Abstract
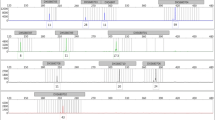
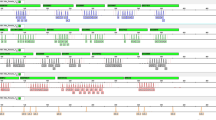
The evaluation of four pairs of tightly linked chromosome X (ChrX) short tandem repeat (STR)s at Xp22, Xq12, Xq26 and Xq28 led to the creation of the Argus X 8 multiplex amplification kit. These eight STRs are distributed as four closely linked pairs over the entire X-chromosome, and for practical reasons, they are assigned to four linkage groups 1–4. To achieve a further considerable enhancement in discrimination power, we suggest to include additional markers. A recent paper referred to the earlier evaluation of STR clusters at Xq12, Xq26 and Xq28, and here we present the pending data of linkage group 1 at Xp22. The newly established STR updates the Xp22 STR cluster which now presents three polymorphic markers: DXS10148 (PIC = 0.8556), DXS10135 (PIC = 0.9093) and DXS 8378 (PIC = 0.6454). Typing of 398 X-chromosomes provided 278 different and 200 unique haplotypes. All the other haplotypes observed appeared with frequencies in the range between 0.005 and 0.015. Considering this STR triple in the context with the three further triple clusters Xq12, Xq26 and Xq28 published earlier, we announced the development of a next generation of a ChrX STR cluster typing kit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asamura H, Sakai H, Kobayashi K et al (2006) MiniX-STR multiplex system population study in Japan and application to degraded DNA analysis. Int J Leg Med 120:174–181
Becker D, Rodig H, Augustin C et al (2008) Population genetic evaluation of eight X-chromosomal short tandem repeat loci using Mentype Argus X-8 PCR amplification kit. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:69–74
Edelmann J, Hering S, Michael M et al (2001) 16 X-chromosome STR loci frequency data from a German population. Forensic Sci Int 124:215–218
Edelmann J, Hering S, Augustin C, Szibor R (2008) Characterisation of the STR markers DXS10146, DXS10134 and DXS10147 located within a 79.1kb region at Xq28. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:41–46
Gomes I, Prinz M, Pereira R et al (2007) Genetic analysis of three US population groups using an X-chromosomal STR decaplex. Int J Leg Med 121:198–203
Hering S, Augustin C, Edelmann J et al (2006) DXS10079, DXS10074 and DXS10075 are STRs located within a 280-kb region of Xq12 and provide stable haplotypes useful for complex kinship cases. Int J Leg Med 120:337–345
Nagaraja R, MacMillan S, Jones C et al (1998) Integrated YAC/STS physical and genetic map of 22.5Mb of human Xq24-q26 at 56-kb inter-STS resolution. Genomics 52:247–266
Pepinski W, Skawronska M, Niemcunowicz-Janica A et al (2005) Polymorphism of four X-chromosomal STRs in a Polish population sample. Forensic Sci Int 151:93–95
Pereira R, Gomes I, Amorim A, Gusmao L (2007) Genetic diversity of 10 X chromosome STRs in northern Portugal. Int J Leg Med 121:192–197
Poetsch M, Petersmann H, Repenning A, Lignitz E (2005) Development of two pentaplex systems with X-chromosomal STR loci and their allele frequencies in a northeast German population. Forensic Sci Int 155:71–76
Robino C, Giolitti A, Gino S, Torre C (2006) Development of two multiplex PCR systems for the analysis of 12 X-chromosomal STR loci in a northwestern Italian population sample. Int J Leg Med 120:315–318
Shin SH, Yu JS, Park SW et al (2005) Genetic analysis of 18 X-linked short tandem repeat markers in Korean population. Forensic Sci Int 147:35–41
Wiegand P, Berger B, Edelmann J, Parson W (2003) Population genetic comparisons of three X-chromosomal STRs. Int J Leg Med 117:62–65
Zalan A, Volgyi A, Brabetz W et al (2008) Hungarian population data of eight X-linked markers in four linkage groups. Forensic Sci Int 175(1):73–78
Zalan A, Volgyi A, Jung M et al (2007) Hungarian population data of four X-linked markers: DXS8378, DXS7132, HPRTB, and DXS7423. Int J Leg Med 121:74–77
Zarrabeitia MT, Amigo T, Sanudo C et al (2002) A new pentaplex system to study short tandem repeat markers of forensic interest on X chromosome. Forensic Sci Int 129:85–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
1Xp22 STRs: Primer sequences and positions (DOC 37.5 KB)
ESM 2
DXS10148, DXS10135 and DXS8378: allele nomenclature, amplicon length and repeat composition primer positions are underlined; ** primer 1 covers 2.2 repeats; A* is present only in the alleles 21.1, 22.1 and 23.1–30.1 and absent in alleles 18–21, 22 and 23. (DOC 19.5 KB)
ESM 3
DXS8378–DXS10135–DXS19145 haplotype frequencies in a sample of 398 chromosomes (DOC 498 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hundertmark, T., Hering, S., Edelmann, J. et al. The STR cluster DXS10148–DXS8378–DXS10135 provides a powerful tool for X-chromosomal haplotyping at Xp22. Int J Legal Med 122, 489–492 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-008-0277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-008-0277-8