Abstract
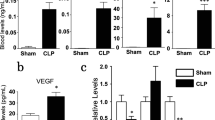
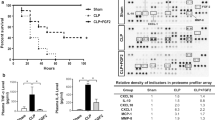
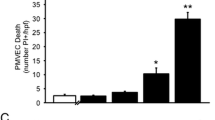
Molecular mechanisms of sepsis-associated acute lung injury (ALI) are poorly defined. Since vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent vascular permeability and mitogenic factor, it might contribute to the development of ALI in sepsis. Thus, using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced (15 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) endotoxemic rat model, we studied the timeline (1, 3, 6, and 10 h) of pulmonary VEGF expression and its signaling machinery. Levels of pulmonary VEGF and its angiogenic-mediating receptor, Flk-1, were downregulated by LPS in a time-dependent manner; levels of plasma VEGF and its permeability-mediating receptor, Flt-1, in contrast, was upregulated with time. In addition, blockade of Flt-1 could improve the downregulated pulmonary VEGF level and attenuate the elevated plasma and pulmonary levels of TNF-α, followed by improvement of arterial oxygenation and wet-to-dry weight ratio of the lung. Expression of signaling, pro- and or apoptotic factors after LPS administration were as follows: phosphorylated Akt, a downstream molecule was downregulated time dependently; endothelial nitric oxide synthase levels were significantly reduced; pro-apoptotic markers caspase 3 and Bax were upregulated whereas levels of Bcl-2 were downregulated. The present findings show that VEGF may play a role through the expression of Flt-1 in LPS-induced ALI. Moreover, downregulation of VEGF signaling cascade may account for LPS-induced apoptosis and impaired physiological angiogenesis in lung tissues, which in turn may contribute to the development of ALI induced by LPS.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baue, A.E., R. Durham, and E. Faist. 1998. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), multiple organ failure (MOF): Are we winning the battle? Shock 10: 79–89.
Bone, C. 1991. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Annals of Internal Medicine 115: 457–469.
Bernard, G.R., A. Artigas, K.L. Brigham, J. Carlet, K. Falke, L. Hudson, M. Lamy, J.R. Legall, A. Morris, and R. Spragg. 1994. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 149: 818–824.
Mauricio, R., C.R. Woods, A.L. Mora, J. Xu, and K.L. Brigham. 2005. Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: Structural, functional, and biochemical responses. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 288: L333–L341.
Dvorak, H.F., L.F. Brown, M. Detmar, and A.M. Dvorak. 1995. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability and angiogenesis. The American Journal of Pathology 146: 1029–1039.
Ferrara, N. 2004. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocrine Reviews 25: 581–611.
Waltenberger, J., L. Claesson-Welsh, A. Siegbahn, M. Shibuya, and C.H. Heldin. 1994. Different signal transduction properties of KDR and Flt1, two receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 269: 26988–26995.
Dimmeler, S., and A.M. Zeiher. 2000. Endothelial cell apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression. Circulation Research 87: 434–439.
Fujio, Y., and K. Walsh. 1999. Akt mediates cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274: 16349–16354.
Gerber, H.P., A. McMurtrey, J. Kowalski, M. Yan, B.A. Keyt, V. Dixit, and N. Ferrara. 1998. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273: 30336–30343.
Nor, J.E., J. Christensen, D.J. Mooney, and P.J. Polverini. 1999. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis is associated with enhanced endothelial cell survival and induction of Bcl-2 expression. The American Journal of Pathology 154: 375–384.
Wort, S.J., and T.W. Evan. 1999. The role of the endothelium in modulating vascular control in sepsis and related conditions. British Medical Bulletin 55: 30–48.
Wu, R., X. Song, Y. Xu, and X. Meng. 2000. Apoptosis of endothelial cells in alteration of microvascular permeability in lung during sepsis. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 38: 385–387.
Munshi, N., A.Z. Fernandis, R.P. Cherla, I.W. Park, and R.K. Ganju. 2002. Lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells and its inhibition by vascular endothelial growth factor. Journal of Immunology 168: 5860–5866.
Pickkers, P., T. Sprong, L. Eijk, H. Hoeven, P. Smits, and M. Deuren. 2005. Vascular endothelial growth factor is increased during the first 48 hours of human septic shock and correlates with vascular permeability. Shock 24: 508–512.
Tsokos, M., T. Pufe, F. Paulsen, S. Anders, and R. Mentlein. 2003. Pulmonary expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in sepsis. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 127: 331–335.
Zaedi, S., S. Jesmin, N. Yamaguchi, N. Shimojo, S. Maeda, S. Gando, I. Yamaguchi, K. Goto, and T. Miyauchi. 2006. Altered expression of endothelin, vascular endothelial growth factor, and its receptor in hepatic tissue in endotoxemic rat. Experimental Biology and Medicine 231: 1182–1186.
Jesmin, S., S. Gando, N. Matsuda, I. Sakuma, S. Kobayashi, F. Sakuraya, and Y. Hattori. 2004. Temporal changes in pulmonary expression of key procoagulant molecules in rabbits with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury: Elevated expression levels of protease-activated receptors. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 92: 966–979.
Kristof, A., P. Goldberg, V.E. Laubach, and S.N.A. Hussain. 1998. Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 158: 1883–1889.
Yamaguchi, N., S. Jesmin, S. Zaedi, N. Shimojo, S. Maeda, S. Gando, A. Koyama, and T. Miyauchi. 2006. Time-dependent expression of renal vaso-regulatory molecules in LPS-induced endotoxemia in rat. Peptides 27: 2258–2270.
Jesmin, S., S. Gando, S. Zaedi, and F. Sakuraya. 2007. Differential expression, time course and distribution of four PARs in rats with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Inflammation 30(1–2): 14–27.
Zaedi, S., S. Jesmin, S. Maeda, N. Shimojo, I. Yamaguchi, K. Goto, and T. Miyauchi. 2006. Alterations in gene expressions encoding preproET-1 and NOS in pulmonary tissue in endotoxemic rats. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood) 231: 992–996.
Jesmin, S., I. Sakuma, A. Salah-Eldin, K. Nonomura, Y. Hattori, and A. Kitabatake. 2003. Diminished penile expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors at the insulin-resistant stage of a type II diabetic rat model: A possible cause for erectile dysfunction in diabetes. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 31: 401–418.
Jesmin, S., H. Togashi, I. Sakuma, C.N. Mowa, K. Ueno, T. Yamaguchi, M. Yoshioka, and A. Kitabatake. 2004. Gonadal hormones and frontocortical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in male stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats, a model for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Endocrinology 145: 4330–4343.
Janicke, R.U., M.L. Sprengart, M.R. Wati, and A.G. Porter. 1998. Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273: 9357–9360.
Thickett, D.R., L. Armstrong, and A.B. Millar. 2002. A role for vascular endothelial growth factor in acute and resolving lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 166: 1332–1337.
Thickett, D.R., L. Armstrong, S.J. Christie, and A.B. Millar. 2001. Vascular endothelial growth factor may contribute to increased vascular permeability in acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 164: 657–664.
Kaner, R.J., R. Ladetto, N. Singh, N. Fukuda, M.A. Matthay, and R.G. Crystal. 2000. Lung over expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene induces pulmonary edema. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 22: 657–664.
Corne, J., G. Chupp, C.G. Lee, R.J. Homer, Z. Zhu, Q. Chen, B. Ma, Y. Du, F. Roux, J. McArdle, A.B. Waxman, and J.A. Elias. 2000. IL-13 stimulates vascular endothelial cell growth factor and protects against hyperoxic acute lung injury. Journal of Clinical Investigation 106: 783–791.
Kaner, R.J., and R.G. Crystal. 2001. Compartmentalization of vascular endothelial growth factor to the epithelial surface of the human lung. Molecular Medicine 7: 240–246.
Kimura, H., and H. Esumi. 2003. Reciprocal regulation between nitric oxide and vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis. Acta Biochimica Polonica 50: 49–59.
Vallance, P., and S. Moncada. 1993. The role of endogenous nitric oxide in septic shock. New Horizons 1: 77–86.
Patterson, C., M.A. Perrella, W.O. Endege, M. Yoshizumi, M.E. Lee, and E. Haber. 1996. Downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation 98: 490–496.
Bardales, R.H., S.S. Xie, R.F. Schaefer, and S.M. Hsu. 1996. Apoptosis is a major pathway responsible for the resolution of type II pneumocytes in acute lung injury. The American Journal of Pathology 149: 845–852.
Fujita, M., K. Kuwano, R. Kunitake, N. Hagimoto, H. Miyazaki, Y. Kaneko, M. Kawasaki, T. Maeyama, and N. Hara. 1998. Endothelial cell apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 117: 202–208.
Hotchkiss, R.S., P.E. Swanson, B.D. Freeman, K.W. Tinsley, J.P. Cobb, G.M. Matuschak, T.G. Buchman, and I.E. Karl. 1999. Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Critical Care Medicine 27: 1230–1251.
Kawasaki, M., K. Kuwano, N. Hagimoto, T. Matsuba, R. Kunitake, T. Tanaka, T. Maeyama, and N. Hara. 2000. Protection from lethal apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by a caspase inhibitor. The American Journal of Pathology 157: 597–603.
Cardone, M.H., N. Roy, H.R. Stennicke, G.S. Salvesen, T.F. Franke, E. Stanbridge, S. Frisch, and J.C. Reed. 1998. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282: 1318–1321.
Del Peso, L., M. Gonzalez-Garcia, C. Page, R. Herrera, and G. Nuñez. 1997. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278: 687–689.
Gerber, H.P., V. Dixit, and N. Ferrara. 1998. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and A1 in vascular endothelial cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273: 13313–13316.
Tran, J., J. Rak, C. Sheehan, S.D. Saibil, E. LaCasse, R.G. Korneluk, and R.S. Kerbel. 1999. Marked induction of the IAP family antiapoptotic roteins survivin and XIAP by VEGF in vascular endothelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 264: 781–788.
Gupta, K., S. Kshirsagar, W. Li, L. Gui, S. Ramakrishnan, P. Gupta, P.Y. Law, and R.P. Hebbel. 1999. VEGF prevents apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells via opposing effects on MAPK/ERK and SAPK/JNK signaling. Experimental Cell Research 247: 495–504.
Kasahara, Y., R.M. Tuder, L. Taraseviciene-Stewart, T.D. Le Cras, S. Abman, P.K. Hirth, J. Waltenberger, and N.F. Voelkel. 2000. Inhibition of VEGF receptors causes lung cell apoptosis and emphysema. Journal of Clinical Investigation 106: 1311–1319.
Hamada, N., K. Kuwano, M. Yamada, N. Hagimoto, K. Hiasa, K. Egashira, N. Nakashima, T. Maeyama, M. Yoshimi, and Y. Nakanishi. 2005. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy attenuates lung injury and fibrosis in mice. Journal of Immunology 175: 1224–1231.
Nolan, A., M.D. Weiden, G. Thurston, and J.A. Gold. 2004. Vascular endothelial growth factor blockade reduces plasma cytokines in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. Inflammation 28: 271–278.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan (22406025, 21249086, and 20790296). The authors greatly thank Dr. Nobutake Shimojo for his excellent advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jesmin, S., Zaedi, S., Islam, A.M.S. et al. Time-Dependent Alterations of VEGF and Its Signaling Molecules in Acute Lung Injury in a Rat Model of Sepsis. Inflammation 35, 484–500 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9337-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9337-1