Abstract
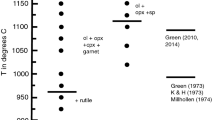
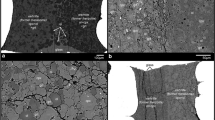
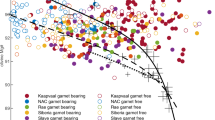
High-Mg basaltic andesites and andesites occur in the central trans-Mexican volcanic belt, and their primitive geochemical characteristics suggest equilibration with mantle peridotite. These lavas may represent slab melts that reequilibrated with overlying peridotite or hydrous partial melts of a peridotite source. Here, we experimentally map the liquidus mineralogy for a high-Mg basaltic andesite (9.6 wt% MgO, 54.4 wt% SiO2, Mg# = 75.3) as a function of temperature and H2O content over a range of mantle wedge pressures. Our results permit equilibration of this composition with a harzburgite residue at relatively high water contents (>7 wt%) and low temperatures (1,080–1,150°C) at 11–14 kbar. However, in contrast to the high Ni contents characteristic of olivine phenocrysts in many such samples from central Mexico, those of olivine phenocrysts in our sample are more typical of mantle melts that have fractionated a small amount of olivine. To account for this and the possibility that the refractory mantle source may have had olivine more Fo-rich than Fo90, we numerically evaluated alternative equilibration conditions, using our starting bulk composition adjusted to be in equilibrium with Fo92 olivine. This shifts equilibration conditions to higher temperatures (1,180–1,250°C) at mantle wedge pressures (11–15 kbar) for H2O contents (>3 wt%) comparable to those analyzed in olivine-hosted melt inclusions from this region. Comparison with geodynamic models shows that final equilibration occurred shallower than the peak temperature of the mantle wedge, suggesting that basaltic melts from the hottest part of the wedge reequilibrated with shallower mantle as they approached the Moho.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asimow PD, Longhi J (2004) The significance of multiple saturation points in the context of polybaric near-fractional melting. J Petrol 45:2349–2367. doi:10.1093/petrology/egh043
Barr JA, Grove TL (2010) AuPdFe ternary solution model and applications to understanding the fO2 of hydrous, high-pressure experiments. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:631–643. doi:10.1007/s00410-010-0497-z
Carmichael IS (2002) The andesite aqueduct: perspectives on the evolution of intermediate magmatism in west-central (105–99°W) Mexico. Contrib Mineral Petrol 143:641–663. doi:10.1007/s00410-002-030-9
Cervantes P, Wallace PJ (2003) Role of H2O in subduction-zone magmatism: new insights from melt inclusions in high-Mg basalts from central Mexico. Geology 31:235–238. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0235
Cooper LB, Plank T, Arculus RJ, Hauri EH, Hall PS, Parman SW (2010) High-Ca boninites from the active Tonga Arc. J Geophys Res 115:B10206. doi:10.1029/2009JB006367
Crawford AJ, Falloon TJ, Green DH (1989) Classification, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of boninites. In: Crawford AJ (ed) Boninites and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 1–49
Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1990) Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 347:662–665
Elkins Tanton LT, Grove TL, Donnelly-Nolan J (2001) Hot, shallow mantle melting under the Cascades volcanic arc. Geology 29:631–634. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0631:HSMMUT>2.0.CO;2
England PC, Katz RF (2010) Melting above the anhydrous solidus controls the location of volcanic arcs. Nature 467:700–703. doi:10.1038/nature09417
Gaetani GA, Grove TL (1998) The influence of water on melting of mantle peridotite. Contrib Mineral Petrol 131:323–346. doi:10.1007/s004100050396
Ghiorso MS, Hirschmann MM, Reiners PW, Kress VC III (2002) The pMELTS: a revision of MELTS aimed at improving calculation of phase relations and major element partitioning involved in partial melting of the mantle at pressures up to 3 GPa. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 3:1030. doi:10.1029/2001GC000217
Gómez-Tuena A, Langmuir CH, Goldstein SL, Straub SM, Ortega-Gutiérrez F (2007) Geochemical evidence for slab melting in the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. J Petrol 48:537–562. doi:10.1093/petrology/egl071
Grove TL (1981) Use of FePt alloys to eliminate the iron loss problem in 1 atmosphere gas mixing experiments: theoretical and practical considerations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 78:298–304
Grove TL, Parman SW, Bowring SA, Price RC, Baker MB (2002) The role of an H2O-rich fluid component in the generation of primitive basaltic andesites and andesites from the Mt. Shasta region, N California. Contrib Mineral Petrol 142:375–396
Grove TL, Elkins-Tanton LT, Parman SW, Chatterjee N, Müntener O, Gaetani GA (2003) Fractional crystallization and mantle-melting controls on calc-alkaline differentiation trends. Contrib Mineral Petrol 145:515–533. doi:10.1007/s00410-003-0448-z
Grove TL, Chatterjee N, Parman SW, Médard E (2006) The influence of H2O on mantle wedge melting. Earth Planet Sci Lett 249:74–89. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.06.043
Grove TL, Till CB, Lev E, Chatterjee N, Médard E (2009) Kinematic variables and water transport control the formation and location of arc volcanoes. Nature 459:694–697. doi:10.1038/nature08044
Guilbaud M, Siebe C, Agustín-Flores J (2009) Eruptive style of the young high-Mg basaltic- andesite Pelagatos scoria cone, southeast of México City. Bull Volc 71:859–880. doi:10.1007/s00445-009-0271-0
Huebner JS, Sato M (1970) The oxygen fugacity-temperature relationships of manganese oxide and nickel oxide buffers. Am Mineral 55:934–952
Ishimaru S, Arai S (2008) Nickel enrichment in mantle olivine beneath a volcanic front. Contrib Mineral Petrol 156:119–131. doi:10.1007/s00410-007-0277-6
Johnson ER, Wallace PJ, Granados HD, Manea VC, Kent AJR, Bindeman IN, Donegan CS (2009) Subduction-related volatile recycling and magma generation beneath Central Mexico: insights from melt inclusions, oxygen isotopes and geodynamic models. J Petrol 50:1729–1764. doi:10.1093/petrology/egp051
Johnston AD (1986) Anhydrous P–T phase relations of near-primary high alumina basalt from the South Sandwich Islands: Implications fort the origin of island arcs and tonalite-trondhjemite series rocks. Contrib Mineral Petrol 92:368–382
Johnston AD, Wyllie PJ (1989) The system tonalite-peridotite-H2O at 30 kbar: with applications to hybridization in subduction zone magmatism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 102:257–264
Kelemen PB (1995) Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust. Contrib Mineral Petrol 120:1–19. doi:10.1007/BF00311004
Kelemen PB, Hart SR, Bernstein S (1998) Silica enrichment in the continental upper mantle via melt/rock reaction. Earth Planet Sci Lett 164:387–406. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00233-7
Kress VC, Carmichael ISE (1991) The compressibility of silicate liquids containing Fe2O3 and the effect of composition, temperature, oxygen fugacity and pressure on their redox states. Contrib Mineral Petrol 108:82–92. doi:10.1007/BF00307328
Lee CA, Luffi P, Plank T, Dalton H, Leeman WP (2009) Constraints on the depths and temperatures of basaltic magma generation on Earth and other terrestrial planets using new thermobarometers for mafic magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 279:20–33. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.12.020
Manea VC, Manea M (2011) Flat-slab thermal structure and evolution beneath Central Mexico. Pure Appl Geophys 168:1475–1487
Manea VC, Manea M, Kostoglodov V, Sewell G (2005) Thermo-mechanical model of the mantle wedge in Central Mexican subduction zone and a blob tracing approach for the magma transport. Phys Earth Planet Int 149:165–186. doi:10.1016/j.pepi.2004.08.024
Matzen AK, Baker MB, Beckett J, Stolper EM (2010) Temperature and pressure dependence of Ni partitioning between olivine and high-MgO silicate melts. Abstract V13F–03. Fall AGU Meeting, San Francisco
Médard E, Grove TL (2008) The effect of H2O on the olivine liquidus of basaltic melts: experiments and thermodynamic models. Contrib Mineral Petrol 155:417–432. doi:10.1007/s00410-007-0250-4
Médard E, McCammon CA, Barr JA, Grove TL (2008) Oxygen fugacity, temperature reproducibility, and H2O contents of nominally anhydrous piston-cylinder experiments using graphite capsules. Am Mineral 93:1838–1844. doi:10.2138/am.2008.2842
Mercer CN, Johnston AD (2008) Experimental studies of the P-T-H2O near-liquidus phase relations of basaltic andesite from North Sister Volcano, High Oregon Cascades: constraints on lower-crustal mineral assemblages. Contrib Mineral Petrol 155:571–592. doi:10.1007/s000410-007-0259-8
Meriggi L, Macías JL, Tommasini S, Capra L, Conticelli S (2008) Heterogeneous magmas of the Quaternary Sierra Chichinautzin volcanic field (central Mexico): the role of an amphibole bearing mantle and magmatic evolution processes. Rev Mex Cien Geol 25:197–216
Métrich N, Wallace PJ (2008) Volatile abundances in basaltic magmas and their degassing paths tracked by melt inclusions. In: Putirka KD, Tepley III FJ (eds) Minerals, inclusions and volcanic processes. Rev Mineral Geochem 69:363–402. doi:10.2138/rmg.2008.69.10
Nielsen CH, Sigurdsson H (1981) Quantitative methods for electron microprobe analysis of sodium in natural and synthetic glasses. Am Mineral 66:547–552
Ortega-Gutiérrez F, Elías-Herrera M, Dávalos-Elizondo MG (2008) On the nature and role of the lower crust in the volcanic front of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt and its fore-arc region southern and central Mexico. Rev Mex Cien Geol 25:346–364
Pardo M, Suárez G (1995) Shape of the subducted Rivera and Cocos plates in southern Mexico: seismic and tectonic implications. J Geophys Res 100:12357–12373
Parman SW, Grove TL (2004) Harzburgite melting with and without H2O: Experimental data and predictive modeling. J Geophys Res 109:B02201. doi:10.1029/2003JB002566
Peréz-Campos X, Kim Y, Husker A, Davis PM, Clayton RW, Iglesias A, Pacheco JF, Singh SK, Manea VC, Gurnis M (2008) Horizontal subduction and truncation of the Cocos Plate beneath central Mexico. Geophys Res Lett 35:L18303. doi:10.1029/2008GL035127
Pickering JM, Schwab BE, Johnston AD (1998) Off-center hot spots: double thermocouple determination of the thermal gradient in a 1.27 cm (1/2 in.) CaF2 piston-cylinder furnace assembly. Am Mineral 83:228–235
Putirka K, Ryerson FJ, Perfit M, Ridley WI (2011) Mineralogy and composition of the oceanic mantle. J Petrol 52:279–313. doi:10.1093/petrology/egq080
Rapp RP, Watson EB (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar—implications for continental growth and crust-mentle recycling. J Petrol 36:891–931
Rapp RP, Shimizu N, Norman MD, Applegate GS (1999) Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa. Chem Geol 160:335–356
Roman DC, Cashman KV, Gardner CA, Wallace PJ, Donovan JJ (2006) Storage and interaction of compositionally heterogeneous magmas from the 1986 eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 68:240–254. doi:10.1007/s00445-005-0003-z
Schaaf P, Stimac J, Siebe C, Macías JL (2005) Geochemical evidence for mantle origin and crustal processes in volcanic rocks from Popocatepetl and surrounding monogenetic volcanoes, Central Mexico. J Petrol 46:1243–1282. doi:10.1093/petrology/egi015
Sobolev AV, Hofmann AW, Sobolev SV, Nikogosian IK (2005) An olivine-free mantle source of Hawaiian shield basalts. Nature 434:590–597. doi:10.1038/nature03411
Stolper E, Newman S (1994) The role of water in the petrogenesis of Mariana trough magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 121:293–325. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(94)90074-4
Straub SM, LaGatta AB, Martin-Del Pozzo AL, Langmuir CH (2008) Evidence from high-Ni olivines for a hybridized peridotite/pyroxenite source for orogenic andesites from the central Mexican Volcanic Belt. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 9:Q030007. doi:10.1029/2007GC001583
Straub SM, Gomez-Tuena A, Stuart FM, Zellmer GF, Espinasa-Perena R, Cai Y, Iizuka Y (2011) Formation of hybrid arc andesites beneath thick continental crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 303:337–347. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.01.013
Tatsumi Y (2006) High-Mg andesites in the Setouchi Volcanic Belt, Southwestern Japan: analogy to Archean magmatism and continental crust formation? Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 34:467–499. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.34.031405.125014
Tatsumi Y, Ishizaka K (1982) Origin of high-magnesian andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt southwest Japan, I. Petrological and chemical characteristics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 60:293–304
Toplis MJ (2005) The thermodynamics of iron and magnesium partitioning between olivine and liquid: criteria for assessing and predicting equilibrium in natural and experimental systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 149:22–39. doi:10.1007/s00410-004-0629-4
Wallace PJ (2005) Volatiles in subduction zone magmas: concentrations and fluxes based on melt inclusion and volcanic gas data. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 140:217–240. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.07.023
Wallace PJ, Carmichael ISE (1999) Quaternary volcanism near the Valley of Mexico: implications for subduction zone magmatism and the effects of crustal thickness variations of primitive magma compositions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 135:291–314. doi:10.1007/s004100050513
Weaver SL, Wallace PJ, Johnston AD (2011) A comparative study of continental vs. intraoceanic arc mantle melting: experimentally determined phase relations of hydrous primitive melts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 308:97–106
Weber RM (2010) Experimental insights into the formation of high-Mg andesites in the Trans- Mexican Volcanic Belt. M.S. thesis, 86 pp, University of Oregon
Witter JB, Kress VC, Newhall CG (2005) Volcán Popocatépetl, Mexico. Petrology, magma mixing, immediate sources of volatiles for the 1994-present eruption. J Petrol 46:2337–2366. doi:10.1093/petrology/egi058
Wood BJ, Turner SP (2009) Origin of primitive high-Mg andesite: constraints from natural examples and experiments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 283:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.03.032
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank L. Meriggi for providing us with the Pelagatos sample used in this study, J. Roberge for providing us with unpublished FTIR data on melt inclusions from Pelagatos tephra, and J. Donovan for assistance with the electron microprobe. We would also like to thank R. Lange, K. Putirka, and an anonymous reviewer for thorough reviews that greatly improved this manuscript. This study was supported by National Science Foundation grant EAR-0739065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Moore.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, R.M., Wallace, P.J. & Dana Johnston, A. Experimental insights into the formation of high-Mg basaltic andesites in the trans-Mexican volcanic belt. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163, 825–840 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-011-0701-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-011-0701-9