Abstract
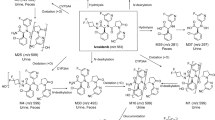
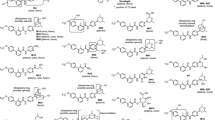
Four phase 1 studies were conducted to assess the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of idebenone (including parent drug and inactive metabolites QS10, QS6, and QS4) and to evaluate the safety of a wide range of idebenone doses and regimens in healthy adult men. After a single oral dose of idebenone 150 mg, 750 mg, or 1050 mg in fasted or fed subjects, blood samples were taken for up to 72 hours. In one study, after a single oral dose and a 7-day washout period, subjects received repeated doses of idebenone 150 mg or 750 mg every 8 hours for 14 days. In the repeated-dose study, urine samples also were taken. Plasma and urine samples were analysed with the use of liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Non-compartmental standard pharmacokinetic methods were used. In these studies, a total of 69 subjects ranging in age from 19 to 41 years (body weight, 57–94.6 kg) were included. Plasma concentrations of parent idebenone were low but increased in proportion to dose and increased approximately five-fold in the presence of food. Total QS4 was the main metabolite in plasma and urine. The most common adverse events were loose stool, fatigue, headache, and disturbances in attention. Idebenone was well tolerated in single oral doses up to 1050 mg and in repeated daily doses up to 2250 mg. Idebenone showed linear pharmacokinetics after single and repeated oral dosing. Administration after a meal resulted in the highest exposure to parent idebenone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lodi R, Cooper JM, Bradley JL,Manners D, Styles P, Taylor DJ,Schapira AHV (1999) Deficit of in vivomitochondrial ATP production in patientswith Friedreich ataxia. PNAS96:11492–11495
Buyse G, Mertens L, Di Salvo G,Matthijs I, Weidemann F, Eyskens B,Goossens W, Goemans N, SutherlandGR, Van Hove JL (2003) Idebenonetreatment in Friedreich’s ataxia: neurological,cardiac, and biochemicalmonitoring. Neurology 60:1679–1681
Hausse AO, Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Sidi D,Munnich A, Rotig A, Rustin P (2002)Idebenone and reduced cardiac hypertrophyin Friedreich’s ataxia. Heart(British Cardiac Society) 87:346–349
Mariotti C, Solari A, Torta D, Marano L,Fiorentini C, Di Donato S (2003)Idebenone treatment in Friedreichpatients: one-year-long randomizedplacebo-controlled trial. Neurology60:1676–1679
Arnold P, Boulat O, Maire R, Kuntzer T(2006) Expanding view of phenotypeand oxidative stress in Friedreich’sataxia patients with and withoutidebenone. Schweiz Arch NeurolPsychiatr 157:169–176
Artuch R, Aracil A, Mas A, Colome C,Rissech M, Monros E, Pineda M (2002)Friedreich’s ataxia: idebenone treatmentin early stage patients. Neuropediatrics33:190–193
Rustin P, Rotig A, Munnich A, Sidi D(2002) Heart hypertrophy and functionare improved by idebenone inFriedreich’s ataxia. Free Radic Res36:467–469
Di Prospero NA, Baker A, Jeaffries N,Fischbeck KH (2007) Neurologicaleffects of high-dose idebenone inpatients with Friedreich’s ataxia:a randomised, placebo controlled trial.Lancet Neurol 6:878–886
Kobayashi T, Yoshida K, Mitani M, ToriiH, Tanayama S (1985) Metabolism ofidebenone (CV-2619), a new cerebralmetabolism improving agent: isolationand identification of metabolites in therat and dog. J Pharmacobiodyn 8:448–456
Bodmer M, Vankan P, Dreier M, KutzKW, Drewe J (2009) Pharmacokineticsand metabolism of idebenone inhealthy male subjects. Eur J Clin PharmacolEpub ahead of print, 06 January
Di Prospero NA, Sumner CJ, PenzakSR, Ravina B, Fischbeck KH, Taylor JP(2007) Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokineticsof high-dose idebenone inpatients with Friedreich ataxia. ArchNeurol 64:803–808
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutz, K., Drewe, J. & Vankan, P. Pharmacokinetic properties and metabolism of idebenone. J Neurol 256 (Suppl 1), 31–35 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-1006-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-1006-z