Abstract
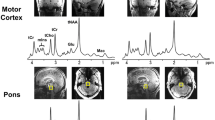
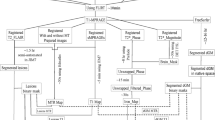
Previous in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (1H–MRSI) studies have found reduced levels of N–acetyl–aspartate (NAA) in multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions, the surrounding normal–appearing white matter (NAWM) and cortical grey matter (CGM), suggesting neuronal and axonal dysfunction and loss. Other metabolites, such as myoinositol (Ins), creatine (Cr), choline (Cho), and glutamate plus glutamine (Glx), can also be quantified by 1H–MRSI, and studies have indicated that concentrations of these metabolites may also be altered in MS. Relatively little is known about the time course of such metabolite changes. This preliminary study aimed to characterise changes in total NAA (tNAA, the sum of NAA and N–acetyl–aspartyl–glutamate), Cr, Cho, Ins and Glx concentrations in NAWM and in CGM, and their relationship with clinical outcome, in subjects with clinically early relapsing–remitting MS (RRMS). Twenty RRMS subjects and 10 healthy control subjects underwent 1H–MRSI examinations yearly for two years. Using the LCModel, tNAA, Cr, Cho, Ins and Glx concentrations were estimated both in NAWM and CGM.At baseline, the concentration of tNAA was significantly reduced in the NAWM of the MS patients compared to the control group (–7%, p = 0.003), as well as in the CGM (–8.7%, p = 0.009). NAWM tNAA concentrations tended to recover from baseline, but otherwise tissue metabolite profiles did not significantly change in the MS subjects, or relatively between MS and healthy control subjects. While neuronal and axonal damage is apparent from the early clinical stages of MS, this study suggests that initially it may be partly reversible. Compared with other MR imaging measures, serial 1H–MRSI may be relatively less sensitive to progressive pathological tissue changes in early RRMS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold DL, Matthews PM, Francis G, Antel J (1990) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain in vivo in the evaluation of multiple sclerosis: assessment of the load of disease. Magn Reson Med 14:154–159
Baltagi H (1995) Econometric analysis of panel data. New York: John Wiley and Sons
Bitsch A, Bruhn H, Vougioukas V, Stringaris A, Lassmann H, Frahm J, Bruck W (1999) Inflammatory CNS demyelination: histopathologic correlation with in vivo quantitative MR spectroscopy. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1619–1627
Bjartmar C, Kidd G, Mörk S, Rudick R, Trapp BD (2000) Neurological disability correlates with spinal cord axonal loss and reduced N–acetyl aspartate in chronic multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol 48:893–901
Bjartmar C, Battistuta J, Terada N, Dupree E, Trapp BD (2002) N–acetylaspartate is an axon–specific marker of mature white matter in vivo: a biochemical and immunohistochemical study on the rat optic nerve. Ann Neurol 51:51–58
Casanova B, Martínez–Bisbal MC, Valero C, Celda B, Marti–Bonmati L, Pascual A, Landente L, Coret F (2003) Evidence of Wallerian degeneration in normal appearing white matter in the early stages of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: a HMRS study. J Neurol 250:22–28
Chard DT, Griffin CM, Parker GJ, Kapoor R, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) Brain atrophy in clinically early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Brain 125:327–337
Chard DT, Griffin CM, McLean MA, Kapeller P, Kapoor R, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) Brain metabolite changes in cortical grey and normalappearing white matter in clinically early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Brain 125:2342–2352
Chard DT, Parker GJ, Griffin CM, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) The reproducibility and sensitivity of brain tissue volume measurements derived from an SPM–based segmentation methodology. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:259–267
Chard DT, McLean MA, Parker GJ, MacManus DG, Miller DH (2002) Reproducibility of in vivo metabolite quantification with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:219–225
Dalton CM, Chard DT, Davies GR, Miszkiel A, Altmann DR, Fernando K, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2004) Early development of multiple sclerosis is associated with progressive grey matter atrophy in patients presenting with clinically isolated syndromes. Brain 127:1101–1107
Dautry C, Vaufrey F, Brouillet E, Bizat N, Henry PG, Conde F, Bloch G, Hantraye P (2000) Early N–acetylaspartate depletion is a marker of neuronal dysfunction in rats and primates chronically treated with the mitochondrial toxin 3–nitropropionic acid. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:789–799
Davie CA, Hawkins CP, Barker GJ, Brennan A, Tofts PS, Miller DH, Mc– Donald WI (1994) Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 117:49–58
Davies GR, Altmann DR, Hadjiprocopis A, Rashid W, Chard DT, Griffin CM, Tofts PS, Barker GJ, Kapoor R, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2005) Increasing normal–appearing grey and white matter magnetisation transfer ratio abnormality in early relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 18
De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Arnold DL (1995) Reversible decreases in Nacetylaspartate after acute brain injury. Magn Reson Med 34:721–727
De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Fu L, Narayanan S, Stanley J, Francis GS, Antel JP, Arnold DL (1998) Axonal damage correlates with disability in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: results of a longitudinal magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Brain 121:1469–1477
De Stefano N, Narayanan S, Francis GS, Arnaoutelis R, Tartaglia MC, Antel JP, Matthews PM, Arnold DL (2001) Evidence of axonal damage in the early stages of multiple sclerosis and its relevance to disability. Arch Neurol 58:65–70
De Stefano N, Narayanan S, Francis SJ, Smith S, Mortilla M, Tartaglia MC, Bartolozzi ML, Guidi L, Federico A, Arnold DL (2002) Diffuse axonal and tissue injury in patients with multiple sclerosis with low cerebral lesion load and no disability. Arch Neurol 59:1565–1571
Degaonkar MN, Khubchandhani M, Dhawan JK, Jayasundar R, Jagannathan NR (2002) Sequential proton MRS study of brain metabolite changes monitored during a complete pathological cycle of demyelination and remyelination in a lysophosphatidyl choline (LCP)–induced experimental demyelinating lesion model. NMR Biomed 15:293–300
Fernando KT, McLean MA, Chard DT, MacManus DG, Dalton CM, Miszkiel KA, Gordon RM, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2004) Elevated white matter myo–inositol in clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Brain 127:1361–1369
Fisher JS, Jak AJ, Kniker JE, Rudick RA, Cutter G (1999) Administration and scoring manual for the multiple sclerosis functional composite measure (MSFC). New York: Demos
Fu L, Matthews PM, De Stefano N, Worsley KJ, Narayanan S, Francis GS, Antel JP, Wolfson C, Arnold DL (1998) Imaging axonal damage of normalappearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Brain 121:103–113
Grimaud J, Lai M, Thorpe J, Adeleine P, Wang L, Barker GJ, Plummer DL, Tofts PS, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1996) Quantification of MRI lesion load in multiple sclerosis: a comparison of three computer–assisted techniques. Magn Reson Imaging 14:495–505
Helms G (2001) Volume correction for edema in single–volume proton MR spectroscopy of contrast–enhancing multiple sclerosis lesions. Magn Reson Med 46:256–263
Kapeller P, McLean MA, Griffin CM, Chard D, Parker GJ, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2001) Preliminary evidence for neuronal damage in cortical grey matter and normal appearing white matter in short duration relapsing– remitting multiple sclerosis: a quantitative MR spectroscopic imaging study. J Neurol 248:131–138
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Mader I, Roser W, Kappos L, Hagberg G, Seelig J, Radue EW, Steinbrich W (2000) Serial proton MR spectroscopy of contrast–enhancing multiple sclerosis plaques: absolute metabolic values over 2 years during a clinical pharmacological study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(7):1220–1227
Matthews PM, Francis G, Antel J, Arnold DL (1991) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy for metabolic characterization of plaques in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 41:1251–1256
McLean MA, Woermann FG, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2000) Quantitative analysis of short echo time 1H–MRSI of cerebral gray and white matter. Magn Reson Med 44:401–411
Peterson JW, Bø L, Mork S, Chang A, Trapp BD (2001) Transected neurites, apoptotic neurons, and reduced inflammation in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol 50:389–400
Plummer DL (1992) Dispimage: a display and analysis tool for medical images. Rev Neuroradiol 5:489–495
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC, Johnson KP, Sibley WA, Silberberg DH, Tourtellotte WW (1983) New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 13:227–231
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30:672–679
Rao SM, Leo GJ, Bernardin L, Unverzagt F (1991) Cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. I. Frequency, patterns, and prediction. Neurology 41:685–691
Sarchielli P, Presciutti O, Pelliccioli GP, Tarducci R, Gobbi G, Chiarini P, Alberti A, Vicinanza F, Gallai V (1999) Absolute quantification of brain metabolites by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in normal–appearing white matter of multiple sclerosis patients. Brain 122:513–521
Sarchielli P, Presciutti O, Tarducci R, Gobbi G, Alberti A, Pelliccioli GP, Chiarini P, Gallai V (2002) Localized (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in mainly cortical gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 249:902–910
Sastre–Garriga J, Ingle GT, Chard DT, Ramiò–Torrenta Lí McLean MA, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2005) Metabolite changes in normal–appearing gray and white matter are linked with disability in early primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:569–573
Tiberio M, Chard DT, Altmann DR, Davies G, Griffin CM, Rashid W, Sastre–Garriga J, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2005) Gray and white matter volume changes in early RRMS. A 2– year longitudinal study. Neurology 64:1001–1007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiberio, M., Chard, D.T., Altmann, D.R. et al. Metabolite changes in early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 253, 224–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0964-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0964-z