Abstract
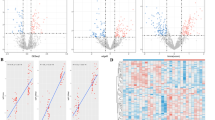
The lifetime presence of psychotic symptoms is associated with more clinical severity, poorer outcome and biological changes in patients affected by bipolar disorder (BD). Epigenetic mechanisms have been evoked to explain the onset of psychotic symptoms in BD as well as the associated biological changes. The main objective of the present study was to evaluate the expression profiles of circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) in drug-free manic psychotic bipolar patients versus healthy controls (HC), to identify possible non-invasive molecular markers of the disorder. 15 drug-free manic psychotic bipolar patients and 9 HC were enrolled and 800 miRNAs expression profile was measured by Nanostring nCounter technology on plasma samples and validated through qPCR. Overall, twelve miRNAs showed a significantly altered expression between the two groups (p < 0.05). Functional annotation of predicted miRNAs targets by MultiMIR R tool showed repression in bipolar patients of genes with a role in neurodevelopment and neurogenesis, and upregulation of genes involved in metabolism regulation. We identified a signature of circulating miRNA characteristic of manic psychotic bipolar patients, suggesting a possible role in neurodevelopment and metabolic processes regulation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merikangas KR, Jin R, He JP, Kessler RC, Lee S, Sampson NA, Viana MC, Andrade LH, Hu C, Karam EG, Ladea M (2011) Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.12
Altamura AC, Serati M, Buoli M (2015) Is duration of illness really influencing outcome in major psychoses? Nord J Psychiatry 69:403–417. https://doi.org/10.3109/08039488.2014.990919
Altamura AC, Buoli M, Caldiroli A, Caron L, Cumerlato Melter C, Dobrea C, Cigliobianco M, Quarantini FZ (2015) Misdiagnosis, duration of untreated illness (DUI) and outcome in bipolar patients with psychotic symptoms: a naturalistic study. J Affect Disord 182:70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.04.024
Baldessarini RJ, Tondo L, Vazquez GH, Undurraga J, Bolzani L, Yildiz A, Yildiz A, Khalsa HM, Lai M, Lepri B, Lolich M, Maffei PM (2012) Age at onset versus family history and clinical outcomes in 1665 international bipolar-I disorder patients. World Psychiatry 11:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wpsyc.2012.01.006
Buoli M, Serati M, Altamura AC (2017) Biological aspects and candidate biomarkers for rapid-cycling in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Psychiatry Res 258:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.08.059
Dell’Osso B, Camuri G, Cremaschi L, Dobrea C, Buoli M, Ketter TA, Altamura AC (2017) Lifetime presence of psychotic symptoms in bipolar disorder is associated with less favorable socio-demographic and certain clinical features. Compr Psychiatry 76:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2017.04.005
van Rossum I, Haro JM, Tenback D, Boomsma M, Goetz I, Vieta E, van Os J, Advisory Board EMBLEM (2008) Stability and treatment outcome of distinct classes of mania. Eur Psychiatry 23:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.02.005
Buoli M, Caldiroli A, Cumerlato Melter C, Serati M, de Nijs J, Altamura AC (2016) Biological aspects and candidate biomarkers for psychotic bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 70:227–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12386
Fries GR, Carvalho AF, Quevedo J (2018) The miRNome of bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 233:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.09.025
Lopez JP, Kos A, Turecki G (2018) Major depression and its treatment: microRNAs as peripheral biomarkers of diagnosis and treatment response. Curr Opin Psychiatry 31:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000379
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Bhatti JS, Reddy PH (2017) MicroRNAs as peripheral biomarkers in aging and age-related diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 146:47–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.013
Sun P, Liu DZ, Jickling GC, Sharp FR, Yin KJ (2018) MicroRNA-based therapeutics in central nervous system injuries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38:1125–1148. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X18773871
McNeill E, Van Vactor D (2012) MicroRNAs shape the neuronal landscape. Neuron 75:363–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.005
Narahari A, Hussain M, Sreeram V (2017) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for psychiatric conditions: a review of current research. Innov Clin Neurosci 14:53–55
Chen H, Wang N, Burmeister M, McInnis MG (2009) MicroRNA expression changes in lymphoblastoid cell lines in response to lithium treatment. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:975–981. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1461145709000029
Rong H, Liu TB, Yang KJ, Yang HC, Wu DH, Liao CP, Hong F, Yang HZ, Wan F, Ye XY, Xu D (2011) MicroRNA-134 plasma levels before and after treatment for bipolar mania. J Psychiatr Res 45:92–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.04.028
Walker RM, Rybka J, Anderson SM, Torrance HS, Boxall R, Sussmann JE, Porteous DJ, McIntosh AM, Evans KL (2015) Preliminary investigation of miRNA expression in individuals at high familial risk of bipolar disorder. J Psychiatr Res 62:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.01.006
Buoli M, Serati M, Grassi S, Pergoli L, Cantone L, Altamura AC, Bollati V (2018) The role of clock genes in the etiology of major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 234:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.11.015
Wang H, Horbinski C, Wu H, Liu Y, Sheng S, Liu J, Liu J, Weiss H, Stromberg AJ, Wang C (2016) NanoStringDiff: a novel statistical method for differential expression analysis based on NanoString nCounter data. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e151. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw677
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (2002) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I disorders, research version, patient edition (SCID-I/P). Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psycol Rep 10:799
Young RC, Biggs JT, Ziegler VE, Meyer DA (1978) A rating scale for mania: reliability, validity and sensitivity. Br J Psychiat 133:429–435
Bourin MS, Severus E, Schronen JP, Gass P, Szamosi J, Eriksson H, Chandrashekar H (2014) Lithium as add-on to quetiapine XR in adult patients with acute mania: a 6-week, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Bipolar Disord 2:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40345-014-0014-9
Davies G et al (2008) Study of 300,486 individuals identifies 148 independent genetic loci influencing general cognitive function. Nat Commun 9:2098. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04362-x
Galimberti D, Villa C, Fenoglio C, Serpente M, Ghezzi L, Cioffi SM, Arighi A, Fumagalli G, Scarpini E (2014) Circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 42:1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-140756
Yuan H, Mischoulon D, Fava M, Otto MW (2018) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for depression: many candidates, few finalists. J Affect Disord 233:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.06.058
Geaghan M, Cairns MJ (2015) MicroRNA and posttranscriptional dysregulation in psychiatry. Biol Psychiatry 78:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.12.009
Buoli M, Dell’Osso B, Caldiroli A, Carnevali GS, Serati M, Suppes T, Ketter TA, Altamura AC (2017) Obesity and obstetric complications are associated with rapid-cycling in Italian patients with bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 208:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.10.010
Fagiolini A, Chengappa KN, Soreca I, Chang J (2008) Bipolar disorder and the metabolic syndrome: causal factors, psychiatric outcomes and economic burden. CNS Drugs 22:655–669
Altamura AC, Buoli M, Pozzoli S (2014) Role of immunological factors in the pathophysiology and diagnosis of bipolar disorder: comparison with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 68:21–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12089
Hibar DP, Westlye LT, Doan NT, Jahanshad N, Cheung JW, Ching CRK et al (2018) Cortical abnormalities in bipolar disorder: an MRI analysis of 6503 individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Mol Psychiatry 23:932–942. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.73
Huang Z (2009) Molecular regulation of neuronal migration during neocortical development. Mol Cell Neurosci 42:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.06.003
Uribe E, Wix R (2012) Neuronal migration, apoptosis and bipolar disorder. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment 5:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpsmen.2011.11.003
Muñoz-Estrada J, Benítez-King G, Berlanga C, Meza I (2015) Altered subcellular distribution of the 75-kDa DISC1 isoform, cAMP accumulation, and decreased neuronal migration in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: implications for neurodevelopment. CNS Neurosci Ther 21:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12377
Schubert KO, Föcking M, Prehn JH, Cotter DR (2012) Hypothesis review: are clathrin-mediated endocytosis and clathrin-dependent membrane and protein trafficking core pathophysiological processes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder? Mol Psychiatry 17:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.123
Hajek T, McIntyre R, Alda M (2016) Bipolar disorders, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the brain. Curr Opin Psychiatry 29:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000215
Wulsin LR, Blom TJ, Durling M, Welge JA, DelBello MP, Adler CM, McNamara RK, Strakowski SM (2018) Cardiometabolic risks and omega-3 index in recent-onset bipolar I disorder. Bipolar Disord 20:658–665. https://doi.org/10.1111/bdi.12633
Vancampfort D, Mitchell AJ, De Hert M, Sienaert P, Probst M, Buys R, Stubbs B (2015) Prevalence and predictors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 76:1490–1499. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.14r09635
Enger C, Jones ME, Kryzhanovskaya L, Doherty M, McAfee AT (2013) Risk of developing diabetes and dyslipidemia among adolescents with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. Int J Adolesc Med Health 25:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijamh-2013-0002
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by University of Milan and Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda—Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Buoli has been a Lundbeck consultant. Prof. Altamura has served as consultant or on Advisory Boards for Otsuka, Janssen/Cilag, Lundbeck and Angelini. Drs Tabano, Caldiroli, Terrasi, Colapietro, Grassi, Carnevali, Fontana, Serati, Vaira and Prof. Miozzo do not have any conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabano, S., Caldiroli, A., Terrasi, A. et al. A miRNome analysis of drug-free manic psychotic bipolar patients versus healthy controls. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270, 893–900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01057-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01057-2