Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) could provide the added value for detecting brain microstructural alterations in the preclinical stage of Machado–Joseph disease/spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (MJD/SCA3) compared with MRI morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).
Methods
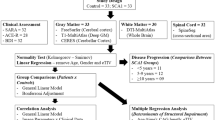
Twenty preclinical MJD/SCA3 patients and 21 healthy controls were enrolled. Three b values DWI and 3D T1-weighted images were acquired at 3.0 T. Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) approach was used to investigate the white matter (WM) alterations in the DTI metrics and NODDI metrics. Gray matter-based spatial statistics (GBSS) approach was used to investigate the grey matter (GM) alterations in the NODDI metrics. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) approach was performed on the 3D T1-weighted images. The relationship between the cytosine–adenine–guanine (CAG) repeat length and brain microstructural alterations of preclinical MJD/SCA3 was identified.
Results
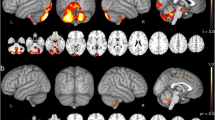
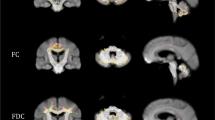
Compared with healthy controls, the preclinical MJD/SCA3 patients showed decreased FA and NDI as well as increased MD, AD, and RD in the WM of cerebellum and brainstem (corrected P < 0.05), and decreased NDI in the GM of cerebellar vermis (corrected P < 0.05). The CAG repeat length in preclinical MJD/SCA3 patients was negatively correlated with the reduced FA and NDI of the infratentorial WM and the reduced NDI of the cerebellum, and positively with the increased MD and RD of the infratentorial WM.
Conclusions
NOODI can provide novel quantitative microstructural changes in MJD/SCA3 carriers, expanding our understanding of the gray and white matter (axons and dendrites) degeneration in this frequent ataxia syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Axial diffusivity
- CAG:
-
Cytosine–adenine–guanine
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DWI:
-
Diffusion weighted imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FWE:
-
Familywise error
- GBSS:
-
Gray matter-based spatial statistics
- GM:
-
Grey matter
- ICP:
-
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
- MCP:
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- MJD:
-
Machado–Joseph disease
- ML:
-
Medial lemniscus
- NDI:
-
Neurite density index
- NODDI:
-
Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging
- ODI:
-
Orientation dispersion index
- PVE:
-
Partial volume effect
- RD:
-
Radial diffusivity
- SARA:
-
Scale for the assessment and rating of ataxia
- SCA:
-
Spinocerebellar ataxia
- SCP:
-
Superior cerebellar peduncle
- TBSS:
-
Tract-based spatial statistics
- VBM:
-
Voxel-based morphometry
- Viso:
-
Volume fraction of isotropic
- WM:
-
White matter
References
Costa MdC, Paulson HL (2012) Toward understanding Machado-Joseph disease. Prog Neurobiol 97:239–257
Koeppen AH (2018) The neuropathology of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3/Machado-Joseph disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 1049:233–241
Wan N, Chen Z, Wan L, Tang B, Jiang H (2020) MR imaging of SCA3/MJD. Front Neurosci 14:749
Maas RP, van Gaalen J, Klockgether T, van de Warrenburg BP (2015) The preclinical stage of spinocerebellar ataxias. Neurology 85:96–103
Kim DH, Kim R, Lee JY, Lee KM (2021) Clinical, imaging, and laboratory markers of premanifest spinocerebellar ataxia 1, 2, 3, and 6: a systematic review. J Clin Neurol 17:187–199
Klockgether T, Mariotti C, Paulson HL (2019) Spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:24
Chen M-L, Lin C-C, Rosenthal LS, Opal P, Kuo S-H (2021) Rating scales and biomarkers for CAG-repeat spinocerebellar ataxias: implications for therapy development. J Neurol Sci 424:117417
Jacobi H, Reetz K, du Montcel ST, Bauer P, Mariotti C, Nanetti L, Rakowicz M, Sulek A, Durr A, Charles P, Filla A, Antenora A, Schöls L, Schicks J, Infante J, Kang J-S, Timmann D, Di Fabio R, Masciullo M, Baliko L, Melegh B, Boesch S, Bürk K, Peltz A, Schulz JB, Dufaure-Garé I, Klockgether T (2013) Biological and clinical characteristics of individuals at risk for spinocerebellar ataxia types 1, 2, 3, and 6 in the longitudinal RISCA study: analysis of baseline data. Lancet Neurol 12:650–658
Rezende TJR, de Paiva JLR, Martinez ARM, Lopes-Cendes I, Pedroso JL, Barsottini OGP, Cendes F, França MC (2018) Structural signature of SCA3: from presymptomatic to late disease stages. Ann Neurol 84:401–408
Guo J, Chen H, Biswal BB, Guo X, Zhang H, Dai L, Zhang Y, Li L, Fan Y, Han S, Liu J, Feng L, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu C, Chen H (2020) Gray matter atrophy patterns within the cerebellum-neostriatum-cortical network in SCA3. Neurology 95:e3036–e3044
Wu X, Liao X, Zhan Y, Cheng C, Shen W, Huang M, Zhou Z, Wang Z, Qiu Z, Xing W, Liao W, Tang B, Shen L (2017) Microstructural alterations in asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: a tract-based spatial statistics study. Front Neurol 8:714
Andica C, Kamagata K, Hatano T, Saito Y, Ogaki K, Hattori N, Aoki S (2020) MR biomarkers of degenerative brain disorders derived from diffusion imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 52:1620–1636
Henf J, Grothe MJ, Brueggen K, Teipel S, Dyrba M (2018) Mean diffusivity in cortical gray matter in Alzheimer’s disease: the importance of partial volume correction. Neuroimage Clin 17:579–586
Kamiya K, Hori M, Aoki S (2020) NODDI in clinical research. J Neurosci Methods 346:108908
Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC (2012) NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 61:1000–1016
Colgan N, Siow B, O’Callaghan JM, Harrison IF, Wells JA, Holmes HE, Ismail O, Richardson S, Alexander DC, Collins EC, Fisher EM, Johnson R, Schwarz AJ, Ahmed Z, O’Neill MJ, Murray TK, Zhang H, Lythgoe MF (2016) Application of neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to a tau pathology model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 125:739–744
Gatto RG, Mustafi SM, Amin MY, Mareci TH, Wu Y-C, Magin RL (2018) Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging can detect presymptomatic axonal degeneration in the spinal cord of ALS mice. Funct Neurol 33:155–163
Fukutomi H, Glasser MF, Zhang H, Autio JA, Coalson TS, Okada T, Togashi K, Van Essen DC, Hayashi T (2018) Neurite imaging reveals microstructural variations in human cerebral cortical gray matter. Neuroimage 182:488–499
Zhang J, Gregory S, Scahill RI, Durr A, Thomas DL, Lehericy S, Rees G, Tabrizi SJ, Zhang H (2018) In vivo characterization of white matter pathology in premanifest huntington’s disease. Ann Neurol 84:497–504
Wen J, Zhang H, Alexander DC, Durrleman S, Routier A, Rinaldi D, Houot M, Couratier P, Hannequin D, Pasquier F, Zhang J, Colliot O, Le Ber I, Bertrand A (2019) Neurite density is reduced in the presymptomatic phase of disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90:387–394
Schmitz-Hübsch T, du Montcel ST, Baliko L, Berciano J, Boesch S, Depondt C, Giunti P, Globas C, Infante J, Kang JS, Kremer B, Mariotti C, Melegh B, Pandolfo M, Rakowicz M, Ribai P, Rola R, Schöls L, Szymanski S, van de Warrenburg BP, Dürr A, Klockgether T, Fancellu R (2006) Scale for the assessment and rating of ataxia: development of a new clinical scale. Neurology 66:1717–1720
Liu X-H, Li Y, Xu H-L, Sikandar A, Lin W-H, Li G-H, Li X-F, Alimu A, Yu S-B, Ye X-H, Wang N, Ni J, Chen W-J, Gan S-R (2020) Quantitative assessment of postural instability in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 7:1360–1370
Tournier JD, Smith R, Raffelt D, Tabbara R, Dhollander T, Pietsch M, Christiaens D, Jeurissen B, Yeh C-H, Connelly A (2019) MRtrix3: a fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage 202:116137
Nazeri A, Mulsant BH, Rajji TK, Levesque ML, Pipitone J, Stefanik L, Shahab S, Roostaei T, Wheeler AL, Chavez S, Voineskos AN (2017) Gray matter neuritic microstructure deficits in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 82:726–736
Vogt NM, Hunt JF, Adluru N, Dean DC, Johnson SC, Asthana S, Yu J-PJ, Alexander AL, Bendlin BB (2020) Cortical microstructural alterations in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Cereb Cortex 30:2948–2960
Guimarães RP, D’Abreu A, Yasuda CL, França MC, Silva BHB, Cappabianco FAM, Bergo FPG, Lopes-Cendes IT, Cendes F (2013) A multimodal evaluation of microstructural white matter damage in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Mov Disord 28:1125–1132
Kang JS, Klein JC, Baudrexel S, Deichmann R, Nolte D, Hilker R (2014) White matter damage is related to ataxia severity in SCA3. J Neurol 261:291
Jao C-W, Soong B-W, Huang C-W, Duan C-A, Wu C-C, Wu Y-T, Wang P-S (2019) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating multiple system atrophy cerebellar type and spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Brain Sci 9:354
Meira AT, Arruda WO, Ono SE, Franklin GL, de Carvalho NA, Raskin S, Ashizawa T, Camargo CHF, Teive HAG (2020) Analysis of diffusion tensor parameters in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 and type 10 patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 78:73–78
Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pengas G, Nestor PJ (2010) Absolute diffusivities define the landscape of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 133:529–539
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Rüb U, Schöls L, Paulson H, Auburger G, Kermer P, Jen JC, Seidel K, Korf H-W, Deller T (2013) Clinical features, neurogenetics and neuropathology of the polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias type 1, 2, 3, 6 and 7. Prog Neurobiol 104:38–66
Wilke C, Haas E, Reetz K, Faber J, Garcia-Moreno H, Santana MM, van de Warrenburg B, Hengel H, Lima M, Filla A, Durr A, Melegh B, Masciullo M, Infante J, Giunti P, Neumann M, de Vries J, Pereira de Almeida L, Rakowicz M, Jacobi H, Schüle R, Kaeser SA, Kuhle J, Klockgether T, Schöls L, Barro C, Hübener-Schmid J, Synofzik M (2020) Neurofilaments in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: blood biomarkers at the preataxic and ataxic stage in humans and mice. EMBO Mol Med 12:e11803
Costa MdC, Radzwion M, McLoughlin HS, Ashraf NS, Fischer S, Shakkottai VG, Maciel P, Paulson HL, Öz G (2020) In vivo molecular signatures of cerebellar pathology in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Mov Disord 35:1774–1786
Barrio-Arranz G, de Luis-García R, Tristán-Vega A, Martín-Fernández M, Aja-Fernández S (2015) Impact of MR acquisition parameters on DTI scalar indexes: a tractography based approach. PLoS ONE 10:e0137905
Edwards LJ, Pine KJ, Ellerbrock I, Weiskopf N, Mohammadi S (2017) NODDI-DTI: estimating neurite orientation and dispersion parameters from a diffusion tensor in healthy white matter. Front Neurosci 11:720
Stezin A, Bhardwaj S, Khokhar S, Hegde S, Jain S, Bharath RD, Saini J, Pal PK (2021) In vivo microstructural white matter changes in early spinocerebellar ataxia 2. Acta Neurol Scand 143:326–332
Chiu Y-J, Lin S-A, Chen W-L, Lin T-H, Lin C-H, Yao C-F, Lin W, Wu Y-R, Chang K-H, Lee-Chen G-J, Chen C-M (2020) Pathomechanism characterization and potential therapeutics identification for SCA3 targeting neuroinflammation. Aging 12:23619–23646
Duarte Lobo D, Nobre RJ, Oliveira Miranda C, Pereira D, Castelhano J, Sereno J, Koeppen A, Castelo-Branco M, Pereira de Almeida L (2020) The blood-brain barrier is disrupted in Machado-Joseph disease/spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: evidence from transgenic mice and human post-mortem samples. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8:152
Broad RJ, Gabel MC, Dowell NG, Schwartzman DJ, Seth AK, Zhang H, Alexander DC, Cercignani M, Leigh PN (2019) Neurite orientation and dispersion density imaging (NODDI) detects cortical and corticospinal tract degeneration in ALS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90:404–411
Scherzed W, Brunt ER, Heinsen H, de Vos RA, Seidel K, Bürk K, Schöls L, Auburger G, Del Turco D, Deller T, Korf HW, den Dunnen WF, Rüb U (2012) Pathoanatomy of cerebellar degeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) and type 3 (SCA3). Cerebellum 11:749–760
Leotti VB, de Vries JJ, Oliveira CM, de Mattos EP, Te Meerman GJ, Brunt ER, Kampinga HH, Jardim LB, Verbeek DS (2021) CAG repeat size influences the progression rate of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Ann Neurol 89:66–73
Peng H, Liang X, Long Z, Chen Z, Shi Y, Xia K, Meng L, Tang B, Qiu R, Jiang H (2019) Gene-Related Cerebellar Neurodegeneration in SCA3/MJD: a case-controlled imaging-genetic study. Front Neurol 10:1025
Huang S-R, Wu Y-T, Jao C-W, Soong B-W, Lirng J-F, Wu H-M, Wang P-S (2017) CAG repeat length does not associate with the rate of cerebellar degeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Neuroimage Clin 13:97
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2019J01435) to JPH and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81971082, Beijing) to SRG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JPH, XYC, and SRG were responsible for study design and conception and drafting of the manuscript. JPH and MCL was responsible for statistical analysis. MCL, HLX, ZQH, NPC, and YQT contributed to data collection and drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Chen, X., Xu, HL. et al. Brain structural abnormalities in the preclinical stage of Machado–Joseph disease/spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (MJD/SCA3): evaluation by MRI morphometry, diffusion tensor imaging and neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging. J Neurol 269, 2989–2998 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10890-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10890-2