Abstract
Purpose
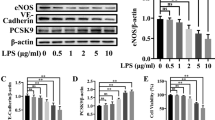
Vascular endothelial cells demonstrate severe injury in sepsis, and a reduction in endothelial inflammation would be beneficial. Inter-α-Inhibitor (IαI) is a family of abundant plasma proteins with anti-inflammatory properties and has been investigated in human and animal sepsis with encouraging results. We hypothesized that IαI may protect endothelia from sepsis-related inflammation.
Methods
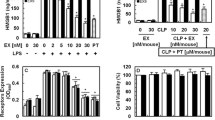
IαI-deficient or sufficient mice were treated with endotoxin or underwent complement-induced lung injury. VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression was measured in blood and lung as marker of endothelial activation. Human endothelia were exposed to activated complement C5a with or without IαI. Blood from human sepsis patients was examined for VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 and levels were correlated with blood levels of IαI.
Results
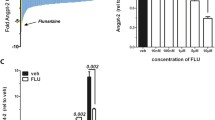
IαI-deficient mice showed increased endothelial activation in endotoxin/sepsis- and complement-induced lung injury models. In vitro, levels of endothelial pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell growth factors induced by activated complement C5a were significantly decreased in the presence of IαI. This effect was associated with decreased ERK and NFκB activation. IαI levels were inversely associated with VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 levels in a human sepsis cohort.
Conclusions
IαI ameliorates endothelial inflammation and may be beneficial as a treatment of sepsis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus DC et al (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29(7):1303–1310
Kaukonen KM et al (2014) Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. Jama 311(13):1308–1316
Ferreira FL et al (2001) Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. Jama 286(14):1754–1758
Schmidt EP et al (2012) The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx regulates neutrophil adhesion and lung injury during experimental sepsis. Nat Med 18(8):1217–1223
Ince C et al (2016) The endothelium in sepsis. Shock 45(3):259–270
Bosmann M, Ward PA (2012) Role of C3, C5 and anaphylatoxin receptors in acute lung injury and in sepsis. Adv Exp Med Biol 946:147–159
Czermak BJ et al (1999) Protective effects of C5a blockade in sepsis. Nat Med 5(7):788–792
Huber-Lang M et al (2001) Role of C5a in multiorgan failure during sepsis. J Immunol 166(2):1193–1199
Goldenberg NM et al (2011) Broken barriers: a new take on sepsis pathogenesis. Sci Transl Med 3(88):88ps25.
Albrecht EA et al (2004) C5a-induced gene expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 164(3):849–859
Kyan-Aung U, Haskard DO, Lee TH (1991) Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and eosinophil adhesion to cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 5(5):445–450
Kyan-Aung U et al (1991) Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mediate the adhesion of eosinophils to endothelial cells in vitro and are expressed by endothelium in allergic cutaneous inflammation in vivo. J Immunol 146(2):521–528
Bochner BS et al (1991) Adhesion of human basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils to interleukin 1-activated human vascular endothelial cells: contributions of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. J Exp Med 173(6):1553–1557
Singh K et al (2010) Inter-alpha inhibitor protein administration improves survival from neonatal sepsis in mice. Pediatr Res 68(3):242–247
Yang S et al (2002) Administration of human inter-alpha-inhibitors maintains hemodynamic stability and improves survival during sepsis. Crit Care Med 30(3):617–622
Jourdain M et al (1997) Effects of inter-alpha-inhibitor in experimental endotoxic shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(6):1825–1833
Garantziotis S et al (2007) Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor attenuates complement activation and complement-induced lung injury. J Immunol 179(6):4187–4192
Opal SM et al (2007) Longitudinal studies of inter-alpha inhibitor proteins in severely septic patients: a potential clinical marker and mediator of severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 35(2):387–392
Skibsted S et al (2013) Biomarkers of endothelial cell activation in early sepsis. Shock 39(5):427–432
Zonneveld R et al (2014) Soluble adhesion molecules as markers for sepsis and the potential pathophysiological discrepancy in neonates, children and adults. Crit Care 18(1):204
Jesmin S et al (2012) Time-dependent alterations of VEGF and its signaling molecules in acute lung injury in a rat model of sepsis. Inflammation 35(2):484–500
Amatschek S et al (2011) CXCL9 induces chemotaxis, chemorepulsion and endothelial barrier disruption through CXCR22-mediated activation of melanoma cells. Br J Cancer 104(3):469–479
Zsebo KM et al (1988) Vascular endothelial cells and granulopoiesis: interleukin-1 stimulates release of G-CSF and GM-CSF. Blood 71(1):99–103
Fuste B et al (2004) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor increases expression of adhesion receptors on endothelial cells through activation of p38 MAPK. Haematologica 89(5):578–585
Burg J et al (2002) GM-CSF expression by human lung microvascular endothelial cells: in vitro and in vivo findings. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283(2):L460–L467
Chandrasekar B et al (2004) Activation of intrinsic and extrinsic proapoptotic signaling pathways in interleukin-18-mediated human cardiac endothelial cell death. J Biol Chem 279(19):20221–20233
Brueckmann M et al (2007) Prognostic value of platelet-derived growth factor in patients with severe sepsis. Growth Factors 25(1):15–24
Monsinjon T et al (2003) Regulation by complement C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins of cytokine production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Faseb J 17(9):1003–1014
Levy MM et al (2014) Surviving sepsis campaign: association between performance metrics and outcomes in a 7.5-year study. Crit Care Med 40(11):1623-1633.
Vallet B (2003) Bench-to-bedside review: endothelial cell dysfunction in severe sepsis: a role in organ dysfunction? Crit Care 7(2):130–138
Kubli S et al (2003) Endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the skin microcirculation of patients with septic shock. Shock 19(3):274–280
Davis JS et al (2009) Sepsis-associated microvascular dysfunction measured by peripheral arterial tonometry: an observational study. Crit Care 13(5):R155
Coletta C et al (2014) Endothelial dysfunction is a potential contributor to multiple organ failure and mortality in aged mice subjected to septic shock: preclinical studies in a murine model of cecal ligation and puncture. Crit Care 18(5):511
Duffy MJ et al (2011) Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilatation is a novel predictor of mortality in intensive care. Crit Care Med 39(4):629–635
Smith WB, Gamble JR, Vadas MA (1994) The role of granulocyte-macrophage and granulocyte colony-stimulating factors in neutrophil transendothelial migration: comparison with interleukin-8. Exp Hematol 22(3):329–334
Lindahl P et al (1997) Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science 277(5323):242–245
Motro B et al (1990) Pattern of interleukin 6 gene expression in vivo suggests a role for this cytokine in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(8):3092–3096
Pintucci G et al (2002) Lack of ERK activation and cell migration in FGF-2-deficient endothelial cells. Faseb J 16(6):598–600
Colotta F et al (1994) Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 by monocytes and endothelial cells exposed to thrombin. Am J Pathol 144(5):975–985
Amalakuhan B et al (2016) Endothelial adhesion molecules and multiple organ failure in patients with severe sepsis. Cytokine 88:267–273
Laudes IJ et al (2004) Disturbed homeostasis of lung intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 during sepsis. Am J Pathol 164(4):1435–1445
Oertli B et al (1998) Mechanisms of hyaluronan-induced up-regulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression by murine kidney tubular epithelial cells: hyaluronan triggers cell adhesion molecule expression through a mechanism involving activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and activating protein-1. J Immunol 161(7):3431–3437
Wuthrich RP (1992) Intercellular adhesion molecules and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 3(6):1201–1211
Kanayama N et al (1997) The role of chondroitin sulfate chains of urinary trypsin inhibitor in inhibition of LPS-induced increase of cytosolic free Ca2+ in HL60 cells and HUVEC cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238(2):560–564
El Maradny E et al (1994) Urinary trypsin inhibitor has a protective effect on the amnion. Gynecol Obstet Invest 38(3):169–172
Kanayama N et al (1995) Urinary trypsin inhibitor prevents uterine muscle contraction by inhibition of Ca++ influx. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173(1):192–199
Kanayama N et al (1998) Urinary trypsin inhibitor suppresses vascular smooth muscle contraction by inhibition of Ca2+ influx. Biochim Biophys Acta 1381(2):139–146
Kanayama S et al (2007) Bikunin suppresses expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by lipopolysaccharide in neutrophils. J Endotoxin Res 13(6):369–376
Chaaban H et al (2015) Inter-alpha inhibitor protein and its associated glycosaminoglycans protect against histone-induced injury. Blood 125(14):2286–2296
Ni K et al (2019) Intravascular heavy chain-modification of hyaluronan during endotoxic shock. Biochem Biophys Rep 17:114–121
Ni K et al (2018) Rapid clearance of heavy chain-modified hyaluronan during resolving acute lung injury. Respir Res 19(1):107
Unnewehr H et al (2013) Changes and regulation of the C5a receptor on neutrophils during septic shock in humans. J Immunol 190(8):4215–4225
Flierl MA, Schreiber H, Huber-Lang MS (2006) The role of complement, C5a and its receptors in sepsis and multiorgan dysfunction syndrome. J Invest Surg 19(4):255–265
Laudes IJ et al (2002) Expression and function of C5a receptor in mouse microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 169(10):5962–5970
Chen BC, Lin WW (2001) PKC- and ERK-dependent activation of I kappa B kinase by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages: enhancement by P2Y receptor-mediated CaMK activation. Br J Pharmacol 134(5):1055–1065
Molor-Erdene P et al (2005) Urinary trypsin inhibitor reduces LPS-induced hypotension by suppressing tumor necrosis factor-alpha production through inhibition of Egr-1 expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(3):H1265–1271
Kobayashi H et al (2003) A Kunitz-type protease inhibitor, bikunin, inhibits ovarian cancer cell invasion by blocking the calcium-dependent transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 278(10):7790–7799
Monk PN, Partridge LJ (1993) Characterization of a complement-fragment-C5a-stimulated calcium-influx mechanism in U937 monocytic cells. Biochem J 295(Pt 3):679–684
Hawlisch H et al (2005) C5a negatively regulates toll-like receptor 4-induced immune responses. Immunity 22(4):415–426
Perumal NB, Kaplan MH (2011) Regulating Il9 transcription in T helper cells. Trends Immunol 32(4):146–150
Bader BL et al (1998) Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis precede lethality in mice lacking all alpha v integrins. Cell 95(4):507–519
Adair JE et al (2009) Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor promotes bronchial epithelial repair after injury through vitronectin binding. J Biol Chem 284(25):16922–16930
Lennon FE, Singleton PA (2011) Hyaluronan regulation of vascular integrity. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 1(3):200–213
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Michael B. Fessler and John House for constructive criticism, and Ms. Ligon Perrow for excellent animal husbandry. This work was supported, in part, by the Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH. Yow-Pin Lim gratefully acknowledges support from NIAID grant 2R42AI062095.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: SG. Experiments, analysis, and interpretation: VPS, Y-PL, SO, KK, and LZ. Darfting of manuscript: VPS and SG. Review of manuscript: VPS, Y-PL, SO, KK, LZ, and SG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y-PL is the President and Chief Scientific Officer at ProThera Biologics, LLC, a company which explores the use of IαI in several systemic inflammatory diseases, including sepsis.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stober, V.P., Lim, YP., Opal, S. et al. Inter-α-inhibitor Ameliorates Endothelial Inflammation in Sepsis. Lung 197, 361–369 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-019-00228-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-019-00228-1