Abstract.
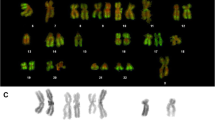
We have studied the distribution and methylation of CpG islands on human chromosomes, using the novel technique of self-primed in situ labeling (SPRINS). The SPRINS technique is a hybrid of the two techniques primed in situ labeling (PRINS) and nick translation in situ. SPRINS detects chromosomal DNA breaks, as in nick translation in situ, and not annealed primers, as is the case in PRINS. We analyzed in situ-generated DNA breaks induced by the restriction enzymes HpaII and MspI. These restriction enzymes enable the detection of chromosomal CpG islands. Both HpaII- and MspI-SPRINS produce a banding pattern resembling R-banding, indicating a higher level of CpG islands in R-positive bands than in R-negative bands. Our SPRINS banding observations also indicate differences in sequence copy number in the satellites of homologous acrocentric chromosomes. Furthermore, a comparison of homologous HpaII-SPRINS-banded X chromosomes of females from lymphocyte cultures grown without methotrexate or bromodeoxyuridine revealed methylation difference between them. The same comparison of homologous X chromosomes from the cell line GM01202D, which has four X chromosomes, one active and three inactive, revealed the active X chromosome to be hypermethylated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 February 1998; in revised form: 8 May 1998 / Accepted: 11 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, C., Koch, J. & Kjeldsen, E. CpG islands detected by self-primed in situ labeling (SPRINS). Chromosoma 107, 260–266 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050306
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050306