Abstract
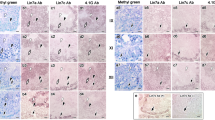
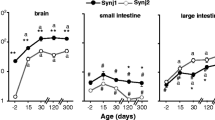
The membrane protein palmitoylated (MPP) family belongs to the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family. MPP1 interacts with the protein 4.1 family member, 4.1R, as a membrane skeletal protein complex in erythrocytes. We previously described the interaction of another MPP family, MPP6, with 4.1G in the mouse peripheral nervous system. In the present study, the immunolocalization of MPP6 in the mouse small intestine was examined and compared with that of E-cadherin, zonula occludens (ZO)-1, and 4.1B, which we previously investigated in intestinal epithelial cells. The immunolocalization of MPP6 was also assessed in the small intestines of 4.1B-deficient (−/−) mice. In the small intestine, Western blotting revealed that the molecular weight of MPP6 was approximately 55-kDa, and MPP6 was immunostained under the cell membranes in the basolateral portions of almost all epithelial cells from the crypts to the villi. The immunostaining pattern of MPP6 in epithelial cells was similar to that of E-cadherin, but differed from that of ZO-1. In intestinal epithelial cells, the immunostained area of MPP6 was slightly different from that of 4.1B, which was restricted to the intestinal villi. The immunolocalization of MPP6 in small intestinal epithelial cells was similar between 4.1B−/− mice and 4.1B+/+ mice. In the immunoprecipitation study, another MAGUK family protein, calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (CASK), was shown to molecularly interact with MPP6. Thus, we herein showed the immunolocalization and interaction proteins of MPP6 in the mouse small intestine, and also that 4.1B in epithelial cells was not essential for the sorting of MPP6.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aartsen WM, Kantardzhieva A, Klooster J, van Rossum AG, van de Pavert SA, Versteeg I, Cardozo BN, Tonagel F, Beck SC, Tanimoto N, Seeliger MW, Wijnholds J (2006) MPP4 recruits Psd-95 and Veli-3 towards the photoreceptor synapse. Hum Mol Genet 15:1291–1302
Alloisio N, Dalla Venezia N, Rana A, Andrabi K, Texier P, Gilsanz F, Cartron J-P, Delaunay J, Chishti AH (1993) Evidence that red blood cell protein p55 may participate in the skeleton-membrane linkage that involves protein 4.1 and glycophorin C. Blood 82:1323–1327
Bachmann A, Draga M, Grawe F, Knust E (2008) On the role of MAGUK proteins encoded by Drosophila Varicose during embryonic and postembryonic development. BMC Dev Biol. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-8-55
Baines AJ, Lu HC, Bennett PM (2013) The protein 4.1 family: hub proteins in animals for organizing membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838:605–619
Baumgartner M, Weiss A, Fritzius T, Heinrich J, Moelling K (2009) The PDZ protein MPP2 interacts with c-Src in epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 315:2888–2898
Bondow BJ, Faber ML, Wojta KJ, Walker E, Battle MA (2012) E-cadherin is required for intestinal morphogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol 371:1–12
Chen J, Terada N, Ohno N, Saitoh S, Saitoh Y, Ohno S (2011) Immunolocalization of membrane skeletal protein, 4.1G, in enteric glial cells in the mouse large intestine. Neurosci Lett 488:193–198
Chen J, Terada N, Saitoh Y, Huang Z, Ohno N, Ohno S (2013) Detection of MAPK signal transduction proteins in an ischemia/reperfusion model of mouse intestine using in vivo cryotechnique. Histochem Cell Biol 140:491–505
Cohen AR, Wood DF, Marfatia SM, Walther Z, Chishti AH, Anderson M (1998) Human CASK/Lin-2 binds syndecan-2 and protein 4.1 and localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 142:129–138
Dimitratos SD, Woods DF, Stathakis DG, Bryant PJ (1999) Signaling pathways are focused at specialized regions of the plasma membrane by scaffolding proteins of the MAGUK family. BioEssays 21:912–921
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998) The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 273:29745–29753
Fukuhara H, Masvuda M, Yageta M, Fukami T, Kuramochi M, Maruyama T, Kitamura T, Murakami Y (2003) Association of a lung tumor suppressor TSLC1 with MPP3, a human homologue of Drosophila tumor suppressor Dlg. Oncogene 22:6160–6165
Hanada T, Takeuchi A, Sondarva G, Chishitis AH (2003) Protein 4.1-mediated membrane targeting of human discs large in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:34445–34450
Hartsock A, Nerson WJ (2008) Adherens and tight junctions: structure, function and connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:660–669
Hermiston ML, Gordon JI (1995) In vivo analysis of cadherin function in the mouse intestinal epithelium: essential roles in adhesion, maintenance of differentiation, and regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 129:489–506
Huber AH, Nelson WJ, Weis WI (1997) Three-dimensional structure of the armadillo repeat region of β-catenin. Cell 90:871–882
Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Moroi S, Tsukita S (1997) Involvement of ZO-1 in cadherin-based cell adhesion through its direct binding to alpha catenin and actin filaments. J Cell Biol 138:181–192
Kamberov E, Makarova O, Roh M, Liu A, Karnak D, Straight S, Margolis B (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of Pals, proteins associated with mLin-7. J Biol Chem 275:11425–11431
Kamijo A, Saitoh Y, Ohno N, Ohno S, Terada N (2014) Immunohistochemical study of mouse sciatic nerves under various stretching conditions with “in vivo cryotechnique”. J Neurosci Methods 227:181–188
Lee S, Fan S, Makarova O, Straight S, Margolis B (2002) A novel and conserved protein–protein interaction domain of mammalian Lin-2/CASK binds and recruits SAP97 to the lateral surface of epithelia. Mol Cell Biol 22:1778–1791
Liu C, Weng H, Chen L, Yang S, Wang H, Debnath G, Guo X, Wu L, Mohandas N, An X (2013) Impaired intestinal calcium absorption in protein 4.1R-deficient mice due to altered expression of plasma membrane calcium ATPase 1b (PMCA1b). J Biol Chem 288:11407–11415
Lozovatsky L, Abayasekara N, Piawah S, Walther Z (2009) CASK deletion in intestinal epithelia causes mislocation of LIN7C and the DLG1/Scrib polarity complex without affecting cell polarity. Mol Biol Cell 20:4489–4499
Lue RA, Marfatia SM, Branton D, Chishti AH (1994) Cloning and characterization of hdlg: the human homologue of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor binds to protein 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9818–9822
Lusching S, Batz T, Armbruster K, Krasnow MA (2006) Serpentine and vermiform encode matrix proteins with chitin binding and deacetylation domains that limit tracheal tube length in Drosophila. Curr Biol 16:186–194
Marfatia SM, Lue RA, Branton D, Chishti AH (1995) Identification of the protein 4.1 binding interface on glycophorin C and p55, a homologue of the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 270:715–719
Moyer KE, Jacobs JR (2008) Varicose: a MAGUK required for the maturation and function of Drosophila septate junctions. BMC Dev Biol. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-8-99
Murakami S, Sakurai-Yageta M, Maruyama T, Murakami Y (2014) Trans-homophilic interaction of CADM1 activates PI3K by forming a complex with MAGuK-family proteins MPP3 and Dlg. PLoS ONE 9:e82894–e82903
Nix SL, Chishti AH, Anderson JM, Walther Z (2000) hCASK and hDlg in epithelia, and their Src homology 3 and guanylate kinase domains participate in both intramolecular and intermolecular interactions. J Biol Chem 275:41192–41200
Ohno N, Terada N, Murata S, Yamakawa H, Newsham IF, Katoh R, Ohara O, Ohno S (2004) Immunolocalization of protein 4.1B/DAL-1 during neoplastic transformation of mouse and human intestinal epithelium. Histochem Cell Biol 122:579–586
Ohno N, Terada N, Komada M, Saitoh S, Costantini F, Pace V, Germann PG, Weber K, Yamakawa H, Ohara O, Ohno S (2009) Dispensable role of protein 4.1B/DAL-1 in rodent adrenal medulla regarding generation of phenochromocytoma and plasmalemmal localization of TSLC1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:506–515
Park B, Alves CH, Lundvig DM, Tanimoto N, Beck SC, Huber G, Richard F, Klooster J, Andlauer TFM, Swindell EC, Jamrich M, Bivic AL, Seeliger MW, Wijnholds J (2011) Pals1 is essential for retinal pigment epithelium structure and neural retina stratification. J Neurosci 31:17230–17241
Perego C, Vanoni C, Massari S, Longhi R, Pietrini G (2000) Mammalian Lin-7 PDZ proteins associate with β-catenin at the cell-cell junctions of epithelia and neurons. EMBO J 19:3978–3989
Reissner C, Missler M (2014) MAGUKs end a tale of promiscuity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:17350–17351
Roberts S, Delury C, Marsh E (2012) The PDZ protein discs-large (DLG): the ‘Jekyll and Hyde’ of the epithelial polarity proteins. FEBS J 279:3549–3558
Roh MH, Makarova O, Liu C-J, Shin K, Lee S, Laurinec S, Goyal M, Wiggins R, Margolis B (2002) The Maguk protein, Pals1, function as an adapter, linking mammalian homologues of Crumbs and Discs Lost. J Cell Biol 157:161–172
Schneider MR, Dahlhoff M, Horst D, Hirschi B, Trülzsch K, Müller-Hücker J, Vogelmann R, Allgäuer M, Gerhard M, Steininger S, Wolf E, Kolligs FT (2010) A key role for E-cadherin in intestinal homeostasis and Paneth cell maturation. PLoS ONE 5:e14325–e14338
Shimo S, Saitoh S, Terada N, Ohno N, Saitoh Y, Ohno S (2010) Immunohistochemical detection of soluble immunoglobulins in living mouse small intestines using an in vivo cryotechnique. J Immunol Methods 361:64–74
Straight SW, Karnak D, Borg JP, Kamberov E, Dare H, Margolis B, Wade JB (2000) mLin-7 is localized to the basolateral surface of renal epithelia via its NH2 terminus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F464–F475
Straight SW, Pieczynski JN, Whiteman EL, Liu CJ, Margolis B (2006) Mammalian Lin-7 stabilizes polarity protein complexes. J Biol Chem 281:37738–37747
Subbaiah VK, Narayan N, Massimi P, Banks L (2012) Regulation of the DLG tumor suppressor by β-catenin. Int J Cancer 131:2223–2233
Takeichi M (1991) Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science 251:1451–1455
te Velthuis AJ, Admiraal JF, Bagowski CP (2007) Molecular evolution of the MAGUK family in metazoan genomes. BMC Evol Biol 7:129
Terada N, Ohno N, Yamakawa H, Baba T, Fujii Y, Ohara O, Ohno S (2004) Immunolocalization of protein 4.1B in rat digestive system. J Mol Histol 35:347–353
Terada N, Saitoh Y, Ohno N, Komada M, Saitoh S, Peles E, Ohno S (2012) Essential function of protein 4.1G targeting of membrane protein palmitoylated 6 into Schmidt-Lanterman incisures in myelinated nerves. Mol Cell Biol 32:199–205
Terada N, Saitoh Y, Ohno N, Komada M, Yamauchi J, Ohno S (2013) Involvement of Src in the membrane skeletal complex, MPP6-4.1G, in Schmidt-Lanterman incisures of mouse myelinated nerve fibers in PNS. Histochem Cell Biol 140:213–222
Tseng TC, Marfatia SM, Bryant PJ, Pack S, Zhuang Z, O’Brien JE, Lin L, Hanada T, Chishti AH (2001) VAM-1: a new member of the MAGUK family binds to human Veli-1 through a conserved domain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1518:249–259
van Rossum AG, Aartsen WM, Meuleman J, Klooster J, Malysheva A, Versteeg I, Arsanto JP, Le Bivic A, Wijinholds J (2006) Pals1/MPP5 is required for correct localization of Crb1 at the subapical region in polarized Muller glia cells. Hum Mol Genet 15:2659–2672
Wang Z, Zhang J, Ye M, Zhu M, Zhang B, Roy M, Liu J, An X (2014) Tumor suppressor role of protein 4.1B/DAL-1. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:4815–4830
Wu VM, Yu MH, Paik R, Banerjee S, Liang Z, Paul SM, Bhat MA, Beitel GJ (2008) Drosophila Varicose, a member of a new subgroup of basolateral MAGUKs, is required for septate junctions and tracheal morphogenesis. Development 134:999–1009
Yageta M, Kuramochi M, Masuda M, Fukami T, Fukuhara H, Murayama T, Shibuya M, Murakami Y (2002) Direct association of TSLC1 and DAL-1, two distinct tumor suppressor proteins in lung cancer. Cancer Res 62:5129–5133
Yang J, Pawlyk B, Wen XH, Adamian M, Soloviev M, Michaud N, Zhao Y, Sandberg MA, Makino CL, Li T (2007) MPP4 is required for proper localization of plasma membrane calcium ATPases and maintenance of calcium homeostasis at the rod photoreceptor synaptic terminals. Hum Mol Genet 16:1017–1029
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by a Grant from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKEN Number 25460267) to N. Terada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Akio Kamijo and Yurika Saitoh have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamijo, A., Saitoh, Y., Ohno, N. et al. Immunohistochemical study of the membrane skeletal protein, membrane protein palmitoylated 6 (MPP6), in the mouse small intestine. Histochem Cell Biol 145, 81–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1374-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1374-7