Abstract
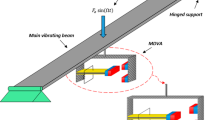
This paper investigates simultaneous vibration suppression and energy harvesting through a continuous dynamic vibration absorber (DVA) with piezoelectric coupling, both numerically and analytically. The proposed system is composed of a simply supported host beam that is under a periodic external forcing or transient excitation in the form of an initial condition. Besides, a DVA is attached to the host beam. First, the governing electromechanical equations of the coupled system are derived. Next, convergence analyses are performed to find the effects of the considering higher modes of the host and absorber beam. Furthermore, the frequency response curves of the mechanical and electrical responses are obtained. It is observed that the DVA can effectively annihilate the host structure vibrations, up to 98.5%, and at the same time harvest considerable levels of voltage/power. Moreover, comprehensive investigations on the role of various mechanical and electrical parameters on the system responses are carried out. To validate the numerical results, an analytical solution is provided and a great agreement between these solution schemes is observed. Also, the dynamics of the considered system under an initial condition is inspected. Finally, the effects of the PZT layers in vibration isolation performance are studied. Results divulged that, upon the proper tuning of the mechanical and electrical parameters, the proposed DVA can significantly scavenge energy and mitigate vibrations.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, M., Zhao, H.: Revisit to the theoretical analysis of a classical piezoelectric vibration energy harvester. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90(11), 2379–2395 (2020)
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R., Rahmanian, S.: Efficient energy harvesting from nonlinear vibrations of PZT beam under simultaneous resonances. Energy 182, 369–380 (2019)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: An experimentally validated bimorph cantilever model for piezoelectric energy harvesting from base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(2), 025009 (2009)
Wang, K.F., et al.: Nonlinear analysis of piezoelectric wind energy harvesters with different geometrical shapes. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90(4), 721–736 (2020)
Beeby, S.P., et al.: A micro electromagnetic generator for vibration energy harvesting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17(7), 1257 (2007)
Castagnetti, D.: A simply tunable electromagnetic pendulum energy harvester. Meccanica 54(6), 749–760 (2019)
Xie, Z., et al.: A hula-hooping-like nonlinear buckled elastic string electromagnetic energy harvester for omnidirectional broadband excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 29(7), 075026 (2020)
Suzuki, Y., et al.: A MEMS electret generator with electrostatic levitation for vibration-driven energy-harvesting applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 20(10), 104002 (2010)
Lallart, M., Pruvost, S., Guyomar, D.: Electrostatic energy harvesting enhancement using variable equivalent permittivity. Phys. Lett. A 375(45), 3921–3924 (2011)
Madinei, H., et al.: A hybrid piezoelectric and electrostatic vibration energy harvester. In: Shock and vibration, aircraft/aerospace, energy harvesting, acoustics and optics, vol. 9, pp. 189–195. Springer (2016)
Rahmani-Naeim-Abadi, M., Saidi, A.R., Askari-Farsangi, M.A.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting via thin annular sectorial plates: an analytical approach. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91(7), 3365–3382 (2021)
Abdelkefi, A.: Aeroelastic energy harvesting: a review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 100, 112–135 (2016)
Xia, G., et al.: Performance analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesters with a tip mass and nonlinearities of geometry and damping under parametric and external excitations. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90(10), 2297–2318 (2020)
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R., Friswell, M.I.: Efficient acoustic energy harvesting by deploying magnetic restoring force. Smart Mater. Struct. 28, 105037 (2019)
Zhu, P., et al.: Improving energy harvesting in a tri-stable piezomagnetoelastic beam with two attractive external magnets subjected to random excitation. Arch. Appl. Mech. 87(1), 45–57 (2017)
Fan, K., et al.: A nonlinear two-degree-of-freedom electromagnetic energy harvester for ultra-low frequency vibrations and human body motions. Renew. Energy 138, 292–302 (2019)
Kim, J., Dorin, P., Wang, K.W.: Vibration energy harvesting enhancement exploiting magnetically coupled bistable and linear harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 29(6), 065006 (2020)
Yang, Z., Tan, Y., Zu, J.: A multi-impact frequency up-converted magnetostrictive transducer for harvesting energy from finger tapping. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 126, 235–241 (2017)
Eghbali, P., et al.: Study in circular auxetic structures for efficiency enhancement in piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 16338 (2020)
Mamaghani, A.E., Khadem, S., Bab, S.: Vibration control of a pipe conveying fluid under external periodic excitation using a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 86(3), 1761–1795 (2016)
Vasques, C., Rodrigues, J.D.: Active vibration control of smart piezoelectric beams: comparison of classical and optimal feedback control strategies. Comput. Struct. 84(22–23), 1402–1414 (2006)
Zhang, C., Wang, H.: Swing vibration control of suspended structure using active rotary inertia driver system: parametric analysis and experimental verification. Appl. Sci. 9(15), 3144 (2019)
Zhang, C., Wang, H.: Robustness of the active rotary inertia driver system for structural swing vibration control subjected to multi-type hazard excitations. Appl. Sci. 9(20), 4391 (2019)
Alam, Z., Zhang, C., Samali, B.: The role of viscoelastic damping on retrofitting seismic performance of asymmetric reinforced concrete structures. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 19(1), 223–237 (2020)
Zhu, X., Chen, Z., Jiao, Y.: Optimizations of distributed dynamic vibration absorbers for suppressing vibrations in plates. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Active Control 37(4), 1188–1200 (2018)
Ari, M., Faal, R.T.: Passive vibration suppression of plate using multiple optimal dynamic vibration absorbers. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90(2), 235–274 (2020)
Liu, Y., et al.: Dynamic characteristics of quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation system for coupled dynamic vibration absorber. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1–20 (2021)
Frahm, H.: Device for damping vibrations of bodies. 1911, Google Patents
Zhang, C., Ali, A.: The advancement of seismic isolation and energy dissipation mechanisms based on friction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 146, 106746 (2021)
Abdelmoula, H., et al.: Control of base-excited dynamical systems through piezoelectric energy harvesting absorber. Smart Mater. Struct. 26(9), 095013 (2017)
Zoka, H., Afsharfard, A.: Double stiffness vibration suppressor and energy harvester: an experimental study. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 121, 1–13 (2019)
Kecik, K.: Assessment of energy harvesting and vibration mitigation of a pendulum dynamic absorber. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 106, 198–209 (2018)
Nili Ahmadabadi, Z., Khadem, S.E.: Nonlinear vibration control and energy harvesting of a beam using a nonlinear energy sink and a piezoelectric device. J. Sound Vib. 333(19), 4444–4457 (2014)
Pennisi, G., et al.: Design and experimental study of a nonlinear energy sink coupled to an electromagnetic energy harvester. J. Sound Vib. 437, 340–357 (2018)
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R., Liao, W.-H.: Exploiting bi-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber for simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration mitigation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 207, 106618 (2021)
Bibo, A., Abdelkefi, A., Daqaq, M.F.: Modeling and characterization of a piezoelectric energy harvester under combined aerodynamic and base excitations. J. Vib. Acoust. 137(3) (2015)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. Wiley (2011)
Rezaei, M., Khadem, S.E., Friswell, M.: Energy harvesting from the secondary resonances of a nonlinear piezoelectric beam under hard harmonic excitation. Meccanica 55(7), 1463–1479 (2020)
Sobhanirad, S., Afsharfard, A.: Improving application of galloping-based energy harvesters in realistic condition. Arch. Appl. Mech. 89(2), 313–328 (2019)
Zhao, X., Zhu, W., Li, Y.: Analytical solutions of nonlocal coupled thermoelastic forced vibrations of micro-/nano-beams by means of Green’s functions. J. Sound Vib 481, 115407 (2020)
Zhao, X., et al.: Forced vibration analysis of Timoshenko double-beam system under compressive axial load by means of Green’s functions. J. Sound Vib. 464, 115001 (2020)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from transverse galloping of bluff bodies. Smart Mater. Struct. 22(1), 015014 (2012)
Rao, S.S.: Vibration of continuous systems. Vol. 464, Wiley (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The orthonormality condition of the upper and lower beams, characteristic equation of the absorber, and \({\text{\rm Z}}_{i}\) relationship are provided in Eqs. (45–48).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R. & Liao, WH. Concurrent energy harvesting and vibration suppression utilizing PZT-based dynamic vibration absorber. Arch Appl Mech 92, 363–382 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02063-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02063-4