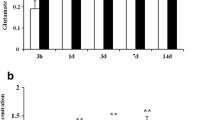
Abstract
Background
It is suggested that hypoxic–ischemic retinal diseases induce loss of retinal ganglion cells. Excess glutamate release is involved in these conditions. A predominant function of Müller cells is to regulate glutamate levels, but in these diseases the function is compromised. The present study was performed to investigate the role of interleukin-1β(IL-1β)on the glutamate uptake in retinal Müller cells under hypoxia and to study the possible mechanism.
Methods
The levels of IL-1β,Kir4.1, and GLAST in retinal Müller cells under hypoxia were analyzed by Western blotting and realtime-RT-PCR, and glutamate uptake assay was undertaken to investigate the activity of GLAST. After being treated with IL-1βunder normoxia, these proteins (Kir4.1 and GLAST) and their mRNAs, and glutamate uptake activity in Müller cells were investigated. To confirm the effect of IL-1βon glutamate uptake activity in Müller cells, addition of IL-1ra was used.
Results
Under hypoxia, Müller cells glutamate uptake, Kir4.1 and GLAST expressions were decreased significantly; however, IL-1βexpression was increased. IL-1βtreatment induced depression of glutamate uptake, decrease of Kir4.1 and GLAST expressions in retinal Müller cells under normoxia. Moreover, addition of IL-1ra significantly ameliorated decreases in Kir4.1 and GLAST expressions, and compromise of glutamate uptake activity in retinal Müller cells under hypoxia.
Conclusions
These findings indicated that decreases in Kir4.1 and GLAST expressions and depression of glutamate uptake in retinal Müller cells under hypoxia may be induced by the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stahl A, Agostini H, Hansen LL, Feltgen N (2007) Bevacizumab in retinal vein occlusion—results of a prospective case series. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245:1429–1436
Linsenmeier RA, Braun RD, McRipley MA, Padnick LB, Ahmed J, Hatchell DL, McLeod DS, Lutty GA (1998) Retinal hypoxia in long-term diabetic cats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39:1647–1657
Flammer J (1994) The vascular concept of glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol 38(Suppl):S3–S6
Tezel G, Wax MB (2004) The immune system and glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 15:80–84
Park SW, Cho CS, Jun HO, Ryu NH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Kim JS, Kim JH (2012) Anti-angiogenic effect of luteolin on retinal neovascularization via blockade of reactive oxygen species production. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:7718–7726
Tezel G, Yang X (2004) Caspase-independent component of retinal ganglion cell death, in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:4049–4059
Tinjust D, Kergoat H, Lovasik JV (2002) Neuroretinal function during mild systemic hypoxia. Aviat Space Environ Med 73:1189–1194
Neal MJ, Cunningham JR, Hutson PH, Hogg J (1994) Effects of ischaemia on neurotransmitter release from the isolated retina. J Neurochem 62:1025–1033
Ohia SE, Awe OS, Opere CA, LeDay AM, Harris LC, Sharif NA (2001) Hypoxia-induced [(3)H]D-aspartate release from isolated bovine retina: modulation by calcium-channel blockers and glutamatergic agonists and antagonists. Curr Eye Res 23:386–392
Rego AC, Santos MS, Oliveira CR (1996) Oxidative stress, hypoxia, and ischemia-like conditions increase the release of endogenous amino acids by distinct mechanisms in cultured retinal cells. J Neurochem 66:2506–2516
Tezel G, Wax MB (1999) Inhibition of caspase activity in retinal cell apoptosis induced by various stimuli in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:2660–2667
Li Q, Puro DG (2002) Diabetes-induced dysfunction of the glutamate transporter in retinal Müller cells. Invest ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:3109–3116
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2001) Glutamate transporters in neurologic disease. Arch Neurol 58:365–370
Harada T, Harada C, Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Sakagawa T, Nakayama N, Sasaki S, Okuyama S, Watase K, Wada K, Tanaka K (1998) Functions of the two glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 958:4663–4666
Rauen T, Taylor WR, Kuhlbrodt K, Wiessner M (1998) High-affinity glutamate transporters in the rat retina: a major role of the glial glutamate transporter GLAST-1 in transmitter clearance. Cell Tissue Res 291:19–31
Lehre KP, Davanger S, Danbolt NC (1997) Localization of the glutamate transporter protein GLAST in rat retina. Brain Res 744:129–137
Xie B, Qin Jiao Y, Cheng YZ, Shen X (2012) Effect of pigment epithelium derived factor on the glutamate uptake in retinal Müller cells under high glucose conditions. Invest Ophthal Vis Sci 53:1023–1032
Francke M, Faude F, Pannicke T, Bringmann A, Eckstein P, Reichelt W, Wiedemann P, Reichenbach A (2001) Electrophysiology of rabbit Müller (glial) cells in experimental retinal detachment and PVR. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:1072–1079
Napper GA, Pianta MJ, Kalloniatis M (1999) Reduced glutamate uptake by retinal glial cells under ischemic/hypoxic conditions. Vis Neurosci 16:149–158
Rehak M, Hollborn M, Iandiev I, Pannicke T, Karl A, Wurm A, Kohen L, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A (2009) Retinal gene expression and Müller cell responses after branch retinal vein occlusion in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:2359–2367
Zurolo E, de Groot M, Iyer A, Anink J, van Vliet EA, Heimans JJ, Reijneveld JC, Gorter JA, Aronica E (2012) Regulation of Kir4.1 expression in astrocytes and astrocytic tumors: a role for interleukin-1 β. J Neuroinflammation 9:280–297
Li SY, Fung FK, Fu ZJ, Wong D, Chan HH, Lo AC (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of lutein in retinal ischemic/hypoxic injury: in vivo and in vitro studies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:5976–5984
Paine SK, Basu A, Mondal LK, Sen A, Choudhuri S, Chowdhury IH, Saha A, Bhadhuri G, Mukherjee A, Bhattacharya B (2012) Association of vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor beta, and interferon gamma gene polymorphisms with proliferative diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol Vis 18:2749–2757
Xin X, Rodrigues M, Umapathi M, Kashiwabuchi F, Ma T, Babapoor-Farrokhran S, Wang S, Hu J, Bhutto I, Welsbie DS, Duh EJ, Handa JT, Eberhart CG, Lutty G, Semenza GL, Montaner S, Sodhi A (2013) Hypoxic retinal Muller cells promote vascular permeability by HIF-1-dependent up-regulation of angiopoietin-like 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E3425–E3434
Sivakumar V, Foulds WS, Luu CD, Ling EA, Kaur C (2011) Retinal ganglion cell death is induced by microglia derived pro-inflammatory cytokines in the hypoxic neonatal retina. J Pathol 224:245–260
Hangai M, Yoshimura N, Yoshida M, Yabuuchi K, Honda Y (1995) Interleukin-1 gene expression in transient retinal ischemia in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 36:571–578
Ward MM, Jobling AI, Kalloniatis M, Fletcher EL (2005) Glutamate uptake in retinal glial cells during diabetes. Diabetologia 48:351–360
Shono NI, Baskaeva EM (1989) Bradford’s method of determining protein: application, advantages and disadvantages. Lab Delo 4:4–7
Kusner L, Sarthy V, Mohr S (2004) Nuclear translocation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: a role in high glucose-induced apoptosis in retinal Müller cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1553–1561
Kowluru RA, Odenbach S (2004) Role of interleukin-1beta in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 88:1343–1347
Vik H, Holen E, Dybendal T, Elsayed S (1989) Reestimations of the protein concentrations of birch pollen allergen extracts selected as candidates for the international standard (IS) preparation. Ann Allergy 62:87–90
Gerhardinger C, McClure KD, Romeo G, Podestà F, Lorenzi M (2001) IGF-I mRNA and signaling in the diabetic retina. Diabetes 50:175–183
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Lange J, Yafai Y, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Eichler W (2008) Regulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor production and release by retinal glial (Müller) cells under hypoxia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:5161–5167
Pannicke T, Iandiev I, Uckermann O, Biedermann B, Kutzera F, Wiedemann P, Wolburg H, Reichenbach A, Bringmann A (2004) A potassium channellinked mechanism of glial cell swelling in the postischemic retina. Mol Cell Neurosci 26:493–502
Birkle DL, Bazan NG (1989) Light exposure stimulates arachidonic acid metabolism in intact rat retina and isolated rod outer segments. Neurochem Res 14:185–190
Tilleux S, Hermans E (2008) Down-regulation of astrocytic GLAST by microglia-related inflammation is abrogated in dibutyryl cAMP-differentiated cultures. J Neurochem 105:2224–2236
Korn T, Magnus T, Jung S (2005) Autoantigen specific T cells inhibit glutamate uptake in astrocytes by decreasing expression of astrocytic glutamate transporter GLAST: a mechanism mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEBJ 19:1878–1880
Liu Y, Biarnés Costa M, Gerhardinger C (2012) IL-1β is upregulated in the diabetic retina and retinal vessels: cell-specific effect of high glucose and IL-1β autostimulation. PLoS One 7:e36949
Beauregard C, Brandt PC, Chiou GC (2003) Induction of nitric oxide synthase and over-production of nitric oxide by interleukin-1b in cultured lacrimal gland acinar cells. Exp Eye Res 77:109–114
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81170860), Shanghai Nature Science Foundation (11ZR1422000) and Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo City (2012A610216).
Declaration of interest: The authors report no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Chen, H., Xu, C. et al. Role of interleukin-1β in hypoxia-induced depression of glutamate uptake in retinal Müller cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252, 51–58 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2516-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2516-z