Abstract
Background
To examine the effects of central corneal thickness on the measures obtained from transpalpebral tonometry (Diaton), and to identify correlations between intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements with Diaton and the Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT).
Methods
In this cross-sectional study, 162 eyes of 81 participants were included. Intraocular pressure measurements were obtained in all patients using Diaton and GAT. Central corneal thickness was determined by ultrasound pachymetry. The participants were stratified by corneal thickness: group I <530 μm (n = 56), group II 530–560 μm (n = 65), and group III >560 μm (n = 41).
Results
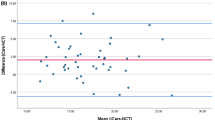
There were moderate correlations between IOP readings obtained using the Diaton and corrected GAT (C-GAT) (r = 0.303; P < 0.0001), and between corrected Diaton (C-Diaton), and C-GAT (r = 0.399; P < 0.0001). The mean Diaton tonometer readings were lower than C-GAT measurements (Diaton-corrected GAT mean difference, 0.9 ± 3.8 mmHg; c-Diaton-corrected GAT mean difference, 0.7 ± 3.5 mmHg). Differences were detected between the groups of patients for the GAT values [2.4 ± 3.6 mmHg for those with the thinnest corneas (<530 μm), 0.7 ± 3.6 mmHg for those with moderate corneas (between 531 μm and 560 μm), and −0.6 ± 3.6 mmHg for those with the thickest (>560 μm) corneas], whereas a significantly lower difference (0.9 ± 3.8 mmHg) was noted for the Diaton values of all individuals.
Conclusions
The Diaton measurements show moderate correlation with those provided by applanation tonometry. The Diaton tonometer seems to be more affected by the corneal thickness, especially in the thinnest corneas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandner D, Bohm A, Kostov S, Pillunat L (2005) Measurement of the intraocular pressure with the “transpalpebral tonometer” TGDc-01 in comparison with applanation tonometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:563–569
Troost A, Yun SH, Specht K, Krummenauer F, Schwenn O (2005) Transpalpebral tonometry: reliability and comparison with Goldmann applanation tonometry and palpation in healthy volunteers. Br J Ophthalmol 89:280–283
Losch A, Scheuerle A, Rupp V, Auffarth G, Becker M (2005) Transpalpebral measurement of intraocular pressure using the TGDc-01 tonometer versus standard Goldmann applanation tonometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243(4):313–316
Johnson M, Kass MA, Moses RA, Grodzki WJ (1978) Increased corneal thickness simulating elevated intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol 96:664–665
Hansen FK (1971) A clinical study of the normal human central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 49:82–89
Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K (1993) The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 115:592–596
Ehlers N, Bransen T, Sperling S (1975) Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol 53:34–43
Argus WA (1995) Ocular hypertension and central corneal thickness. Ophthalmology 102:1810–1812
Shah S, Chatterjee A, Mathai M et al (1999) Relationship between corneal thickness and measured intraocular pressure in a general ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmology 106:2154–2160
Copt RP, Thomas R, Mermoud A (1999) Corneal thickness in ocular hypertension, primary open-angle glaucoma and normal tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 117:14–16
Wolfs RCW, Klaver CCW, Vingerling JR, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, De Jong PTVM (1997) Distribution of central corneal thickness and its association with intraocular pressure: The Rotterdam Eye Study. Am J Ophthalmol 123:767–772
Stodtmeister R (1998) Applanation tonometry and correction according to corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 76:319–324
Evereklioglu C, Madenci E, Bayazit YA, Yilmaz K, Balat A, Bekir NA (2002) Central corneal thickness is lower in osteogenesis imperfecta and negatively correlates with the presence of blue sclera. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 22(6):511–515
Oliveira C, Tello C, Liebmann J, Ritch R (2006) Central corneal thickness is not related to anterior scleral thickness or axial length. J Glaucoma 15(3):190–194
Troost A, Specht K, Krummenauer F, Yun SH, Schwenn O (2005) Deviations between transpalpebral tonometry using TGDc-01 and Goldmann applanation tonometry depending on the IOP level. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243(9):853–858
Goldmann H, Schmidt T (1957) Applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologica 134:221–242
Kohlhaas M, Boehm AG, Spoerl E, Pursten A, Grein HJ, Pillunat LE (2006) Effect of corneal thickness, curvature and axial length on Goldmann applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol 124:471–476
Schlote T, Landenberger H (2005) Intraocular pressure difference in Goldmann applanation tonometry versus a transpalpebral tonometer TGDc-01“PRA” in glaucoma patients. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 222:123–131
Nesterov AP, Piletskii GK, Piletskii NG (2003) Transpalpebral tonometer for measuring intraocular pressure. Vestn Oftalmol 119:3–5
Meyer MW, Gockeln R, Hoy L, Meyer A, Erb C (2004) Comparison of intraocular pressure measurements with the digital tonometer TGDc-01 ‘PRA’ and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Ophthalmic Res 36:250–254
Muller A, Godenschweger L, Lang GE, Kampmeier J (2004) Prospective comparison of the new indentation tonometer TGdC-01, the non-contact tonometer PT100 and the conventional Goldmann applanation tonometer. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 221:762–768
van der Jagt LH, Jansonius NM (2005) Three portable tonometers, the TGDc-01, the ICARE and the Tonopen XL, compared with each other and with Goldmann applanation tonometry*. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:429–435
Lam AK, Lam CH, Chan R (2005) The validity of a digital eyelid tonometer (TGDc-01) and its comparison with Goldmann applanation tonometry – a pilot study. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:205–210
Garcia Resua C, Giraldez Fernandez MJ, Cervino Exposito A, Gonzalez Perez J, Yebra-Pimentel E (2005) Clinical evaluation of the new TGDc-01 “PRA” palpebral tonometer: comparison with contact and non-contact tonometry. Optom Vis Sci 82:143–150
Rombold F, Thiel MJ, Neubauer AS, Hirneiss C, Kampik A (2005) Evaluation of portable TGDc-01 tonometers and comparison with the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Ophthalmologe 102:158–162
Amm M, Hedderich J (2005) Transpalpebral tonometry with a digital tonometer in healthy eyes and after penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmologe 102:70–76
Acknowledgement
This study were not financed by any sponsor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No author has a financial interest in any product mentioned in the article.
No author has a conflict of interest in any product mentioned in the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toker, M.I., Vural, A., Erdogan, H. et al. Central corneal thickness and Diaton transpalpebral tonometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 881–889 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0769-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0769-8