Abstract
Background
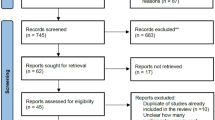
At present, studies regarding the efficacy and safety of tenecteplase for the treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) are still limited and inconsistent. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to compare the efficacy and safety of tenecteplase with alteplase for the treatment of AIS patients.
Methods
Literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library up to May 10, 2022. Primary outcomes of this study included 90-day good outcome (defined as an mRS score of 0–2) and 90-day excellent outcome (defined as an mRS score of 0–1). Risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were calculated using a random-effect model for each outcome.
Results
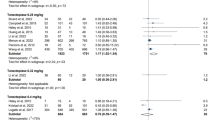
Fourteen studies with a total of 3537 patients were finally included in this meta-analysis. There was no statistical difference between patients receiving tenecteplase and those receiving alteplase in the rates of 90-day good outcome (RR 1.01; 95% CI 0.91–1.13; P = 0.79) and 90-day excellent outcome (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.92–1.19; P = 0.50). Patients receiving tenecteplase might associated with higher incidence of early neurologic improvement compared with those receiving alteplase (RR 1.29; 95% CI 1.04–1.61; P = 0.02). In addition, no statistical difference was observed between the two groups in other outcomes.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis indicated that tenecteplase in AIS patients is as safe and effective as alteplase and might provide more benefit than alteplase. However, due to several inherent limitations of this study, more prospective studies should be conducted to confirm the above results.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data available in article supplementary material.
References
Neumann-Haefelin T, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Fiebach JB, Gass A, Nolte C, Kucinski T et al (2004) Effect of incomplete (spontaneous and postthrombolytic) recanalization after middle cerebral artery occlusion: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 35(1):109–114
Bhatia R, Hill MD, Shobha N, Menon B, Bal S, Kochar P et al (2010) Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 41(10):2254–2258
Whiteley WN, Emberson J, Lees KR, Blackwell L, Albers G, Bluhmki E et al (2016) Risk of intracerebral haemorrhage with alteplase after acute ischaemic stroke: a secondary analysis of an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 15(9):925–933
Tanswell P, Modi N, Combs D, Danays T (2002) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tenecteplase in fibrinolytic therapy of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(15):1229–1245
Llevadot J, Giugliano RP, Antman EM (2001) Bolus fibrinolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA 286(4):442–449
Nepal G, Kharel G, Ahamad ST, Basnet B (2018) Tenecteplase versus alteplase for the management of acute ischemic stroke in a low-income country-Nepal: cost, efficacy, and safety. Cureus 10(2):e2178
Cannon CP, Gibson CM, McCabe CH, Adgey AA, Schweiger MJ, Sequeira RF et al (1998) TNK-tissue plasminogen activator compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: results of the TIMI 10B trial. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) 10B Investigators. Circulation 98(25):2805–2814
Van De Werf F, Adgey J, Ardissino D, Armstrong PW, Aylward P, Barbash G et al (1999) Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet (Lond, Engl) 354(9180):716–722
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H et al (2018) 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 39(2):119–177
Chen G, Bai C, Zhu Z, Li J, Shao S (2021) Effectiveness and safety of different doses of tenecteplase in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 100(3):e23805
Potla N, Ganti L (2022) Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Int J Emerg Med 15(1):1
David M, Alessandro L et al (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8:336–341
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 18(343):d5928
Seners P, Caroff J, Chausson N, Turc G, Denier C, Piotin M et al (2019) Recanalization before thrombectomy in tenecteplase vs. alteplase-treated drip-and-ship patients. J Stroke 21(1):105–107
Parsons MW, Miteff F, Bateman GA, Spratt N, Loiselle A, Attia J et al (2009) Acute ischemic stroke: imaging-guided tenecteplase treatment in an extended time window. Neurology 72(10):915–921
Haley EC Jr, Thompson JL, Grotta JC, Lyden PD, Hemmen TG, Brown DL et al (2010) Phase IIB/III trial of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke: results of a prematurely terminated randomized clinical trial. Stroke 41(4):707–711
Parsons M, Spratt N, Bivard A, Campbell B, Chung K, Miteff F et al (2012) A randomized trial of tenecteplase versus alteplase for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 366(12):1099–1107
Huang X, Cheripelli BK, Lloyd SM, Kalladka D, Moreton FC, Siddiqui A et al (2015) Alteplase versus tenecteplase for thrombolysis after ischaemic stroke (ATTEST): a phase 2, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint study. Lancet Neurol 14(4):368–376
Logallo N, Novotny V, Assmus J, Kvistad CE, Alteheld L, Rønning OM et al (2017) Tenecteplase versus alteplase for management of acute ischaemic stroke (NOR-TEST): a phase 3, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint trial. Lancet Neurol 16(10):781–788
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Churilov L, Yassi N, Kleinig TJ, Dowling RJ et al (2018) Tenecteplase versus alteplase before thrombectomy for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 378(17):1573–1582
Alemseged F, Ng FC, Williams C, Puetz V, Boulouis G, Kleinig TJ et al (2021) Tenecteplase vs alteplase before endovascular therapy in basilar artery occlusion. Neurology 96(9):e1272–e1277
George M, Baby N, Paul R, Zabeer M, Thomas C (2021) Comparison of thrombolytic agents in treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke; findings from a single centre follow up study in real-life settings. J Clin Neurosci 91:299–305
Mahawish K, Gommans J, Kleinig T, Lallu B, Tyson A, Ranta A (2021) Switching to tenecteplase for stroke thrombolysis: real-world experience and outcomes in a regional stroke network. Stroke 52(10):e590–e593
Psychogios K, Palaiodimou L, Katsanos AH, Magoufis G, Safouris A, Kargiotis O et al (2021) Real-world comparative safety and efficacy of tenecteplase versus alteplase in acute ischemic stroke patients with large vessel occlusion. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 14:1756286420986727
Bivard A, Zhao H, Churilov L, Campbell BCV, Coote S, Yassi N et al (2022) Comparison of tenecteplase with alteplase for the early treatment of ischaemic stroke in the Melbourne Mobile Stroke Unit (TASTE-A): a phase 2, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol 21(6):520–527
Kvistad CE, Næss H, Helleberg BH, Idicula T, Hagberg G, Nordby LM et al (2022) Tenecteplase versus alteplase for the management of acute ischaemic stroke in Norway (NOR-TEST 2, part A): a phase 3, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Neurol 21(6):511–519
Li S, Pan Y, Wang Z, Liang Z, Chen H, Wang D et al (2022) Safety and efficacy of tenecteplase versus alteplase in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (TRACE): a multicentre, randomised, open label, blinded-endpoint (PROBE) controlled phase II study. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7(1):47–53
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50(12):e344–e418
Tsivgoulis G, Kargiotis O, De Marchis G, Kohrmann M, Sandset EC, Karapanayiotides T et al (2021) Off-label use of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a critical appraisal of randomized and real-world evidence. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 14:1756286421997368
Ugur U, Platko S, Peters D, Bensabeur F, Terry J, Ludwig B et al (2021) Initial experience with tenecteplase as the intravenous thrombolytic of choice before mechanical thrombectomy for large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke. J NeuroIntervent Surg 13(SUPPL 1):A49–A50
Miller S, Warach SJ (2021) Tenecteplase versus alteplase reduces interfacility (door-in-door-out) transfer times. Stroke. 52(suppl 1)
Warach SJ, Winegar A, Ottenbacher A, Miller C, Gibson D (2022) Reduced hospital costs for ischemic stroke treated with tenecteplase. Stroke. 53(Suppl 1)
Oliveira M, Fidalgo M, Fontão L, Antão J, Marques S, Afreixo V et al (2021) Tenecteplase for thrombolysis in stroke patients: systematic review with meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med 42:31–37
Huang X, MacIsaac R, Thompson JL, Levin B, Buchsbaum R, Haley EC Jr et al (2016) Tenecteplase versus alteplase in stroke thrombolysis: an individual patient data meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Stroke 11(5):534–543
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Churilov L, Yassi N, Kleinig TJ, Dowling RJ et al (2020) Effect of intravenous tenecteplase dose on cerebral reperfusion before thrombectomy in patients with large vessel occlusion ischemic stroke: the EXTEND-IA TNK part 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 323(13):1257–1265
Li S, Campbell BCV, Schwamm LH, Fisher M, Parsons M, Li H et al (2022) Tenecteplase Reperfusion therapy in Acute ischaemic Cerebrovascular Events-II (TRACE II): rationale and design. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7(1):71–76
Coutts SB, Yu AYX (2022) Tenecteplase for acute stroke: the thrombolysis puzzle. Lancet Neurol 21:496–497
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ et al (2015) A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(1):11–20
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A et al (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2296–2306
Zhang J, Chen S, Shi S, Zhang Y, Kong D, Xie Y et al (2022) Direct endovascular treatment versus bridging therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for intravenous thrombolysis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 14(4):321–325
Campbell BCV, Kappelhof M, Fischer U (2022) Role of intravenous thrombolytics prior to endovascular thrombectomy. Stroke 31:101161strokeaha122036929
Katsanos AH, Safouris A, Sarraj A, Magoufis G, Leker RR, Khatri P et al (2021) Intravenous thrombolysis with tenecteplase in patients with large vessel occlusions: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 52(1):308–312
Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Burn J, Warlow C (1991) Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 337(8756):1521–1526
Greving JP, Schonewille WJ, Wijman CA, Michel P, Kappelle LJ, Algra A (2012) Predicting outcome after acute basilar artery occlusion based on admission characteristics. Neurology 78(14):1058–1063
Schulz UG, Fischer U (2017) Posterior circulation cerebrovascular syndromes: diagnosis and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88(1):45–53
Zhao Y, Zhao W, Guo Y, Li Y (2022) Endovascular thrombectomy versus standard medical treatment for stroke patients with acute basilar artery occlusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg
Smadja D, Olindo S, Saint-Vil M, Chausson N (2009) Sequential combination of two intravenous thrombolytics (recombinant tissue plasminogen activator/tenecteplase) in a patient with stroke and cardioembolic basilar artery occlusion. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 18(1):68–71
Alemseged F, Campbell BCV (2021) Tenecteplase thrombolysis in posterior circulation stroke. Front Neurol 12:678887
Muir K, Murray A, Wardlaw J, Ford I, Ford G (2018) Alteplase-tenecteplase trial evaluation for stroke thrombolysis (attest 2). Stroke 49
Coutts S, Kenney C, Yu A, Hill M (2016) TEMPO-2: TNK-tPA for minor ischaemic stroke with proven acute symptomatic occlusion trial-2. Int J Stroke 11(4):45
Dong Y, Sui Y, Cheng X, Wang DZ (2022) Is tenecteplase ready to replace alteplase to treat acute ischaemic stroke? The knowns and unknowns. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7(1):1–5
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PM and LH contributed to interpretation of the data, drafting the original manuscript, and the conception and design of this meta-analysis. PM, YZ, and LC contributed to literature search and selection, data extraction, and literature quality assessment. XL, YD, and HC contributed to data analysis, drafting the figures and tables, and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval was not required in this study, given the public nature of the data analyzed.
Informed consent
Not required.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P., Zhang, Y., Chang, L. et al. Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for the treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 269, 5262–5271 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11242-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11242-4