001.0435
Watanabe, Y., Isogai, K., Suzuki, S., et al.: A theoretical study of paper flutter. J. Fluids Struct. 16, 543–560 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jfls.2001.0436
Doare, O., Michelin, S.: Piezoelectric coupling in energy-harvesting fluttering flexible plates: linear stability analysis and conversion efficiency. J. Fluids Struct. 27(8), 1357–1375 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2011.04.008
Tang, D.M., Dowell, E.H.: Aeroelastic response and energy harvesting from a cantilevered piezoelectric laminated plate. J. Fluids Struct. 76, 14–36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2017.09.007
Lucey, A.D.: The excitation of waves on a flexible panel in a uniform flow. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond, A 356, 2999–3039 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1998.0306
de Breuker, R., Abdalla, M.M., Gürdal, Z.: Flutter of partially rigid cantilevered plates in axial flow. AIAA J. 46, 936–946 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.31887
Zhang, J., Liu, N.S., Lu, X.Y.: Locomotion of a passively flapping flat plate. J. Fluid Mech. 659, 43–68 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112010002387
Dugundji, J., Dowell, E.H., Perkin, B.: Subsonic flutter of panels on continuous elastic foundations. AIAA J. 5, 1146–1154 (1963). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.1738
Kornecki, A., Dowell, E.H., O’brien, J.: On the aeroelastic instability of two-dimensional panels in uniform incompressible flow. J. Sound Vib. 47(2), 163–178 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(76)90715-X
Huang, L.: Flutter of cantilevered plates in axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 9(2), 127–147 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1006/jfls.1995.1007
Shelley, M.J., Zhang, J.: Flapping and bending bodies interacting with fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 43, 449–465 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-121108-145456
Yu, Y., Liu, Y., Amandolese, X.: A review on fluid-induced flag vibrations. Appl. Mech. Rev. 71(1), 010801 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042446
Michelin, S., Doaré, O.: Energy harvesting efficiency of piezoelectric flags in axial flows. J. Fluid Mech. 714, 489–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2012.494
Shoele, K., Mittal, R.: Energy harvesting by flow-induced flutter in a simple model of an inverted piezoelectric flag. J. Fluid Mech. 790, 582–606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.40
Silva-Leon, J., Cioncolini, A., Nabawy, M.R., et al.: Simultaneous wind and solar energy harvesting with inverted flags. Appl. Energy 239, 846–858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.246
Mazharmanesh, S., Young, J., Tian, F.B., et al.: Energy harvesting of two inverted piezoelectric flags in tandem, side-by-side and staggered arrangements. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 83, 108589 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108589
Park, S.G., Kim, B., Chang, C.B., et al.: Enhancement of heat transfer by a self-oscillating inverted flag in a Poiseuille channel flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 96, 362–370 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5037747
Fan, B.: Fluid-structure Interactions of Inverted Leaves and Flags. Doctoral dissertation, California Institute of Technology (2015)
Buchak, P., Eloy, C., Reis, P.M.: The clapping book: wind-driven oscillations in a stack of elastic sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(19), 194301 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.194301
Tavallaeinejad, M., Païdoussis, M.P., Legrand, M.: Nonlinear static response of low-aspect-ratio inverted flags subjected to a steady flow. J. Fluids Struct. 83, 413–428 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2018.09.003
Tavallaeinejad, M., Païdoussis, M.P., Legrand, M., et al.: Instability and the post-critical behaviour of two-dimensional inverted flags in axial flow. J. Fluid Mech. 890A14, 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2020.111
Serry, M., Tuffaha, A.: Static stability analysis of a thin plate with a fixed trailing edge in axial subsonic flow: Possion integral equation approach. Appl. Math. Model. 63, 644–659 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.07.005
Kim, D., Cossé, J., Cerdeira, C.H., et al.: Flapping dynamics of an inverted flag. J. Fluid Mech. 736R1, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2013.555
Goza, A., Colonius, T., Sader, J.E.: Global modes and nonlinear analysis of inverted-flag flapping. J. Fluid Mech. 857, 312–344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.728
Zhang, D., Liang, S., Li, P., et al.: A numerical and experimental study on the divergence instability of an inverted cantilevered plate in wall effect. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 1509–1528 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01681-8
Ryu, J., Park, S.G., Kim, B., et al.: Flapping dynamics of an inverted flag in a uniform flow. J. Fluids Struct. 57, 159–169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.06.006
Tang, C., Liu, N.S., Lu, X.Y.: Dynamics of an inverted flexible plate in a uniform flow. Phys. Fluids 27(7), 073601 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4923281
Sader, J.E., Cossé, J., Kim, D., Fan, B., et al.: Large-amplitude flapping of an inverted flag in a uniform steady flow-a vortex-induced vibration. J. Fluid Mech. 793, 524–555 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.139
Balakrishnan, A.V., IIiff, K.W.: Continuum aeroelastic model for inviscid subsonic bending-torsion wing flutter. J. Aerosp. Eng. 20, 152–164 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0893-1321(2007)20:(3152)
Balakrishnan, A.V.: Aeroelasticity: The Continuum Theory. Springer (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.: 12072298; 11772273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Zhang, D., Yin, H. et al. On the static aeroelastic instability of an inverted plate in wall effect: a continuum model and its solution approximation. Arch Appl Mech 93, 1825–1840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02358-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02358-0