Abstract
Background
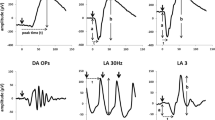
Automated detection of subtle changes in peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness (RNFLT) over time using optical coherence tomography (OCT) is limited by inherent image quality before layer segmentation, stabilization of the scan on the peripapillary retina and its precise placement on repeated scans. The present study evaluates image quality and reproducibility of spectral domain (SD)-OCT comparing different rates of automatic real-time tracking (ART).
Methods
Peripapillary RNFLT was measured in 40 healthy eyes on six different days using SD-OCT with an eye-tracking system. Image brightness of OCT with unaveraged single frame B-scans was compared to images using ART of 16 B-scans and 100 averaged frames. Short-term and day-to-day reproducibility was evaluated by calculation of intraindividual coefficients of variation (CV) and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) for single measurements as well as for seven repeated measurements per study day.
Results
Image brightness, short-term reproducibility, and day-to-day reproducibility were significantly improved using ART of 100 frames compared to one and 16 frames. Short-term CV was reduced from 0.94 ± 0.31 % and 0.91 ± 0.54 % in scans of one and 16 frames to 0.56 ± 0.42 % in scans of 100 averaged frames (P ≤ 0.003 each). Day-to-day CV was reduced from 0.98 ± 0.86 % and 0.78 ± 0.56 % to 0.53 ± 0.43 % (P ≤ 0.022 each). The range of ICC was 0.94 to 0.99. Sample size calculations for detecting changes of RNFLT over time in the range of 2 to 5 μm were performed based on intraindividual variability.
Conclusion
Image quality and reproducibility of mean peripapillary RNFLT measurements using SD-OCT is improved by averaging OCT images with eye-tracking compared to unaveraged single frame images. Further improvement is achieved by increasing the amount of frames per measurement, and by averaging values of repeated measurements per session. These strategies may allow a more accurate evaluation of RNFLT reduction in clinical trials observing optic nerve degeneration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sergott RC (2007) Historical perspective and future prospective for retinal nerve fiber loss in optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis. Int Ophthalmol Clin 47:15–24
Albrecht P, Ringelstein M, Mueller A, Keser N, Dietlein T, Lappas A, Foerster A, Hartung H, Aktas O, Methner A (2012) Degeneration of retinal layers in multiple sclerosis subtypes quantified by optical coherence tomography. Mult Scler 18(10):1422–1429. doi:10.1177/1352458512439237
Parisi V, Restuccia R, Fattapposta F, Mina C, Bucci MG, Pierelli F (2011) Morphological and functional retinal impairment in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1860–1867
Rohani M, Langroodi AS, Ghourchian S, Falavarjani KG, Soudi R, Shahidi G (2012) Retinal nerve changes in patients with tremor dominant and akinetic rigid Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci Jun 3 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1125-7
Schuman JS, Pedut-Kloizman T, Hertzmark E, Hee MR, Wilkins JR, Coker JG, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG, Swanson EA (1996) Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 103:1889–1898
Knight OJ, Chang RT, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL (2009) Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurements using time-domain and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 116:1271–1277
Budenz DL, Chang RT, Huang X, Knighton RW, Tielsch JM (2005) Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements using the stratus OCT in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:2440–2443
Menke MN, Knecht P, Sturm V, Dabov S, Funk J (2008) Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using 3D fourier-domain OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:5386–5391
González-García AO, Vizzeri G, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN (2009) Reproducibility of RTVue retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disc measurements and agreement with Stratus optical coherence tomography measurements. Am J Ophthalmol 147:1067–1074
Vizzeri G, Weinreb RN, Gonzalez-Garcia AO, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Sample PA, Zangwill LM (2009) Agreement between spectral-domain and time-domain OCT for measuring RNFL thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 93:775–781
Kim JS, Ishikawa H, Sung KR, Xu J, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Gabriele ML, Kagemann L, Duker JS, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS (2009) Retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement reproducibility improved with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol 93:1057–1063
Wu H, de Boer JF, Chen TC (2011) Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma 20:470–476
Castro Lima V, Rodrigues EB, Nunes RP, Sallum JF, Farah ME, Meyer CH (2011) Simultaneous confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy combined with high-resolution spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a review. J Ophthalmol 2011:743670
Kramer MS, Feinstein AR (1981) Clinical biostatistics. LIV. The biostatistics of concordance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29:111–123
Pierro L, Gagliardi M, Iuliano L, Ambrosi A, Bandello F (2012) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness reproducibility using seven different OCT instruments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:5912–5920
Budenz DL, Fredette MJ, Feuer WJ, Anderson DR (2008) Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements with stratus OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmology 115:661–666
Tzamalis A, Kynigopoulos M, Schlote T, Haefliger I (2009) Improved reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements with the repeat-scan protocol using the Stratus OCT in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247:245–252
Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, Qiu Q, Liu S, Li H, Xu G, Fan N, Huang L, Pang CP, Lam DS (2009) Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study. Ophthalmology 116:1257–1263
Mwanza JC, Chang RT, Budenz DL, Durbin MK, Gendy MG, Shi W, Feuer WJ (2010) Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic nerve head parameters measured with cirrus HD-OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:5724–5730
Talman LS, Bisker ER, Sackel DJ, Long DA Jr, Galetta KM, Ratchford JN, Lile DJ, Farrell SK, Loguidice MJ, Remington G, Conger A, Frohman TC, Jacobs DA, Markowitz CE, Cutter GR, Ying GS, Dai Y, Maguire MG, Galetta SL, Frohman EM, Calabresi PA, Balcer LJ (2010) Longitudinal study of vision and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 67:749–760
Garcia-Martin E, Pueyo V, Martin J, Almarcegui C, Ara JR, Dolz I, Honrubia FM, Fernandez FJ (2010) Progressive changes in the retinal nerve fiber layer in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur J Ophthalmol 20:167–173
Costello F, Hodge W, Pan YI, Eggenberger E, Coupland S, Kardon RH (2008) Tracking retinal nerve fiber layer loss after optic neuritis: a prospective study using optical coherence tomography. Mult Scler 14:893–905
Fisher JB, Jacobs DA, Markowitz CE, Galetta SL, Volpe NJ, Nano-Schiavi ML, Baier ML, Frohman EM, Winslow H, Frohman TC, Calabresi PA, Maguire MG, Cutter GR, Balcer LJ (2006) Relation of visual function to retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in multiple sclerosis. Ophthalmology 113:324–332
Henderson AP, Trip SA, Schlottmann PG, Altmann DR, Garway-Heath DF, Plant GT, Miller DH (2008) An investigation of the retinal nerve fibre layer in progressive multiple sclerosis using optical coherence tomography. Brain 131:277–287
Gordon-Lipkin E, Chodkowski B, Reich DS, Smith SA, Pulicken M, Balcer LJ, Frohman EM, Cutter G, Calabresi PA (2007) Retinal nerve fiber layer is associated with brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 69:1603–1609
Sepulcre J, Murie-Fernandez M, Salinas-Alaman A, García-Layana A, Bejarano B, Villoslada P (2007) Diagnostic accuracy of retinal abnormalities in predicting disease activity in MS. Neurology 68:1488–1494
Hood DC, Anderson SC, Wall M, Raza AS, Kardon RH (2009) A test of a linear model of glaucomatous structure-function loss reveals sources of variability in retinal nerve fiber and visual field measurements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:4254–4266
Garcia-Martin E, Pueyo V, Pinilla I, Ara JR, Martin J, Fernandez J (2011) Fourier-domain OCT in multiple sclerosis patients: reproducibility and ability to detect retinal nerve fiber layer atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:4124–4131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was not sponsored by an organization, therefore no financial relationship exists for any author. The authors have no proprietary or financial interest in any aspect of this study.
The authors have full control of all primary data, and agree to allow Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review their data upon request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pemp, B., Kardon, R.H., Kircher, K. et al. Effectiveness of averaging strategies to reduce variance in retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurements using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251, 1841–1848 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2337-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2337-0