Abstract.
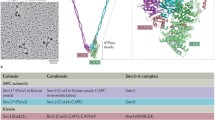
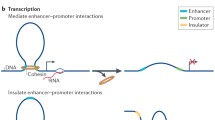
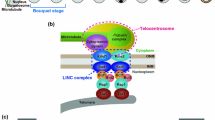
Diverse studies indicate that certain nonhistone proteins may be responsible for maintaining the integrity of the eukaryotic chromosomes. In view of their dispersal during nuclear division and their acknowledged role in gene expression, none of the nuclear matrix proteins can be regarded as integral proteins of the chromosome. Topoisomerase II, structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC) proteins and high-mobility-group (HMG) proteins exhibit characteristic enzymatic and mechanochemical roles as well as transitory association with chromosomes. Hence they may be regarded as accessory chromosome proteins. In contrast, certain high molecular weight synaptonemal complex proteins (SCPs) exhibit chemical and physical properties that suggest a structural role as the chromosome axis. It is proposed in an experimentally testable model that, in the minimal structure of a eukaryotic chromosome, the terminals of the loops of DNA-histone solenoids are constitutively affixed to chromosome axis proteins that have elastic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De, D.N. Protein constitution of the chromosome axis. Chromosoma 111, 69–79 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-002-0189-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-002-0189-1