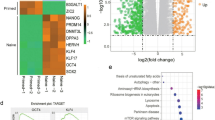
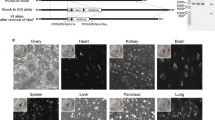
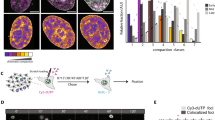
Abstract
Since Robert Feulgen first stained DNA in the cell, visualizing genome chromatin has been a central issue in cell biology to uncover how chromatin is organized and behaves in the cell. To approach this issue, we have developed single-molecule imaging of nucleosomes, a basic unit of chromatin, to unveil local nucleosome behavior in living cells. In this study, we investigated behaviors of nucleosomes with various histone H4 mutants in living HeLa cells to address the role of H4 tail acetylation, including H4K16Ac and others, which are generally associated with more transcriptionally active chromatin regions. We ectopically expressed wild-type (wt) or mutated H4s (H4K16 point; H4K5,8,12,16 quadruple; and H4 tail deletion) fused with HaloTag in HeLa cells. Cells that expressed wtH4-Halo, H4K16-Halo mutants, and multiple H4-Halo mutants had euchromatin-concentrated distribution. Consistently, the genomic regions of the wtH4-Halo nucleosomes corresponded to Hi-C contact domains (or topologically associating domains, TADs) with active chromatin marks (A-compartment). Utilizing single-nucleosome imaging, we found that none of the H4 deacetylation or acetylation mimicked H4 mutants altered the overall local nucleosome motion. This finding suggests that H4 mutant nucleosomes embedded in the condensed euchromatic domains with excess endogenous H4 nucleosomes cannot cause an observable change in the local motion. Interestingly, H4 with four lysine-to-arginine mutations displayed a substantial freely diffusing fraction in the nucleoplasm, whereas H4 with a truncated N-terminal tail was incorporated in heterochromatic regions as well as euchromatin. Our study indicates the power of single-nucleosome imaging to understand individual histone/nucleosome behavior reflecting chromatin environments in living cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data have been deposited with links to BioProject accession numbers PRJDB17378 (H2B-HaloTag pull-down) and PRJDB17379 (H4-HaloTag pull-down) in the DDBJ BioProject database.
References
Allahverdi A, Yang R, Korolev N, Fan Y, Davey CA, Liu CF, Nordenskiold L (2011) The effects of histone H4 tail acetylations on cation-induced chromatin folding and self-association. Nucleic Acids Res 39(5):1680–1691. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq900
Amitai A, Seeber A, Gasser SM, Holcman D (2017) Visualization of chromatin decompaction and break site extrusion as predicted by statistical polymer modeling of single-locus trajectories. Cell Rep 18(5):1200–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.018
Ashwin SS, Nozaki T, Maeshima K, Sasai M (2019) Organization of fast and slow chromatin revealed by single-nucleosome dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(40):19939–19944. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907342116
Benedum J, Meusch M (1999) Robert Fuelgen (1884–1955) - some biographical thoughts. Histochem Cell Biol 111(5):337–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004180050366
Bennett RL, Bele A, Small EC, Will CM, Nabet B, Oyer JA, Huang X, Ghosh RP, Grzybowski AT, Yu T, Zhang Q, Riva A, Lele TP, Schatz GC, Kelleher NL, Ruthenburg AJ, Liphardt J, Licht JD (2019) A mutation in histone H2B represents a new class of oncogenic driver. Cancer Discov 9(10):1438–1451. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0393
Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF (2006) Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313(5793):1642–1645. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127344
Bone JR, Lavender J, Richman R, Palmer MJ, Turner BM, Kuroda MI (1994) Acetylated histone H4 on the male X chromosome is associated with dosage compensation in Drosophila. Genes Dev 8(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.8.1.96
Consortium EP (2012) An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489(7414):57–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11247
Cremer T, Cremer M, Hubner B, Silahtaroglu A, Hendzel M, Lanctot C, Strickfaden H, Cremer C (2020) The interchromatin compartment participates in the structural and functional organization of the cell nucleus. BioEssays 42(2):e1900132. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201900132
Davey CA, Sargent DF, Luger K, Maeder AW, Richmond TJ (2002) Solvent mediated interactions in the structure of the nucleosome core particle at 1.9 a resolution. J Mol Biol 319(5):1097–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00386-8
Davis CA, Hitz BC, Sloan CA, Chan ET, Davidson JM, Gabdank I, Hilton JA, Jain K, Baymuradov UK, Narayanan AK, Onate KC, Graham K, Miyasato SR, Dreszer TR, Strattan JS, Jolanki O, Tanaka FY, Cherry JM (2018) The encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): data portal update. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D794–D801. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1081
Dion V, Gasser SM (2013) Chromatin movement in the maintenance of genome stability. Cell 152(6):1355–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.010
Dion MF, Altschuler SJ, Wu LF, Rando OJ (2005) Genomic characterization reveals a simple histone H4 acetylation code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(15):5501–5506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500136102
Dorigo B, Schalch T, Bystricky K, Richmond TJ (2003) Chromatin fiber folding: requirement for the histone H4 N-terminal tail. J Mol Biol 327(1):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00025-1
Ewels PA, Peltzer A, Fillinger S, Patel H, Alneberg J, Wilm A, Garcia MU, Di Tommaso P, Nahnsen S (2020) The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Nat Biotechnol 38(3):276–278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0439-x
Ewels PA, Peltzer A, Fillinger S, Patel H, Alneberg J, Wilm A, Garcia MU, Di Tommaso P, Nahnsen S (2022) The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7139814
Gatto A, Forest A, Quivy JP, Almouzni G (2022) HIRA-dependent boundaries between H3 variants shape early replication in mammals. Mol Cell 82(10):1909-1923.e1905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.017
Gorisch SM, Wachsmuth M, Toth KF, Lichter P, Rippe K (2005) Histone acetylation increases chromatin accessibility. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 24):5825–5834. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02689
Grunstein M (1997) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389(6649):349–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/38664
Hansen AS, Woringer M, Grimm JB, Lavis LD, Tjian R, Darzacq X (2018) Robust model-based analysis of single-particle tracking experiments with spot-on. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33125
Hansen JC, Maeshima K, Hendzel MJ (2021) The solid and liquid states of chromatin. Epigenetics Chromatin 14(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-021-00424-5
Hihara S, Pack CG, Kaizu K, Tani T, Hanafusa T, Nozaki T, Takemoto S, Yoshimi T, Yokota H, Imamoto N, Sako Y, Kinjo M, Takahashi K, Nagai T, Maeshima K (2012) Local nucleosome dynamics facilitate chromatin accessibility in living mammalian cells. Cell Rep 2(6):1645–1656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.008
Ide S, Sasaki A, Kawamoto Y, Bando T, Sugiyama H, Maeshima K (2021) Telomere-specific chromatin capture using a pyrrole-imidazole polyamide probe for the identification of proteins and non-coding RNAs. Epigenetics Chromatin 14(1):46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-021-00421-8
Ide S, Tamura S, Maeshima K (2022) Chromatin behavior in living cells: lessons from single-nucleosome imaging and tracking. BioEssays 44(7):e2200043. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.202200043
Iida S, Shinkai S, Itoh Y, Tamura S, Kanemaki MT, Onami S, Maeshima K (2022) Single-nucleosome imaging reveals steady-state motion of interphase chromatin in living human cells. Sci Adv 8(22):eabn5626. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abn5626
Iida S, Ide S, Tamura S, Tani T, Goto T, Shribak M, Maeshima K (2023) Orientation-Independent-DIC imaging reveals that a transient rise in depletion force contributes to mitotic chromosome condensation. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.11.566679
Izeddin I, Recamier V, Bosanac L, Cisse II, Boudarene L, Dugast-Darzacq C, Proux F, Benichou O, Voituriez R, Bensaude O, Dahan M, Darzacq X (2014) Single-molecule tracking in live cells reveals distinct target-search strategies of transcription factors in the nucleus. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02230
Jaqaman K, Loerke D, Mettlen M, Kuwata H, Grinstein S, Schmid SL, Danuser G (2008) Robust single-particle tracking in live-cell time-lapse sequences. Nat Methods 5(8):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1237
Kimura H, Cook PR (2001) Kinetics of core histones in living human cells: little exchange of H3 and H4 and some rapid exchange of H2B. J Cell Biol 153(7):1341–1353. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.153.7.1341
Koyama M, Kurumizaka H (2018) Structural diversity of the nucleosome. J Biochem 163(2):85–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvx081
Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Rahl PB, Abraham BJ, Reddy J, Ficarro SB, Dastur A, Amzallag A, Ramaswamy S, Tesar B, Jenkins CE, Hannett NM, McMillin D, Sanda T, Sim T, Kim ND, Look T, Mitsiades CS, Weng AP, Brown JR, Benes CH, Marto JA, Young RA, Gray NS (2014) Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Nature 511(7511):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13393
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lakadamyali M (2022) Single nucleosome tracking to study chromatin plasticity. Curr Opin Cell Biol 74:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2021.12.005
Lerner J, Gomez-Garcia PA, McCarthy RL, Liu Z, Lakadamyali M, Zaret KS (2020) Two-parameter mobility assessments discriminate diverse regulatory factor behaviors in chromatin. Mol Cell 79(4):677-688.e676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.05.036
Lewis CD, Laemmli UK (1982) Higher order metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for metalloprotein interactions. Cell 29(1):171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(82)90101-5
Li X, Li L, Pandey R, Byun JS, Gardner K, Qin Z, Dou Y (2012) The histone acetyltransferase MOF is a key regulator of the embryonic stem cell core transcriptional network. Cell Stem Cell 11(2):163–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.023
Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ (1997) Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 389(6648):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/38444
Maeshima K, Yahata K, Sasaki Y, Nakatomi R, Tachibana T, Hashikawa T, Imamoto F, Imamoto N (2006) Cell-cycle-dependent dynamics of nuclear pores: pore-free islands and lamins. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 21):4442–4451. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.03207
Maeshima K, Iida S, Tamura S (2021) Physical nature of chromatin in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a040675
Maeshima K, Iida S, Shimazoe MA, Tamura S, Ide S (2024) Is euchromatin really open in the cell? Trends Cell Biol 34(1):7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2023.05.007
Mann RK, Grunstein M (1992) Histone H3 N-terminal mutations allow hyperactivation of the yeast GAL1 gene in vivo. EMBO J 11(9):3297–3306. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05408.x
McGinty RK, Tan S (2015) Nucleosome structure and function. Chem Rev 115(6):2255–2273. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500373h
Mersfelder EL, Parthun MR (2006) The tale beyond the tail: histone core domain modifications and the regulation of chromatin structure. Nucleic Acids Res 34(9):2653–2662. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl338
Millan-Zambrano G, Burton A, Bannister AJ, Schneider R (2022) Histone post-translational modifications - cause and consequence of genome function. Nat Rev Genet 23(9):563–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-022-00468-7
Miron E, Oldenkamp R, Brown JM, Pinto DMS, Xu CS, Faria AR, Shaban HA, Rhodes JDP, Innocent C, de Ornellas S, Hess HF, Buckle V, Schermelleh L (2020) Chromatin arranges in chains of mesoscale domains with nanoscale functional topography independent of cohesin. Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba8811
Misteli T (2020) The self-organizing genome: principles of genome architecture and function. Cell 183(1):28–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.014
Mizushima S, Nagata S (1990) pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res 18(17):5322. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/18.17.5322
Nacev BA, Feng L, Bagert JD, Lemiesz AE, Gao J, Soshnev AA, Kundra R, Schultz N, Muir TW, Allis CD (2019) The expanding landscape of “oncohistone” mutations in human cancers. Nature 567(7749):473–478. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1038-1
Nagashima R, Hibino K, Ashwin SS, Babokhov M, Fujishiro S, Imai R, Nozaki T, Tamura S, Tani T, Kimura H, Shribak M, Kanemaki MT, Sasai M, Maeshima K (2019) Single nucleosome imaging reveals loose genome chromatin networks via active RNA polymerase II. J Cell Biol 218(5):1511–1530. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201811090
Nozaki T, Imai R, Tanbo M, Nagashima R, Tamura S, Tani T, Joti Y, Tomita M, Hibino K, Kanemaki MT, Wendt KS, Okada Y, Nagai T, Maeshima K (2017) Dynamic organization of chromatin domains revealed by super-resolution live-cell imaging. Mol Cell 67(2):282-293.e287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.018
Nozaki T, Shinkai S, Ide S, Higashi K, Tamura S, Shimazoe MA, Nakagawa M, Suzuki Y, Okada Y, Sasai M, Onami S, Kurokawa K, Iida S, Maeshima K (2023) Condensed but liquid-like domain organization of active chromatin regions in living human cells. Sci Adv 9(14):eadf1488. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adf1488
Olins DE, Olins AL (2003) Chromatin history: our view from the bridge. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(10):809–814. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1225
Otsuka A, Minami K, Higashi K, Kawaguchi A, Tamura S, Ide S, Hendzel MJ, Kurokawa K, Maeshima K (2024) Chromatin organization and behavior in HRAS-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Chromosoma. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-024-00817-x
Parthun MR (2007) Hat1: the emerging cellular roles of a type B histone acetyltransferase. Oncogene 26(37):5319–5328. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210602
Pepenella S, Murphy KJ, Hayes JJ (2014) Intra- and inter-nucleosome interactions of the core histone tail domains in higher-order chromatin structure. Chromosoma 123(1–2):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0435-8
Presman DM, Benitez B, Lafuente AL, Vazquez Lareu A (2024) Chromatin structure and dynamics: one nucleosome at a time. Histochem Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-024-02281-1
Rao SS, Huntley MH, Durand NC, Stamenova EK, Bochkov ID, Robinson JT, Sanborn AL, Machol I, Omer AD, Lander ES, Aiden EL (2014) A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 159(7):1665–1680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.021
Ricci MA, Manzo C, Garcia-Parajo MF, Lakadamyali M, Cosma MP (2015) Chromatin fibers are formed by heterogeneous groups of nucleosomes in vivo. Cell 160(6):1145–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.054
Robinson PJ, An W, Routh A, Martino F, Chapman L, Roeder RG, Rhodes D (2008) 30 nm chromatin fibre decompaction requires both H4–K16 acetylation and linker histone eviction. J Mol Biol 381(4):816–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.050
Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang X (2006) Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods 3(10):793–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth929
Selvin PR, Lougheed T, Tonks Hoffman M, Park H, Balci H, Blehm BH, Toprak E (2007) Fluorescence imaging with one-nanometer accuracy (FIONA). CSH Protoc 2007:pdb top27. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.top27
Shimamoto Y, Tamura S, Masumoto H, Maeshima K (2017) Nucleosome-nucleosome interactions via histone tails and linker DNA regulate nuclear rigidity. Mol Biol Cell 28(11):1580–1589. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-11-0783
Shogren-Knaak M, Ishii H, Sun JM, Pazin MJ, Davie JR, Peterson CL (2006) Histone H4–K16 acetylation controls chromatin structure and protein interactions. Science 311(5762):844–847. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1124000
Strickfaden H, Tolsma TO, Sharma A, Underhill DA, Hansen JC, Hendzel MJ (2020) Condensed chromatin behaves like a solid on the mesoscale in vitro and in living cells. Cell 183(7):1772-1784.e1713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.027
Taylor GC, Eskeland R, Hekimoglu-Balkan B, Pradeepa MM, Bickmore WA (2013) H4K16 acetylation marks active genes and enhancers of embryonic stem cells, but does not alter chromatin compaction. Genome Res 23(12):2053–2065. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.155028.113
Tinevez JY, Perry N, Schindelin J, Hoopes GM, Reynolds GD, Laplantine E, Bednarek SY, Shorte SL, Eliceiri KW (2017) TrackMate: an open and extensible platform for single-particle tracking. Methods 115:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.09.016
Tokunaga M, Imamoto N, Sakata-Sogawa K (2008) Highly inclined thin illumination enables clear single-molecule imaging in cells. Nat Methods 5(2):159–161. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1171
Ura K, Kaneda Y (2001) Reconstitution of chromatin in vitro. Methods Mol Biol 181:309–325. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-211-2:309
Wagh K, Stavreva DA, Jensen RAM, Paakinaho V, Fettweis G, Schiltz RL, Wustner D, Mandrup S, Presman DM, Upadhyaya A, Hager GL (2023) Dynamic switching of transcriptional regulators between two distinct low-mobility chromatin states. Sci Adv 9(24):eade1122. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ade1122
Watson JD, Crick FH (1953) Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature 171(4356):737–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/171737a0
Xiong K, Ma J (2019) Revealing Hi-C subcompartments by imputing inter-chromosomal chromatin interactions. Nat Commun 10(1):5069. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12954-4
Yusa K, Zhou L, Li MA, Bradley A, Craig NL (2011) A hyperactive piggyBac transposase for mammalian applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(4):1531–1536. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008322108
Zakirov AN, Sosnovskaya S, Ryumina ED, Kharybina E, Strelkova OS, Zhironkina OA, Golyshev SA, Moiseenko A, Kireev II (2021) Fiber-like organization as a basic principle for euchromatin higher-order structure. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:784440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.784440
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Myers RM, Brown M, Li W, Liu XS (2008) Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9(9):R137. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137
Zhang J, Lee D, Dhiman V, Jiang P, Xu J, McGillivray P, Yang H, Liu J, Meyerson W, Clarke D, Gu M, Li S, Lou S, Xu J, Lochovsky L, Ung M, Ma L, Yu S, Cao Q, Harmanci A, Yan KK, Sethi A, Gürsoy G, Schoenberg MR, Rozowsky J, Warrell J, Emani P, Yang YT, Galeev T, Kong X, Liu S, Li X, Krishnan J, Feng Y, Rivera-Mulia JC, Adrian J, Broach JR, Bolt M, Moran J, Fitzgerald D, Dileep V, Liu T, Mei S, Sasaki T, Trevilla-Garcia C, Wang S, Wang Y, Zang C, Wang D, Klein RJ, Snyder M, Gilbert DM, Yip K, Cheng C, Yue F, Liu XS, White KP, Gerstein M (2020) An integrative ENCODE resource for cancer genomics. Nat Commun 11(1):3696. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14743-w
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. K. M. Marshall for critical reading and editing of this manuscript. We thank Dr. H. Kimura for providing his antibodies, Dr. K. Hibino, Mr. M. A. Shimazoe, and Maeshima laboratory members for their helpful discussions and support. This work was supported by JSPS grants JP24H00061 (K. Maeshima), JP21H02453 (K. Maeshima), JP20H05936 (K. Maeshima), JP22H05606 (S. Ide), JP23K17398 (K. Maeshima, S. Ide), JP21H02535 (S. Ide), JP22H04925 (PAGS) (K. Maeshima), and Takeda Science Foundation (K. Maeshima). A.S. is a MEXT Scholar. S. Iida and K. Minami were SOKENDAI Special Researchers (JST SPRING JPMJSP2104) and are currently JSPS Fellows (S. Iida, JP23KJ0996; K. Minami, JP23KJ0998).
Funding
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, JP23KJ0996, JP23KJ0998, JP22H05606, JP23K17398, JP24H00061, JP21H02453, JP20H05936, JP21H02535, JP22H04925 (PAGS), Japan Science and Technology Agency, JPMJSP2104, and Takeda Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S. and K. Maeshima designed the project. A.S. constructed mutants of histone H4 and created the cell lines with help of S. Ide and S. Iida. A. S. and S. Iida performed single-nucleosome imaging, tracking, and analysis. A.S. performed the cell biology experiments with help of S. Iida. S.T. and K. Minami purified H4-Halo labeled nucleosomal DNA and prepared sequencing library with help of S. Ide. A.T. performed sequencing. K.H. and K.K. analyzed the sequencing data. A.S., S. Iida., and K. Maeshima wrote the manuscript with input from all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (AVI 3289 KB)
Supplementary file3 (AVI 3756 KB)
Supplementary file4 (AVI 2836 KB)
Supplementary file5 (AVI 3539 KB)
Supplementary file6 (AVI 4199 KB)
Supplementary file7 (AVI 3057 KB)
Supplementary file8 (AVI 2720 KB)
Supplementary file9 (AVI 12836 KB)
Supplementary file10 (AVI 10785 KB)
Supplementary file11 (AVI 9985 KB)
Supplementary file12 (AVI 11291 KB)
Supplementary file13 (AVI 3077 KB)
Supplementary file14 (AVI 12284 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Semeigazin, A., Iida, S., Minami, K. et al. Behaviors of nucleosomes with mutant histone H4s in euchromatic domains of living human cells. Histochem Cell Biol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-024-02293-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-024-02293-x