Abstract
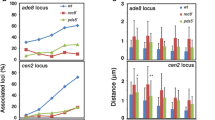
The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex is required for numerous cellular processes that involve interactions with DNA double-strand breaks. For the majority of these processes, the MRN complex is thought to act as a unit, with each protein aiding the activity of the others. We have examined the relationship between Mre11 and Rad50 during meiosis in the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus (Coprinopsis cinerea), investigating to what extent activities of Mre11 and Rad50 are interdependent. We showed that mre11-1 is epistatic to rad50-1 with respect to the time of meiotic arrest, indicating that Mre11 activity facilitates the diffuse diplotene arrest of rad50 mutants. Anti-Mre11 and anti-Rad50 antibodies were used to examine MRN complex localization in a wild-type strain and in spo11, mre11, and rad50 mutants. In wild type, numbers of Mre11 and Rad50 foci peaked at time points corresponding to leptotene and early zygotene. In the spo11-1 mutant, which is defective in meiotic double-strand break formation, foci accumulated throughout prophase I. Of seven MRN mutants examined, only two rad50 strains exhibited Mre11 and Rad50 foci that localized to chromatin, although Mre11 protein was found in the cell for all of them. Analysis of predicted mutant structures showed that stable localization of Mre11 and Rad50 does not depend upon a wild-type hook-proximal coiled coil, but does require the presence of the Rad50 ATPase/adenylate cyclase domains. We found that Mre11 and Rad50 were interdependent for binding to meiotic chromosomes. However, the majority of foci observed apparently contained only one of the two proteins. Independent Mre11 and Rad50 foci might indicate disassociation of the complex during meiosis or could reflect independent structural roles for the two proteins in meiotic chromatin.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya SN, Many AM, Schroeder AP, Kennedy FM, Savytskyy OP, Grubb JT, Vincent JA, Friedle EA, Celerin M, Maillet DS, Palmerini HJ, Greischar MA, Moncalian G, Williams RS, Tainer JA, Zolan ME (2008) Coprinus cinereus rad50 mutants reveal an essential structural role for Rad50 in axial element and synaptonemal complex formation, homolog pairing and meiotic recombination. Genetics 180:1889–1907
Adams KE, Medhurst AL, Dart DA, Lakin ND (2006) Recruitment of ATR to sites of ionising radiation-induced DNA damage requires ATM and components of the MRN protein complex. Oncogene 25:3894–3904
Ajimura M, Leem SH, Ogawa H (1993) Identification of new genes required for meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 133:51–66
Alani E, Subbiah S, Kleckner N (1989) The yeast RAD50 gene encodes a predicted 153-kD protein containing a purine nucleotide-binding domain and two large heptad-repeat regions. Genetics 122:47–57
Anderson DE, Trujillo KM, Sung P, Erickson HP (2001) Structure of the Rad50 x Mre11 DNA repair complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem 276:37027–37033
Borde V, Lin W, Novikov E, Petrini JH, Lichten M, Nicolas A (2004) Association of Mre11p with double-strand break sites during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell 13:389–401
Buscemi G, Savio C, Zannini L, Micciche F, Masnada D, Nakanishi M, Tauchi H, Komatsu K, Mizutani S, Khanna K, Chen P, Concannon P, Chessa L, Delia D (2001) Chk2 activation dependence on Nbs1 after DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 21:5214–5222
Carney JP, Maser RS, Olivares H, Davis EM, Le Beau M, Yates JR 3rd, Hays L, Morgan WF, Petrini JH (1998) The hMre11/hRad50 protein complex and Nijmegen breakage syndrome: linkage of double-strand break repair to the cellular DNA damage response. Cell 93:477–486
Carson CT, Schwartz RA, Stracker TH, Lilley CE, Lee DV, Weitzman MD (2003) The Mre11 complex is required for ATM activation and the G2/M checkpoint. Embo J 22:6610–6620
Celerin M, Merino ST, Stone JE, Menzie AM, Zolan ME (2000) Multiple roles of Spo11 in meiotic chromosome behavior. Embo J 19:2739–2750
Chai W, Sfeir AJ, Hoshiyama H, Shay JW, Wright WE (2006) The involvement of the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex in the generation of G-overhangs at human telomeres. EMBO Rep 7:225–230
Chen L, Trujillo KM, Van Komen S, Roh DH, Krejci L, Lewis LK, Resnick MA, Sung P, Tomkinson AE (2005) Effect of amino acid substitutions in the rad50 ATP binding domain on DNA double strand break repair in yeast. J Biol Chem 280:2620–2627
Costanzo V, Robertson K, Bibikova M, Kim E, Grieco D, Gottesman M, Carroll D, Gautier J (2001) Mre11 protein complex prevents double-strand break accumulation during chromosomal DNA replication. Mol Cell 8:137–147
D'Amours D, Jackson SP (2001) The yeast Xrs2 complex functions in S phase checkpoint regulation. Genes Dev 15:2238–2249
Daoudal-Cotterell S, Gallego ME, White CI (2002) The plant Rad50-Mre11 protein complex. FEBS Lett 516:164–166
de Jager M, van Noort J, van Gent DC, Dekker C, Kanaar R, Wyman C (2001) Human Rad50/Mre11 is a flexible complex that can tether DNA ends. Mol Cell 8:1129–1135
de Jager M, Wyman C, van Gent DC, Kanaar R (2002) DNA end-binding specificity of human Rad50/Mre11 is influenced by ATP. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4425–4431
Desai-Mehta A, Cerosaletti KM, Concannon P (2001) Distinct functional domains of nibrin mediate Mre11 binding, focus formation, and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol 21:2184–2191
Dolganov GM, Maser RS, Novikov A, Tosto L, Chong S, Bressan DA, Petrini JH (1996) Human Rad50 is physically associated with human Mre11: identification of a conserved multiprotein complex implicated in recombinational DNA repair. Mol Cell Biol 16:4832–4841
Dong Z, Zhong Q, Chen PL (1999) The Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein is essential for Mre11 phosphorylation upon DNA damage. J Biol Chem 274:19513–19516
Eijpe M, Offenberg H, Goedecke W, Heyting C (2000) Localisation of RAD50 and MRE11 in spermatocyte nuclei of mouse and rat. Chromosoma 109:123–132
Falck J, Petrini JH, Williams BR, Lukas J, Bartek J (2002) The DNA damage-dependent intra-S phase checkpoint is regulated by parallel pathways. Nat Genet 30:290–294
Frelet A, Klein M (2006) Insight in eukaryotic ABC transporter function by mutation analysis. FEBS Lett 580:1064–1084
Gallego ME, White CI (2001) RAD50 function is essential for telomere maintenance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1711–1716
Gatei M, Young D, Cerosaletti KM, Desai-Mehta A, Spring K, Kozlov S, Lavin MF, Gatti RA, Concannon P, Khanna K (2000) ATM-dependent phosphorylation of nibrin in response to radiation exposure. Nat Genet 25:115–119
Gatei M, Sloper K, Sorensen C, Syljuasen R, Falck J, Hobson K, Savage K, Lukas J, Zhou BB, Bartek J, Khanna KK (2003) Ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) and NBS1-dependent phosphorylation of Chk1 on Ser-317 in response to ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 278:14806–14811
Gerecke EE, Zolan ME (2000) An mre11 mutant of Coprinus cinereus has defects in meiotic chromosome pairing, condensation and synapsis. Genetics 154:1125–1139
Girard PM, Riballo E, Begg AC, Waugh A, Jeggo PA (2002) Nbs1 promotes ATM dependent phosphorylation events including those required for G1/S arrest. Oncogene 21:4191–4199
Grelon M, Vezon D, Gendrot G, Pelletier G (2001) AtSPO11–1 is necessary for efficient meiotic recombination in plants. Embo J 20:589–600
Grenon M, Gilbert C, Lowndes NF (2001) Checkpoint activation in response to double-strand breaks requires the Mre11/Rad50/Xrs2 complex. Nat Cell Biol 3:844–847
Hirano M, Hirano T (2006) Opening closed arms: long-distance activation of SMC ATPase by hinge-DNA interactions. Mol Cell 21:175–186
Hopfner KP, Karcher A, Shin D, Fairley C, Tainer JA, Carney JP (2000a) Mre11 and Rad50 from Pyrococcus furiosus: cloning and biochemical characterization reveal an evolutionarily conserved multiprotein machine. J Bacteriol 182:6036–6041
Hopfner KP, Karcher A, Shin DS, Craig L, Arthur LM, Carney JP, Tainer JA (2000b) Structural biology of Rad50 ATPase: ATP-driven conformational control in DNA double-strand break repair and the ABC-ATPase superfamily. Cell 101:789–800
Hopfner KP, Karcher A, Craig L, Woo TT, Carney JP, Tainer JA (2001) Structural biochemistry and interaction architecture of the DNA double- strand break repair Mre11 nuclease and Rad50-ATPase. Cell 105:473–485
Hopfner KP, Craig L, Moncalian G, Zinkel RA, Usui T, Owen BA, Karcher A, Henderson B, Bodmer JL, McMurray CT, Carney JP, Petrini JH, Tainer JA (2002) The Rad50 zinc-hook is a structure joining Mre11 complexes in DNA recombination and repair. Nature 418:562–566
Ivanov EL, Korolev VG, Fabre F (1992) XRS2, a DNA repair gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is needed for meiotic recombination. Genetics 132:651–664
Johzuka K, Ogawa H (1995) Interaction of Mre11 and Rad50: two proteins required for DNA repair and meiosis-specific double-strand break formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 139:1521–1532
Jongmans W, Vuillaume M, Chrzanowska K, Smeets D, Sperling K, Hall J (1997) Nijmegen breakage syndrome cells fail to induce the p53-mediated DNA damage response following exposure to ionizing radiation. Mol Cell Biol 17:5016–5022
Kee K, Keeney S (2002) Functional interactions between SPO11 and REC102 during initiation of meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 160:111–122
Keeney S (2007) Spo11 and the formation of DNA double-strand breaks in meiosis. In: Egel R, Lankenau D-H (eds) Recombination and meiosis. Springer, Berlin, pp 81–123
Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N (1997) Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell 88:375–384
Kim ST, Lim DS, Canman CE, Kastan MB (1999) Substrate specificities and identification of putative substrates of ATM kinase family members. J Biol Chem 274:37538–37543
Koronakis E, Hughes C, Milisav I, Koronakis V (1995) Protein exporter function and in vitro ATPase activity are correlated in ABC-domain mutants of HlyB. Mol Microbiol 16:87–96
Larrivee M, LeBel C, Wellinger RJ (2004) The generation of proper constitutive G-tails on yeast telomeres is dependent on the MRX complex. Genes Dev 18:1391–1396
Lee JH, Paull TT (2004) Direct activation of the ATM protein kinase by the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex. Science 304:93–96
Lewis LK, Storici F, Van Komen S, Calero S, Sung P, Resnick MA (2004) Role of the nuclease activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mre11 in repair of DNA double-strand breaks in mitotic cells. Genetics 166:1701–1713
Lim DS, Kim ST, Xu B, Maser RS, Lin J, Petrini JH, Kastan MB (2000) ATM phosphorylates p95/nbs1 in an S-phase checkpoint pathway. Nature 404:613–617
Lohmiller LD, De Muyt A, Howard B, Offenberg HH, Heyting C, Grelon M, Anderson LK (2008) Cytological analysis of MRE11 protein during early meiotic prophase I in Arabidopsis and tomato. Chromosoma 117:277–288
Lombard DB, Guarente L (2000) Nijmegen breakage syndrome disease protein and MRE11 at PML nuclear bodies and meiotic telomeres. Cancer Res 60:2331–2334
Maser RS, Monsen KJ, Nelms BE, Petrini JH (1997) hMre11 and hRad50 nuclear foci are induced during the normal cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol 17:6087–6096
McKim KS, Hayashi-Hagihara A (1998) mei-W68 in Drosophila melanogaster encodes a Spo11 homolog: evidence that the mechanism for initiating meiotic recombination is conserved. Genes Dev 12:2932–2942
Merino ST, Cummings WJ, Acharya SN, Zolan ME (2000) Replication-dependent early meiotic requirement for Spo11 and Rad50. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:10477–10482
Mirzoeva OK, Petrini JH (2001) DNA damage-dependent nuclear dynamics of the Mre11 complex. Mol Cell Biol 21:281–288
Mirzoeva OK, Petrini JH (2003) DNA replication-dependent nuclear dynamics of the Mre11 complex. Mol Cancer Res 1:207–218
Moncalian G, Lengsfeld B, Bhaskara V, Hopfner KP, Karcher A, Alden E, Tainer JA, Paull TT (2004) The rad50 signature motif: essential to ATP binding and biological function. J Mol Biol 335:937–951
Moore D (1985) Coprinus cinereus: an ideal organism for studies of genetics and developmental biology. J Biol Educ 19:31–40
Morales M, Theunissen JW, Kim CF, Kitagawa R, Kastan MB, Petrini JH (2005) The Rad50S allele promotes ATM-dependent DNA damage responses and suppresses ATM deficiency: implications for the Mre11 complex as a DNA damage sensor. Genes Dev 19:3043–3054
Moreno-Herrero F, de Jager M, Dekker NH, Kanaar R, Wyman C, Dekker C (2005) Mesoscale conformational changes in the DNA-repair complex Rad50/Mre11/Nbs1 upon binding DNA. Nature 437:440–443
Nakada D, Matsumoto K, Sugimoto K (2003) ATM-related Tel1 associates with double-strand breaks through an Xrs2-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev 17:1957–1962
Neale MJ, Keeney S (2006) Clarifying the mechanics of DNA strand exchange in meiotic recombination. Nature 442:153–158
Neale MJ, Pan J, Keeney S (2005) Endonucleolytic processing of covalent protein-linked DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 436:1053–1057
Nelms BE, Maser RS, MacKay JF, Lagally MG, Petrini JH (1998) In situ visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in human fibroblasts. Science 280:590–592
Ohta K, Nicolas A, Furuse M, Nabetani A, Ogawa H, Shibata T (1998) Mutations in the MRE11, RAD50, XRS2, and MRE2 genes alter chromatin configuration at meiotic DNA double-stranded break sites in premeiotic and meiotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:646–651
Panagiotidis CH, Reyes M, Sievertsen A, Boos W, Shuman HA (1993) Characterization of the structural requirements for assembly and nucleotide binding of an ATP-binding cassette transporter. The maltose transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 268:23685–23696
Paull TT, Gellert M (1998) The 3' to 5′ exonuclease activity of Mre 11 facilitates repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell 1:969–979
Paull TT, Gellert M (1999) Nbs1 potentiates ATP-driven DNA unwinding and endonuclease cleavage by the Mre11/Rad50 complex. Genes Dev 13:1276–1288
Paull TT, Lee JH (2005) The Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex and its role as a DNA double-strand break sensor for ATM. Cell Cycle 4:737–740
Petrini JH, Walsh ME, DiMare C, Chen XN, Korenberg JR, Weaver DT (1995) Isolation and characterization of the human MRE11 homologue. Genomics 29:80–86
Ramesh MA, Zolan ME (1995) Chromosome dynamics in rad12 mutants of Coprinus cinereus. Chromosoma 104:189–202
Raynard S, Niu H, Sung P (2008) DNA double-strand break processing: the beginning of the end. Genes Dev 22:2903–2907
Redhead SA, Viligalys R, Moncalvo J-M, Johnson J, Hopple JSJ (2001) Coprinus Pers. and the disposition of Coprinus species sensu lato. Taxon 50:203–241
\Robison JG, Elliott J, Dixon K, Oakley GG (2004) Replication protein A and the Mre11.Rad50.Nbs1 complex co-localize and interact at sites of stalled replication forks. J Biol Chem 279:34802–34810
Romanienko PJ, Camerini-Otero RD (1999) Cloning, characterization, and localization of mouse and human SPO11. Genomics 61:156–169
Schneider E, Hunke S (1998) ATP-binding-cassette (ABC) transport systems: functional and structural aspects of the ATP-hydrolyzing subunits/domains. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:1–20
Seitz LC, Tang K, Cummings WJ, Zolan ME (1996) The rad9 gene of Coprinus cinereus encodes a proline-rich protein required for meiotic chromosome condensation and synapsis. Genetics 142:1105–1117
Sharples GJ, Leach DR (1995) Structural and functional similarities between the SbcCD proteins of Escherichia coli and the RAD50 and MRE11 (RAD32) recombination and repair proteins of yeast. Mol Microbiol 17:1215–1217
Shyamala V, Baichwal V, Beall E, Ames GF (1991) Structure-function analysis of the histidine permease and comparison with cystic fibrosis mutations. J Biol Chem 266:18714–18719
Takata H, Tanaka Y, Matsuura A (2005) Late S phase-specific recruitment of Mre11 complex triggers hierarchical assembly of telomere replication proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell 17:573–583
Tavassoli M, Shayeghi M, Nasim A, Watts FZ (1995) Cloning and characterisation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad32 gene: a gene required for repair of double strand breaks and recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 23:383–388
Trujillo KM, Yuan SS, Lee EY, Sung P (1998) Nuclease activities in a complex of human recombination and DNA repair factors Rad50, Mre11, and p95. J Biol Chem 273:21447–21450
Trujillo KM, Roh DH, Chen L, Van Komen S, Tomkinson A, Sung P (2003) Yeast xrs2 binds DNA and helps target rad50 and mre11 to DNA ends. J Biol Chem 278:48957–48964
Tseng SF, Chang CY, Wu KJ, Teng SC (2005) Importin KPNA2 is required for proper nuclear localization and multiple functions of NBS1. J Biol Chem 280:39594–39600
Tsukamoto Y, Taggart AK, Zakian VA (2001) The role of the Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 complex in telomerase- mediated lengthening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomeres. Curr Biol 11:1328–1335
Usui T, Ohta T, Oshiumi H, Tomizawa J, Ogawa H, Ogawa T (1998) Complex formation and functional versatility of Mre11 of budding yeast in recombination. Cell 95:705–716
Usui T, Ogawa H, Petrini JH (2001) A DNA damage response pathway controlled by Tel1 and the Mre11 complex. Mol Cell 7:1255–1266
Usui T, Petrini JH, Morales M (2006) Rad50S alleles of the Mre11 complex: questions answered and questions raised. Exp Cell Res 312:2694–2699
Uziel T, Lerenthal Y, Moyal L, Andegeko Y, Mittelman L, Shiloh Y (2003) Requirement of the MRN complex for ATM activation by DNA damage. Embo J 22:5612–5621
Valentine G, Wallace YJ, Turner FR, Zolan ME (1995) Genetic pathway analysis of radiation-sensitive, meiotic mutants of Coprinus cinereus. Molec Gen Genet 247:169–179
van Veelen LR, Cervelli T, van de Rakt MW, Theil AF, Essers J, Kanaar R (2005) Analysis of ionizing radiation-induced foci of DNA damage repair proteins. Mutat Res 574:22–33
Varon R, Vissinga C, Platzer M, Cerosaletti KM, Chrzanowska KH, Saar K, Beckmann G, Seemanova E, Cooper PR, Nowak NJ, Stumm M, Weemaes CM, Gatti RA, Wilson RK, Digweed M, Rosenthal A, Sperling K, Concannon P, Reis A (1998) Nibrin, a novel DNA double-strand break repair protein, is mutated in Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Cell 93:467–476
Wiltzius JJ, Hohl M, Fleming JC, Petrini JH (2005) The Rad50 hook domain is a critical determinant of Mre11 complex functions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:403–407
Wu X, Ranganathan V, Weisman DS, Heine WF, Ciccone DN, O'Neill TB, Crick KE, Pierce KA, Lane WS, Rathbun G, Livingston DM, Weaver DT (2000) ATM phosphorylation of Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein is required in a DNA damage response. Nature 405:477–482
Zolan ME, Tremel CJ, Pukkila PJ (1988) Production and characterization of radiation-sensitive meiotic mutants of Coprinus cinereus. Genetics 120:379–387
Zolan M, Stassen NY, Ramesh MA, Lu BC, Valentine G (1995) Meiotic mutants and DNA repair genes of Coprinus cinereus. Can J Bot 73:S226–S233
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Claire Walczak and Joel Ybe for assistance in developing antibody purification techniques and Ellen Quardokus for immunofluorescence advice. We also thank Elisabeth A. Sierra, Heather J. Palmerini, Claire Burns, and Pat Pukkila for critical manuscript review. This work was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (GM43930) to MEZ. CM was supported by the National Science Foundation under REU Grant No. 0244087.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: S. Keeney
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Mre11 and Rad50 foci on mre11-1 and rad50-1 nuclear spreads. All chromatin spreads shown are from K+2 mushrooms. (a, b, and c) mre11-1 chromosome spread stained with DAPI, anti-Mre11, and anti-Rad50 respectively. (d, e, and f) rad50-1 chromosome spread stained as in (a, b, and c). Images are displayed as described for Fig. 4. Scale bars represent 2 μm (GIF 142 kb)
Fig. S2
Mre11 and Rad50 exhibit low levels of colocalization in meiotic prophase. Image is the wild type K+2 panel (c) from Fig. 3. Arrows point to representative overlapping foci. Arrowheads point to representative adjacent foci. Examples of nearby yet distinct foci are seen above each asterisk. The scale bar represents 2 μm (GIF 93 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Many, A.M., Melki, C.S., Savytskyy, O.P. et al. Meiotic localization of Mre11 and Rad50 in wild type, spo11-1, and MRN complex mutants of Coprinus cinereus . Chromosoma 118, 471–486 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-009-0209-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-009-0209-5