Abstract
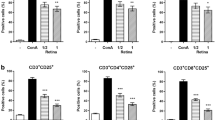
· Background: The suppressive effect of human fetal retinal pigment epithelium (HFRPE) on the activation of human CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells was evaluated in vitro. · Methods: Pure populations of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were isolated from human peripheral blood-derived buffy coats by negative immunomagnetic selection. The purity of the cells was examined by flow cytometry using anti-CD3-FITC, anti-CD4-FITC, anti-CD8-PE, and anti-CD20-PE mAbs. HFRPE cells were isolated from fetal eyes and pure cultures were obtained. The effect of normal or IFN-γ-activated HFRPE cells at early (P3) or late (P6) passages on the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells was assessed in two different T-cell activation assays. In both activation models anti-CD3 mAb (OKT3) provided the antigen-specific signal. The secondary signal for the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells was provided with anti-CD18 mAb (TS1/18) and anti-CD28 mAb (9.3) in the first and the second assay respectively. Cross-linking of these soluble mAbs was performed with sheep-anti-mouse IgG-coated latex beads. The T-cell activation was determined by cell proliferation measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation. In each activation assay T-cells were incubated with HFRPE cells in a ratio of T-cells to HFRPE of 1:1 or 1:4. · Results: CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were activated by cross-linking CD3 and CD18 in the first assay (CD3/CD18) and CD3 and CD28 in the second assay (CD3/CD28). In both assays HFRPE inhibited the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. IFN-γ-activated HFRPE cells totally suppressed the T-cell activation at a 1:1 ratio. This suppressive effect was weaker at lower cell ratios. Some donor variation was observed in the inhibition at the lower cell ratios, especially for the inhibition of CD8+ T-cell activation with anti-CD3/CD18. The passaging of HFRPE cells did not alter their suppressive effect on CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. · Conclusions: HFRPE cells suppressed the activation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in vitro. These findings suggest that RPE-induced immune suppression may play a significant role in maintaining immune privilege in the subretinal space.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 November 1998 Revised version received: 8 March 1999 Accepted: 8 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrokh-Siar, L., Rezai, K., Semnani, R. et al. Human fetal retinal pigment epithelium suppresses the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 237, 934–939 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004170050389
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004170050389