Abstract
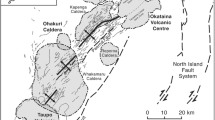
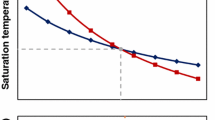
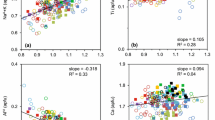
A new phase equilibria geobarometer determines magmatic storage and crystallization conditions, including pressure, temperature, oxygen fugacity (\({f_{{{\text{o}}_2}}}\)), and the presence of a fluid phase for glass-bearing rocks containing the assemblage plagioclase + pyroxene(s). This newly developed geobarometer can better constrain crystallization conditions of shallow (< 500 MPa; <~ 20 km), glass-bearing andesites to dacites. The geobarometer utilizes rhyolite-MELTS to determine crystallization conditions in natural pumice and scoria samples. The validity of the geobarometer is tested by comparing it to results from experiments. Uncertainties are assessed using Monte Carlo simulations. We apply the geobarometer to the plag + opx + cpx-bearing system of Mt. Ruapehu, in the southern Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. The samples from Mt. Ruapehu are tested from ~ 5 to ~ 400 MPa and from super-liquidus to 90% crystalline (~ 1200 to ~ 700 °C). Mt. Ruapehu serves as a methodological testing ground for the geobarometer, and results from our geobarometer agree with recent Mt. Ruapehu studies. Results show a distribution of crystallization pressures ranging from 50 to 150 MPa (~ 2.0 to 5.9 km) for different eruptions, with modes of 110 MPa (~ 4.3 km) and 130 MPa (~ 5.1 km). These are consistent with field interpretations of different eruptive styles based on juvenile clast textures and previous knowledge of the magma plumbing system. Mt. Ruapehu magmas are fluid saturated, with \({f_{{{\text{o}}_2}}}\) of ΔQFM ~ + 1 (NNO).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker LL, Rutherford MJ (1996) The effect of dissolved water on the oxidation state of silicic MELTS. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:2179–2187
Bégué F, Gualda GAR, Ghiorso MS et al (2014) Phase-equilibrium geobarometers for silicic rocks based on rhyolite-MELTS. Part 2: application to Taupo Volcanic Zone rhyolites. Contrib to Miner Pet 168:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-1082-7
Blundy JD, Cashman KV (2008) Petrologic reconstruction of magmatic system variables and processes. Rev Miner Geochem 69:179–239. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2008.69.6
Blundy JD, Wood BJ (1991) Crystal-chemical controls on the partitioning of Sr and Ba between plagioclase feldspar, silicate MELTS, and hydrothermal solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:193–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(91)90411-W
Bryan SE, Ukstins Peate I, Peate DW et al (2010) The largest volcanic eruptions on Earth. Earth Sci Rev 102:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.07.001
Carmichael ISE, Nicholls J (1967) Iron–titanium oxides and oxygen fugacities in volcanic rocks. J Geophys Res 72:4665–4687. https://doi.org/10.1029/JZ072i018p04665
Cole JW (1990) Structural control and origin of volcanism in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. Bull Volcanol 52:445–459
Cowlyn JD (2016) Pyroclastic density currents at Ruapehu volcano; New Zealand. PhD Dissertation, University of Canterbury
Dingwell DB (1996) Volcanic dilemma: flow or blow? Science 273:1054–1055. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5278.1054
Donoghue SL, Gamble JA, Palmer AS, Stewart RB (1995a) Magma mingling in an andesite pyroclastic flow of the Pourahu Member, Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 68:177–191
Donoghue SL, Neall VE, Palmer AS (1995b) Stratigraphy and chronology of late quaternary andesitic tephra deposits, Tongariro Volcanic Centre, New Zealand. J R Soc New Zeal 25:115–206
Donoghue SL, Neall VE, Palmer AS, Stewart RB (1997) The volcanic history of Ruapehu during the past 2 millennia based on the record of Tufa Trig tephras. Bull Volcanol 59:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004450050181
Ferry JM, Watson EB (2007) New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib to Miner Pet 154:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
Gamble JA, Wood CP, Price RC et al (1999) A fifty year perspective of magmatic evolution on Ruapehu Volcano, New Zealand: verification of open system behaviour in an arc volcano. Earth Planet Sci Lett 170:301–314
Gamble JA, Price RC, Smith IEM et al (2003) 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of magmatic activity, magma flux and hazards at Ruapehu volcano, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 120:271–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00407-9
Ghiorso MS, Evans BW (2008) Thermodynamics of rhombohedral oxide solid solutions and a revision of the Fe–Ti two-oxide geothermometer and oxygen-barometer. Am J Sci 308:957–1039
Ghiorso MS, Gualda GAR (2015a) Chemical thermodynamics and the study of magmas. Encycl Volcanoes 143–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385938-9.00006-7
Ghiorso MS, Gualda GAR (2015b) An H2O–CO2 mixed fluid saturation model compatible with rhyolite-MELTS. Contrib to Miner Petrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1141-8
Ghiorso MS, Kress VC (2004) An equation of state for silicate MELTS. II. Calibration of volumetric properties at 105 Pa. Am J Sci 304:679–751. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.304.8-9.679
Ghiorso MS, Sack RO (1991) Fe–Ti oxide geothermometry: thermodynamic formulation and the estimation of intensive variables in silicic magmas. Contrib Miner Petrol 108:485–510
Giordano D, Russell JK, Dingwell DB (2008) Viscosity of magmatic liquids: a model. Earth Planet Sci Lett 271:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.03.038
Graham IJ, Hackett WR (1987) Petrology of calc-alkaline lavas from Ruapehu volcano and related vents, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. J Petrol 28:531–567
Grove TL, Kinzler RJ (1986) Petrogenesis of andesites. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 14:417–454
Grove TL, Donnelly-Nolan JM, Housh T (1997) Magmatic processes that generated the rhyolite of Glass Mountain, Medicine Lake volcano, N. California. Contrib Miner Petrol 127:205–224
Gualda GAR, Ghiorso MS (2014) Phase-equilibrium geobarometers for silicic rocks based on rhyolite-MELTS. Part 1: principles, procedures, and evaluation of the method. Contrib Miner Petrol 168:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-1033-3
Gualda GAR, Ghiorso MS (2015) MELTS-Excel: a microsoft excel-based MELTS interface for research and teaching of magma properties and evolution. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 16:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GC005545
Gualda GAR, Ghiorso MS, Lemons RV, Carley TL (2012) Rhyolite-MELTS: a modified calibration of MELTS optimized for silica-rich, fluid-bearing magmatic systems. J Petrol 53:875–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egr080
Hackett WR, Houghton BF (1989) A facies model for a quaternary andesitic composite volcano: Ruapehu, New Zealand. Bull Volcanol 51:51–68
Hackett WR (1985) Geology and petrology of Ruapehu Volcano and related vents. PhD Dissertation, Victoria University of Wellington
Harrison AJ, White RS (2004) Crustal structure of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand: stretching and igneous intrusion. Geophys Res Lett 31:2–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL019885
Humphreys MCS, Edmonds M, Klöcking MS (2016) The validity of plagioclase-melt geothermometry for degassing-driven magma crystallization. Am Miner 101:7679–7779. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2016-5314
Ingham MR, Bibby HM, Heise W et al (2009) A magnetotelluric study of Mount Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand. Geophys J Int 179:887–904. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04317.x
Johnson ME, Rutherford MJ (1989) Experimental calibration of the aluminum-in-hornblende geobarometer with application to Long Valley caldera (California). Geology 17:837–841
Kawamoto T (1996) Experimental constraints on differentiation and H2O abundance of calc-alkaline magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144:577–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(96)00182-3
Kent AJR, Darr C, Koleszar AM et al (2010) Preferential eruption of andesitic magmas through recharge filtering. Nat Geosci 9:631–636
Kilgour G, Blundy JD, Cashman KV, Mader HM (2013) Small volume andesite magmas and melt–mush interactions at Ruapehu, New Zealand: evidence from melt inclusions. Contrib Miner Petrol 166:371–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-013-0880-7
Kilgour GN, Saunders K, Blundy JD et al (2014) Timescales of magmatic processes at Ruapehu volcano from diffusion chronometry and their comparison to monitoring data. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 288:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.09.010
Kilgour GN, Mader HM, Blundy JD, Brooker RA (2016) Rheological controls on the eruption potential and style of an andesite volcano: a case study from Mt. Ruapehu, New Zealand. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 327:273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.08.001
Kilinc A, Carmichael ISE, Rivers ML, Sack RO (1983) The ferric-ferrous ratio of natural silicate liquids equilibrated in air. Contrib Miner Petrol 83:136–140
Lange RA, Carmichael ISE (1990) Thermodynamic properties of silicate liquids with an emphasis on density, thermal expansion and compressibility. In: Nicholls J, Russell K (eds) Reviews in mineralogy: modern methods of igneous petrology, vol 24. Mineralogical Society of America, pp 25–64
Lange RA, Frey HM, Hector J (2009) A thermodynamic model for the plagioclase-liquid hygrometer/thermometer. Am Miner 94:494–506. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2009.3011
Lawford J, Smith DR (1995) The effects of temperature and \({f_{{{\text{o}}_2}}}\) on the Al-in-hornblende barometer. Am Miner 80:549–559
Liebske C, Behrens H, Holtz F, Lange RA (2003) The influence of pressure and composition on the viscosity of andesitic MELTS. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:473–485
Lindsley DH (ed) (1991) Oxide minerals: petrologic and magnetic significance. Reviews in mineralogy, vol 25. Mineralogical Society of America, pp 1–509
Lindsley DH, Spiedel DH, Nafziger RH (1968) P–T–\({f_{{{\text{o}}_2}}}\) relations for the system Fe–O–SiO2. Am J Sci 266:342–360
Lipman PW, Steven TA, Mehnert HH (1970) Volcanic History of the San Juan Mountains, Colorado, as Indicated by Potassium–Argon dating. Geol Soc Am Bull 81:2329–2352. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[2329:VHOTSJ]2.0.CO;2
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Behrens H (2005) Solubility of H2O in rhyolitic MELTS at low pressures and a new empirical model for mixed H2O–CO2 solubility in rhyolitic MELTS. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 143:219–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.09.019
Prouteau G, Scaillet B (2003) Experimental Constraints on the origin of the 1991 Pinatubo Dacite. J Petrol 44:2203–2241. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egg075
Martel C, Brooker RA, Andújar J et al (2017) Experimental simulations of magma storage and ascent. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–10
Mason BG, Pyle DM, Oppenheimer C (2004) The size and frequency of the largest explosive eruptions on Earth. Bull Volcanol 66:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-004-0355-9
McLeod CL, Davidson JP, Nowell GM, de Silva SL (2012) Disequilibrium melting during crustal anatexis and implications for modeling open magmatic systems. Geology 40:435–438. https://doi.org/10.1130/G33000.1
Mo X, Carmichael ISE, Rivers ML, Stebbins J (1982) The partial molar volume of Fe2O3 in multicomponent silicate liquids and the pressure-dependence of oxygen fugacity in magmas. Miner Mag 45:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1982.045.337.27
Moore G (2008) Interpreting H2O and CO2 contents in melt inclusions: constraints from solubility experiments and modeling. Rev Miner Geochem 69:333–362. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2008.69.9
Moore G, Carmichael ISE (1998) The hydrous phase equilibria (to 3 kbar) of an andesite and basaltic andesite from western Mexico: constraints on water content and conditions of phenocryst growth. Contrib Miner Petrol 130:304–319
Moore G, Righter K, Carmichael ISE (1995) The effect of dissolved water on the oxidation state of iron in natural silicate liquids. Contrib Miner Petrol 120:170–179
Moore G, Vennemann T, Carmichael ISE (1998) An empirical model for the solubility of H2O in magmas to 3 kbars. Am Miner 83:36–42
Mysen BO (1990) Relationships between silicate melt structure and petrologic processes. Earth Sci Rev 27:281–365
Mysen BO, Virgo D, Neumann E-R, Seifert FA (1985) Redox equilibria and the structural states of ferric and ferrous iron in MELTS in the system CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–FeO: relationships between redox equilibria, melt structure and liquidus phase equilibria. Am Miner 70:317–331
Nakagawa M, Wada K, Thordarson T et al (1999) Petrologic investigations of the 1995 and 1996 eruptions of Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand: formation of discrete and small magma pockets and their intermittent discharge. Bull Volcanol 61:15–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004450050259
Nakagawa M, Wada K, Wood CP (2002) Mixed Magmas, mush chambers and eruption triggers: evidence from zoned clinopyroxene phenocrysts in andesitic scoria from the 1995 eruptions of Ruapehu Volcano, New Zealand. J Petrol 43:2279–2303. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/43.12.2279
Pamukcu AS, Gualda GAR, Ghiorso MS et al (2015) Phase-equilibrium geobarometers for silicic rocks based on rhyolite-MELTS, Part 3: application to the peach spring tuff (Arizona, California, Nevada, USA). Contrib Miner Petrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1122-y
Pardo N, Cronin SJ, Palmer AS, Németh K (2011) Reconstructing the largest explosive eruptions of Mt. Ruapehu, New Zealand: lithostratigraphic tools to understand subplinian–plinian eruptions at andesitic volcanoes. Bull Volcanol 74:617–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-011-0555-z
Pardo N, Cronin SJ, Wright HMN et al (2014) Pyroclast textural variation as an indicator of eruption column steadiness in andesitic Plinian eruptions at Mt. Ruapehu. Bull Volcanol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-014-0822-x
Pardo Villaveces N (2012) Andesitic Plinian eruptions at Mt. Ruapehu (New Zealand): from lithofacies to eruption dynamics. Massey University
Powell R, Holland T (1999) Relating formulations of the thermodynamics of mineral solid solutions: activity modeling of pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas. Am Miner 84:1–14
Price RC, George R, Gamble JA et al (2007) U–Th–Ra fractionation during crustal-level andesite formation at Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand. Chem Geol 244:437–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.07.001
Price RC, Gamble JA, Smith IEM et al (2012) The anatomy of an andesite volcano: a time-stratigraphic study of andesite petrogenesis and crustal evolution at Ruapehu Volcano, New Zealand. J Petrol 53:2139–2189. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egs050
Putirka KD (2008) Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. Rev Miner Geochem 69:61–120. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2008.69.3
Putirka KD, Mikaelian H, Ryerson F, Shaw H (2003) New clinopyroxene-liquid thermobarometers for mafic, evolved, and volatile-bearing lava compositions, with applications to lavas from Tiber and the Snake River Plain, Idaho. Am Miner 88:1542–1554. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2017-5704
Reubi O, Blundy JD (2009) A dearth of intermediate MELTS at subduction zone volcanoes and the petrogenesis of arc andesites. Nature 461:1269–1274. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08510
Rudnick RL (1995) Making continental crust. Nature 378:571–578
Sack RO, Carmichael ISE, Rivers ML, Ghiorso MS (1980) Ferric-ferrous equilibria in natural silicate liquids at 1 Bar. Contrib Miner Petrol 75:369–376
Schmidt MW (1992) Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure: an experimental calibration of the Al-in-hornblende barometer. Contrib Miner Petrol 110:304–310
Thomas WM, Ernst WG (1990) The aluminum content of hornblende in calc-alkaline granitic rocks: a mineralogic barometer calibrated experimentally to 12 kbars. Geochem Soc Spec Publ Fluid Mine 2:59–63
Toplis MJ, Carroll MR (1995) An experimental study of the influence of oxygen fugacity on Fe–Ti oxide stability, phase relations, and mineral—melt equilibria in ferro-basaltic systems. J Petrol 36:1137–1170
Vander Auwera J, Longhi J (1994) Experimental study of a jotunite (hypersthene monzodiorite): constrains on the parent magma composition and crystallization conditions (P, T, \({f_{{{\text{o}}_2}}}\)) of the Bjerkreim-Sokndal layered intrusion (Norway). Contrib Miner Petrol 118:60–78
Wark DA, Watson EB (2006) TitaniQ: a titanium-in-quartz geothermometer. Contrib Miner Petrol 152:743–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0132-1
Waters LE, Lange RA (2015) An updated calibration of the plagioclase-liquid hygrometer–thermometer applicable to basalts through rhyolites. Am Miner 100:2172–2184. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2015-5232
Wilson CJN, Houghton BF, Mcwilliams MO et al (1995) Volcanic and structural evolution of Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand: a review. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 68:1–28
Acknowledgements
Funding support provided by NSF grants EAR-1151337 to Gualda and EAR-1321924 to Ghiorso, by University of Canterbury Doctoral Scholarship, the University of Canterbury Mason Trust Fund, a Project Tongariro Memorial Award and a Royal Society of New Zealand International Mobility Fund Grant (IMF14-02) to Cowlyn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Timothy L. Grove.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harmon, L.J., Cowlyn, J., Gualda, G.A.R. et al. Phase-equilibrium geobarometers for silicic rocks based on rhyolite-MELTS. Part 4: Plagioclase, orthopyroxene, clinopyroxene, glass geobarometer, and application to Mt. Ruapehu, New Zealand. Contrib Mineral Petrol 173, 7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1428-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1428-z