Abstract
Background
To report the efficacy of combination photodynamic therapy and intravitreal ranibizumab for juxtafoveal, subretinal neovascular membrane (SRNVM) associated with type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia (IMT).
Methods
A 56-year-old woman with visual loss due to SRNVM secondary to IMT underwent primary treatment with a combination of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and intravitreal ranibizumab (0.5 mg). PDT was done as per the TAP study protocol, except that the laser spot size was same as the greatest linear diameter (GLD) of the lesion. This was followed by intravitreal ranibizumab (0.5 mg), 2 days later.
Results
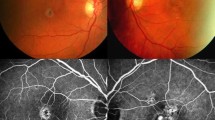
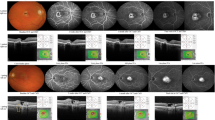
At the 16-week follow-up, clinical examination revealed regression of the SRNVM, with no evidence of subretinal fluid, exudates or fresh hemorrhages. Visual acuity improved by 2 Snellen lines (from 6/36 to 6/18). Clinical findings were confirmed on FFA and OCT. At the last follow-up at 9 months, the SRNVM remained quiescent and visual acuity stable. No treatment-related adverse effects were noted.
Conclusion
Combination therapy with PDT and intravitreal ranibizumab appears to be efficacious in the treatment of SRNVM associated with proliferative type 2 IMT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yannuzzi LA, Bardal AM, Freund KB, Chen KJ, Eandi CM, Blodi B (2006) Idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Arch Ophthalmol 124(4):450–460
Lee BL (1996) Bilateral subretinal neovascular membrane in idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Retina 16:344–346
Berger AS, McCuen BW, Brown GC, Brownlow RL (1997) Surgical removal of subfoveal neovascularization in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Retina 17:94–98
Potter MJ, Szabo SM, Sarraf D, Michels R, Schmidt-Erfurth U (2006) Photodynamic therapy for subretinal neovascularization in type 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Can J Ophthalmol 41:34–37
Jorge R, Costa RA, Calucci D, Scott IU (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) associated with the regression of subretinal neovascularization in idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245:1045–1048
Ruys J, De Laey JJ, Vanderhaeghen Y, Van Aken EH (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for the treatment of bilateral acquired juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasis associated with choroidal neovascular membrane. Eye 21:1433–1434
Treatment of Age-related Macular Degeneration by Photodynamic therapy (TAP) Study Group (1999) Photodynamic therapy of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in age related macular degeneration with verteporfin. Arch Ophthalmol 117:1329–1345
Engelbrecht NE, Aaberg TM Jr, Sung J, Lewis ML (2002) Neovascular membranes associated with idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol 120:320–324
Spaide RF (2006) Rationale for combination therapies for choroidal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 141(1):149–156
Shanmugam MP, Agarwal M (2005) RPE Atrophy following Photodynamic therapy in type 2A Idiopathic Parafoveal Telangiectasis. Indian J Ophthalmol 53:61–63
Dhalla MS, Shah GK, Blinder KJ, Ryan EH Jr, Mittra RA, Tewari A (2006) Combined photodynamic therapy with verteporfin and intravitreal bevacizumab for choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 26:988–993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have full control of all primary data and they agree to allow Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review their data upon request. There are no funding or other conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rishi, P., Shroff, D. & Rishi, E. Combined photodynamic therapy and intravitreal ranibizumab as primary treatment for subretinal neovascular membrane (SRNVM) associated with type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 619–621 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0732-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0732-0